|
West Wales Line
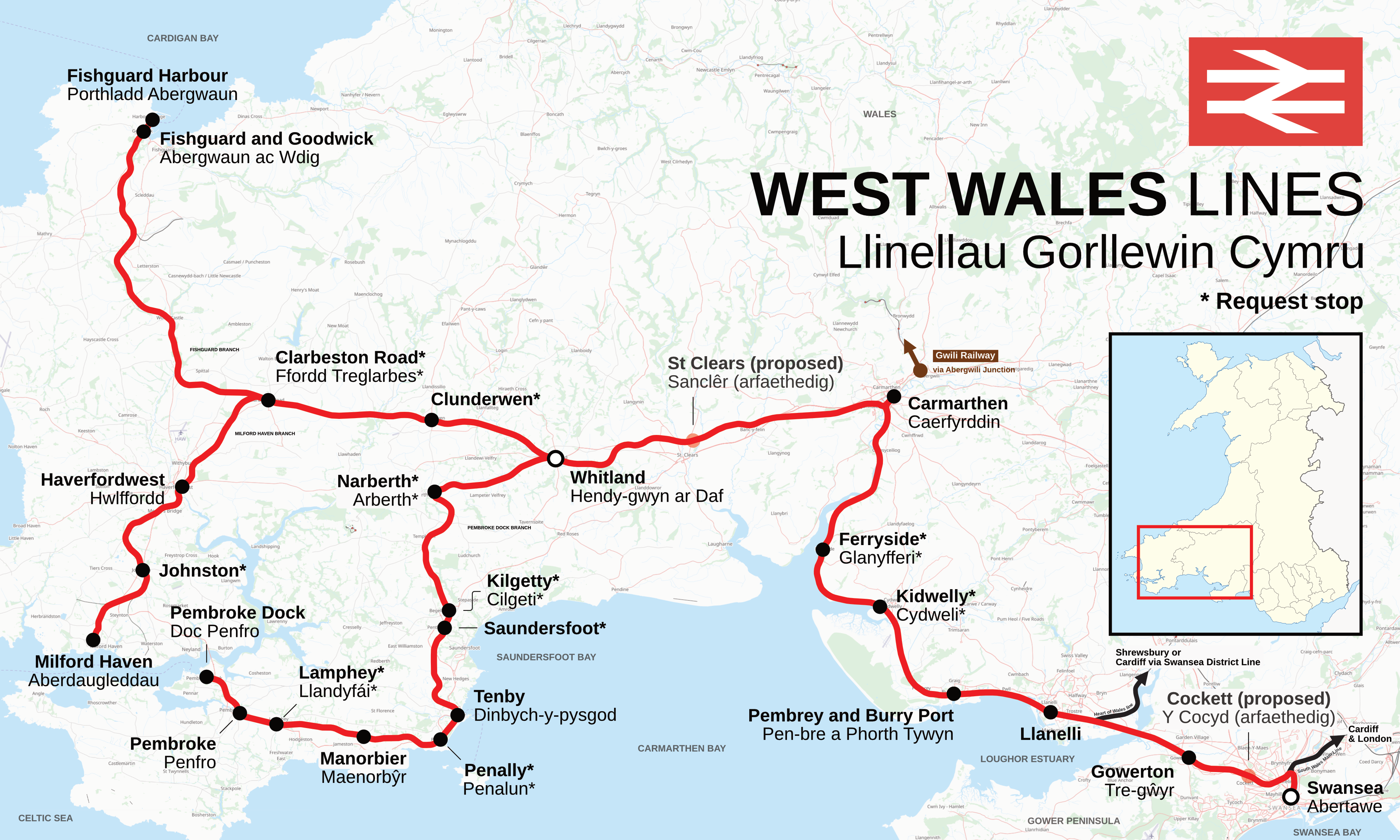
The West Wales lines () are a group of railway lines from Swansea through Carmarthenshire to Pembrokeshire, West Wales. The main part runs from Swansea to Carmarthen and Whitland, where it becomes three branches to Fishguard, Milford Haven and Pembroke Dock. Before the rail cuts of the 1960s, there were routes to Cardigan, Newcastle Emlyn, Llandysul, and via Lampeter, cross-country from Carmarthen to Aberystwyth. History The railway to west Wales was first projected in 1844, and the proposal was for a line to run from the Great Western Railway near Gloucester to Fishguard, with a branch from Whitland to Pembroke. The railway was called the South Wales Railway, and although it was in theory independent of the GWR, in practice it was very closely linked. This was shown by the fact that Isambard Kingdom Brunel was the engineer, and the line was laid to the broad gauge. Construction began in 1847, but the company ran into financial difficulties. In addition, the Great Famin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
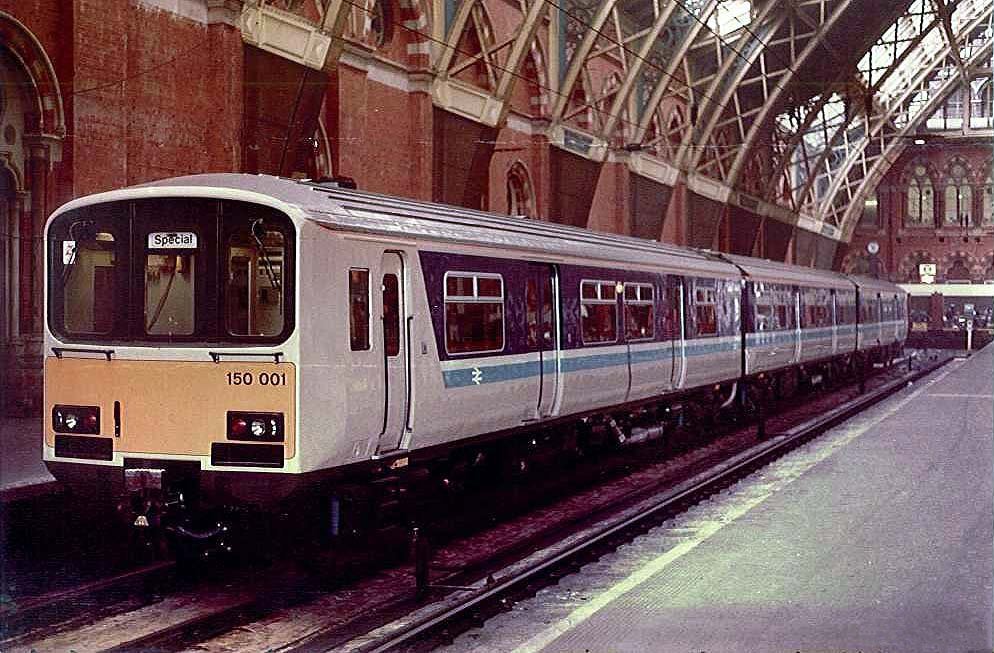
British Rail Class 150
The British Rail Class 150 '' Sprinter'' is a class of diesel-hydraulic multiple unit passenger trains, developed and built by British Rail Engineering Limited at York Carriage Works between 1984 and 1987 for use on regional services across Great Britain. The type is a second-generation design, built to more modern standards and based on BR's Mark 3 body design for longer-distance services. It was developed alongside the lower-cost Pacers, which were built using bus parts, for use on short-distance services. Two prototype units were built, followed by 135 production units in two batches. Subsequently, further members of the Sprinter family were developed and introduced to service, including the Class 155, Class 156, Class 158 and Class 159. Background By the beginning of the 1980s, British Rail (BR) was operating a large fleet of first-generation DMUs of various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, BR planners recognised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west; it is sited from Monmouth, from Bristol, and east of the England and Wales border, border with Wales. Gloucester has a population of around 132,000, including suburban areas. It is a port, linked via the Gloucester and Sharpness Canal to the Severn Estuary. Gloucester was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans and became an important city and ''Colonia (Roman), colony'' in AD 97, under Nerva, Emperor Nerva as ''Glevum, Colonia Glevum Nervensis''. It was granted its first charter in 1155 by Henry II of England, Henry II. In 1216, Henry III of England, Henry III, aged only nine years, was crowned with a gilded iron ring in the Chapter House of Gloucester Cathedral. Gloucester's significance in the Middle Ages is unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London & North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world. Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connected four of the largest cities in England; London, Birmingham, Manchester and Liverpool, and, through cooperation with their Scottish partners, the Caledonian Railway also connected Scotland's largest cities of Glasgow and Edinburgh. Today this route is known as the West Coast Main Line. The LNWR's network also extended into Wales and Yorkshire. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the ( 9 & 10 Vict. c. cciv), which authorised the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vale Of Towy Railway
The Vale of Towy Railway (VoTR) was a Welsh railway that provided an 11.25 mile-long extension of the Llanelly Railway from Llandeilo to Llandovery. It was incorporated by act of Parliament (UK), the ( 17 & 18 Vict. c. cl), of 10 July 1854 and opened on 1 April 1858.Baughan page 203 Overview The VoTR was a standard gauge route that provided an alternative to the Great Western Railway and Llandovery became a potential endpoint for other rail companies in North Wales North Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdon ... and the West of England. Stations Intermediate stations were built at (from north to south) , , (closed) and (closed). The route today The route remains in use as part of the Heart of Wales Line. References * * * Pre-grouping British railway companies Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanelly Railway
The Llanelly Railway and Dock Company was an early Welsh railway system. It opened its first short line and a wet dock at Llanelli in 1834, and soon went on to build a longer line from Llanelly to serve pits in the Amman Valley, and then on to Llandilo, reached in 1857. The Llanelly Railway and Dock Company leased and worked the Vale of Towy Railway on to Llandovery, from 1858. Responding to competitive pressure the company obtained authorisation to connect its network to Swansea and Carmarthen, but the failure of a contractor put the company into financial difficulty, and a financial reconstruction later led to the Swansea and Carmarthen lines passing to the London and North Western Railway, while the original core system was taken over by the Great Western Railway. The line from Swansea to Llandovery became part of the Central Wales Line connecting to Shrewsbury and the north-west, but after the 1960s only the Llanelli to Llandovery line and short colliery connections in the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Szlumper
Sir James Weeks Szlumper JP DL (29 January 1834 – 27 October 1926) was an English civil engineer. He was Chief Engineer on a number of key railway engineering projects in the Victorian era. Biography Szlumper was born in Westminster to Albert Szlumper, a Polish tailor, and his first wife, Eliza. He began his career with a London firm of engineers, and in 1853 was appointed surveyor to the county of Cardiganshire, a position in which he held for 25 years. In this position, he was often in correspondence and conflict with the local landowners, particularly John Waddingham, the then owner of thHafod Estate His younger half-brother Alfred Weeks Szlumper (1858–1934) was also a railway engineer. Railway engineer Szlumper had a dual career as a railway engineer, laying out some of key lines linking the major routes to the wider countryside of Wales and the West. He started his railway career engineering parts of the London Underground in employment in London. When he took the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Magazine
''The Railway Magazine'' is a monthly British railway magazine, aimed at the railway enthusiast market, that has been published in London since July 1897. it was, for three years running, the railway magazine with the largest circulation in the United Kingdom, having a monthly average sale during 2009 of 34,715 (the figure for 2007 being 34,661). It was published by IPC Media until October 2010, and in 2007 won IPC's 'Magazine of the Year' award. Since November 2010, ''The Railway Magazine'' has been published by Mortons of Horncastle. History ''The Railway Magazine'' was launched by Joseph Lawrence and ex-railwayman Frank E. Cornwall of Railway Publishing Ltd, who thought there would be an amateur enthusiast market for some of the material they were then publishing in a railway staff magazine, the ''Railway Herald''. They appointed as its first editor a former auctioneer, George Augustus Nokes (1867–1948), who wrote under the pseudonym "G. A. Sekon". He quickly built th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Break-of-gauge
With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge (the distance between the rails, or between the wheels of trains designed to run on those rails) meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally cannot run through without some form of conversion between gauges, leading to passengers having to change trains, and freight having to be transloaded or transshipped. That can cause delays, added costs, and inconvenience to those travelling on affected routes. History Break of gauge was a common problem in the early days of railways, because standards had not yet been set and different organizations each used their own favored gauge on the lines they controlled. That was sometimes for mechanical and engineering reasons (optimizing for geography or particular types of load and rolling stock), and sometimes for commercial and competitive reasons (interoperability, or the lack of it, within and between companies and alliances were often key st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except High-speed rail in Russia, those in Russia, High-speed rail in Finland, Finland, High-speed rail in Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in High-speed rail in Spain, Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in Imperial and US customary measurement systems, U.S. customary/Imperial units, British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembroke And Tenby Railway
The Pembroke and Tenby Railway was a locally promoted railway in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It was built by local supporters and opened in 1863. The line, now known as the Pembroke Dock branch line, remains in use at the present day. In 1814 a Royal Navy Dockyard had been established at Pembroke Dock.M R C Price, ''The Pembroke and Tenby Railway'', Oakwood Press, Headington, 1986, The South Wales Railway had been authorised to build a branch line to Pembroke, but had failed to do so. Their terminus in Neyland was a short ferry crossing from Pembroke Dock. In 1866, the Pembroke and Tenby Railway was extended to Whitland; Whitland was on the South Wales Railway broad gauge main line (railway), main line but being on the narrow gaugelater known as standard gaugeit was not possible to run Pembroke and Tenby trains on the South Wales Railway lines to Carmarthen. The intention of the Pembroke and Tenby Railway was to make an alliance with other narrow gauge railways at Carmarthen, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neyland
Neyland is a town and community in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Cleddau and the upstream end of the Milford Haven estuary. The Cleddau Bridge carrying the A477 links Pembroke Dock with Neyland. In 2011 it had a population of 3,464. Etymology The name of the town is a reduction of an earlier form of the English word ' preceded by the Middle English ' "at the". It was formerly known as New Milford by contrast with Milford Haven. History Neyland was a small fishing village in the parish of Llanstadwell, but in 1856 it became the site for the western terminus of Isambard Kingdom Brunel's Great Western Railway with a transatlantic terminal for the largest ships of the time. It was selected instead of the other possible location Abermawr. The town then grew rapidly to serve the port. The construction of a more substantial port at Goodwick based on an earlier plan of 1846, was revived in 1899, and opened in 1906. Many people relocated from Neyland to Goodwick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |