|
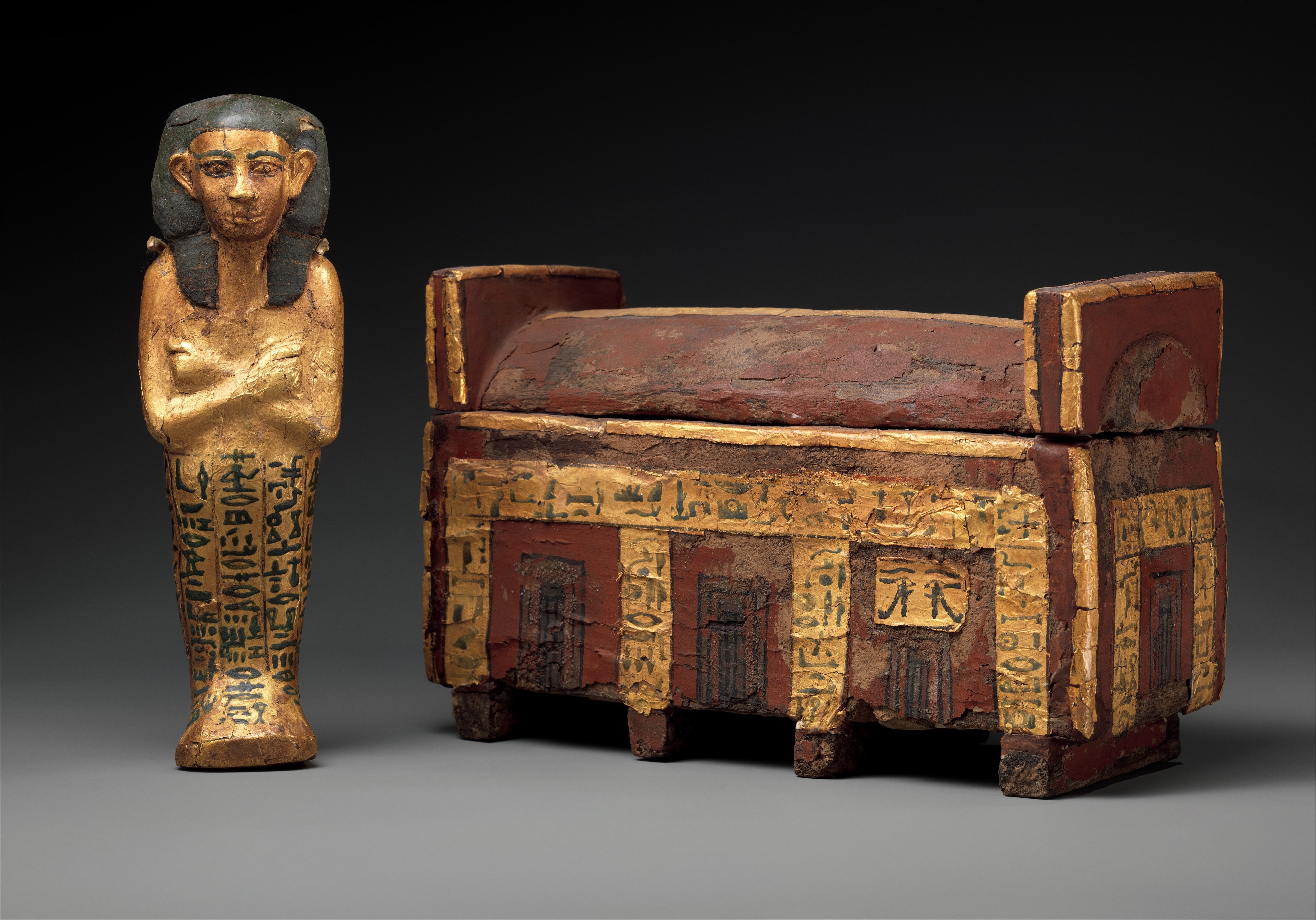
Wahneferhotep
Wahneferhotep was an ancient Egyptian ''king's son'' who lived in the Thirteenth Dynasty, around 1700 BC. Attestation Wahneferhotep is only known from a shabti and model coffin found in the mortuary temple of the pyramid of Senusret I at Lisht, and now at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. On both objects he bears the title ''king's son''. His name means ''Neferhotep endures''. Theories Neferhotep might refer to king Neferhotep I, who was one of the most powerful rulers of the Thirteenth Dynasty; some scholars argue that this king is the most likely ruler that is mentioned in the name. However, the pottery found near the model coffins points to a later date, making it more likely that ''Neferhotep'' refers to another, later, king with the same name.Dieter Arnold: ''The Pyramid of Senwosret I, South Cemeteries of Lisht I'', New York 1988, , pp. 37-40 References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferhotep I
Khasekhemre Neferhotep I was an Ancient Egypt, Egyptian pharaoh of the mid Thirteenth dynasty of Egypt, Thirteenth Dynasty ruling in the second half of the 18th century BCKim Ryholt, Ryholt, K.S.B: The Political Situation in Egypt During the Second Intermediate Period, c.1800–1550 BC', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, (1997). . . . during a time referred to as the late Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom or early Second Intermediate Period, depending on the scholar. One of the best attested rulers of the 13th Dynasty, Neferhotep I reigned for 11 years according to the Turin King List. The grandson of a non-royal townsman from a Thebes, Egypt, Theban family with a military background, Neferhotep I's relation to his predecessor Sobekhotep III is unclear and he may have usurped the throne. Neferhotep I was likely contemporaneous with kings Zimri-Lim of Mari, Syria, Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon. Little is known of his activities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteenth Dynasty
The Thirteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty XIII) was a series of rulers from approximately 1803 BC until approximately 1649 BC, i.e. for 154 years. It is often classified as the final dynasty of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom (which includes Dynasty XI, Dynasties XI, Dynasty XII, XII and Dynasty XIV, XIV), but some historians instead group it in the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period (with Dynasties Dynasty XIV, XIV through Dynasty XVII, XVII). Dynasty XIII initially ruled from the Nile Delta to the Cataracts of the Nile, second cataract of the Nile. However, the dynasty marked a period of decline and instability, with Dynasty XIV rising concurrently and the Hyksos Dynasty XV taking control shortly after. Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep is usually considered Dynasty XIII's first pharaoh, and Merneferre Ay, while not the final pharaoh, was the last to occupy the Middle Kingdom capital of Itjtawy, and the last of the dynasty wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Coffin And Shabti Of Wahneferhotep
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), a person p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shabti
The ushabti (also called shabti or shawabti, with a number of variant spellings) was a funerary figurine used in ancient Egyptian funerary practices. The Egyptological term is derived from , which replaced earlier , perhaps the nisba of "''Persea'' tree". Ushabtis were placed in tombs among the grave goods and were intended to act as servants or minions for the deceased, should they be called upon to do manual labor in the afterlife. The figurines frequently carried a hoe on their shoulder and a basket on their backs, implying they were intended to farm for the deceased. They were usually written on by the use of hieroglyphs typically found on the legs. They carried inscriptions asserting their readiness to answer the gods' summons to work. The practice of using ushabtis originated in the Old Kingdom of Egypt ( to 2100 BC), with the use of life-sized reserve heads made from limestone, which were buried with the mummy. Most ushabtis were of minor size, and many produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortuary Temple
Mortuary temples (or funerary temples) were temples that were erected adjacent to, or in the vicinity of, royal tombs in Ancient Egypt. The temples were designed to commemorate the reign of the Pharaoh under whom they were constructed, as well as for use by the king's cult after death. These temples were also used to make sacrifices of food and animals. A mortuary temple is categorized as a monument. History Mortuary temples were built around pyramids in the Old Kingdom and Middle Kingdom. However, once the New Kingdom pharaohs began constructing tombs in the Valley of the Kings, they built their mortuary temples separately. These New Kingdom temples were called "mansions of millions of years" by the Egyptians. The mortuary temples were also used as a resting place for the boat of Amun at the time of the Beautiful Festival of the Valley, during which the cult statue of the deity visited the west bank of Thebes. The king wanted to build his mortuary temple so that he could con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Senusret I
The pyramid of Senusret I is an Ancient Egypt, Egyptian pyramid built to be the burial place of the Pharaoh Senusret I. The pyramid was built during the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt at el-Lisht, near the pyramid of his father, Amenemhat I. Its ancient name was ''Senusret Peter Tawi'' (''Senusret beholds the upper and Lower Egypt, two lands'').Lehner, M. (1997). ''The Complete Pyramids.'' London:Thames and Hudson Ltd. The pyramid was 105 meters on each side with a height of 61.25 meters; the slope of the four faces was 49° 24'. The pyramid used a method of construction never before seen in an Egyptian pyramid; four stone walls radiated from the center built of rough-hewn blocks that decreased in size the higher their placement. The eight sections formed by these walls were then subdivided by three more walls, splitting the pyramid into 32 different units which were then filled with slabs of stone as well as debris. An exoskeleton of fine limestone then covered the structure. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisht
Lisht or el-Lisht () is an Egyptian village located south of Cairo. It is the site of Middle Kingdom royal and elite burials, including two pyramids built by Amenemhat I and Senusret I. The two main pyramids were surrounded by smaller pyramids of members of the royal family, and many mastaba tombs of high officials and their family members. They were constructed throughout the Twelfth and Thirteenth Dynasties. The site is also known for the tomb of Senebtisi, found undisturbed and from which a set of jewelry has been recovered. The pyramid complex of Senusret I is the best preserved from this period. The coffins in the tomb of Sesenebnef present the earliest versions of the Book of the Dead. Overview The ancient Egyptian site of el-Lisht can be found on the west bank of the Nile River, around 65 km south of the city of Cairo. It is a Twelfth Dynasty necropolis, close to the city of Itj-Tawy from which the modern village assumably (given the proposed older form Al-Isht) ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Museum Of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of largest art museums, largest art museum in the Americas. With 5.36 million visitors in 2023, it is the List of most-visited museums in the United States, most-visited museum in the United States and the List of most-visited art museums, fifth-most visited art museum in the world. In 2000, its permanent collection had over two million works; it currently lists a total of 1.5 million works. The collection is divided into 17 curatorial departments. The Met Fifth Avenue, The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile, New York, Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's list of largest art museums, largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieter Arnold
Dieter Arnold (born 1936 in Heidelberg) is a German archaeology, archaeologist. Biography He received his doctorate on 31 January 1961 from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, University of Munich with the thesis "Wall relief and spatial function in Egyptian temples of the New Kingdom". Arnold worked for the German Archaeological Institute in Cairo during excavations in Dahshur, Deir el-Bahari and El-Tarif. From 1979 to 1984 he was a professor at the University of Vienna and then a curator at the Egyptian Department of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, New York. Arnold's specialty is the architecture of Ancient Egypt. As an employee of the Metropolitan Museum, he leads the museum's annual expeditions to el-Lisht and Dahshur. In 1981 he published a proposal for the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, Great Pyramid. The ramp runs first outside and then in a corridor inside the pyramid. Arnold was aware that the construction method could not be explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Thirteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of Person, persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independence, independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |