|
WAP-1 Locomotive At Delhi
The Indian locomotive class WAP-1 was a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1980 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) locomotive, 1st generation (1). They entered service in late 1981. A total of 65 WAP-1 were built at CLW between 1980 and 1996, which made them the most numerous class of mainline electric passenger locomotive until its successor, the WAP-4. The WAP-1 was India's first dedicated electric passenger locomotive of Indian Railways, and has provided the basic design for a number of other locomotives like WAP-3 and WAP-4 models. However, with the advent of new 3-phase locomotives like WAP-5 and WAP-7, the WAP-1 locomotives were relegated to hauling smaller express and passenger trains and now the aging fleet the WAP-1 locomotives are being slowly withdrawn from mainline duties and scrapped. Development Background In the early 1980s, Indian R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) is an electric locomotive manufacturer based in India. The works are located at Chittaranjan in the Asansol Sadar subdivision of West Bengal, with an ancillary unit in Dankuni. The main unit is 32 km from Asansol’s City Bus Terminus and 237 km from Kolkata. CLW has stores and offices in Kolkata, as well as inspection cells in New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Bangalore. It is the largest locomotive manufacturer unit in the world. In FY 2024–25, it produced 700 locomotives surpassing the United States and Europe. History Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) has been named after the great freedom fighter, leader and statesmen Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das. A new survey led to the present site at Chittaranjan being established, which was approved by the Ministry of Railways (India), railway board in 1947. A survey of the proposed area began on 9 January 1948; the rocky soil was an advantage in erecting structural foundations, and the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Locomotive Class WAP-5
The Indian locomotive class WAP-5 is a class of electric locomotives used by Indian Railways. The first ten locomotives were imported from Adtranz in Switzerland in 1995 and later manufactured by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works in India. On 3 July 2014, a WAP-5 set an Indian speed record by hauling a train between Delhi and Agra at a speed of . The locomotive has regenerative braking, flexible gear coupling, wheel-mounted disc brakes, and a potential for speed enhancement to . Braking systems include regenerative brakes, disc brakes, automatic train air brakes and a charged spring parking brake. Locomotive sheds Last updated:- June 2025 Variants In October 2015, a WAP-5A locomotive (no. 30086) was rolled-out with a gear ratio of 59:35:19 capable of speeds up to for trial runs. In March 2018, a WAP-5 locomotive (no. 30136) with an enhanced power output of was released which was later adopted as a standard based on successful trials. Some locomotives of this class are equip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotives Of India
Indian Railways operates India's railway system and comes under the purview of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of Government of India. , it maintains over of tracks and operates over 13,000 trains daily with a fleet of 14,800 locomotives. The railways primarily operates a fleet of Electric locomotive, electric and diesel locomotives along with a few Compressed Natural Gas, compressed natural gas (CNG) locomotives. Steam locomotives are operated on Mountain railways of India, mountain railways and on restored train, heritage trains. History The history of the Indian Railway began in 1832 with the proposal to construct the first railway line in India at Madras. In 1837, the first train ran on Red Hill railway railway track, line between Red Hills, Chennai, Red Hills and Chintadripet in Madras and was hauled by a Rotary engine, rotary steam engine imported from England. In 1852, a steam locomotive imported from England was tried at Byculla. In 1853, the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
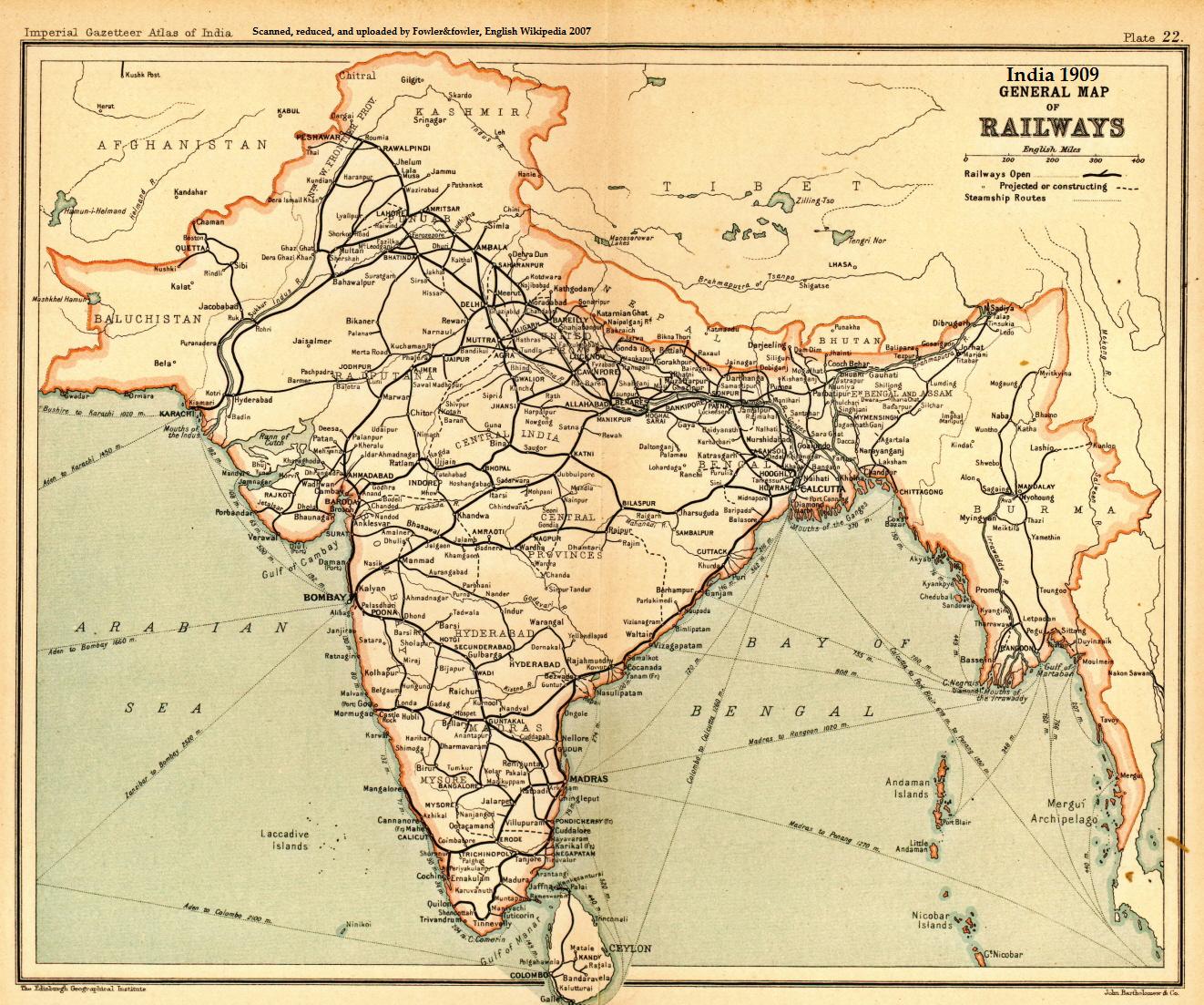
Rail Transport In India
Rail transport in India consists of primarily of passenger train, passenger and Rail freight transport, freight shipments along an integrated rail network. Indian Railways (IR), a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of the Government of India, operates India's national railway system. It is the primary owner and operator of Rail transport, rail operations throughout the country, including suburban rail, suburban rail in major metros. Economic studies indicate positive effects of the Indian railway network on the economy of the country. The majority of the metro Urban rail transit in India, urban rail networks are operated by independent bodies constituted for the respective operations. Privately owned rails exist in few places, mostly used to connect freight to the integrated rail network. Inter-city rail services are operated primarily by Indian Railways, though efforts have been made to introduce privately operated trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Loco Shed, Erode
Diesel Loco Shed, Erode is an engine shed located on Erode–Chennimalai road in Erode, Tamil Nadu, India. Being closely located to Erode Junction Railway Station, the shed falls under Salem railway division of Southern Railway zone. History The shed was opened and became operationally active since September 1966, spreading over a total area of and covered area of . Operations Being one of the four diesel engine sheds in Southern Railway under the territory of Salem railway division, various major and minor maintenance schedules of diesel locomotives are being carried out here. Apart from serving the parent division, the locos belonging to the shed also serves the unelectrified routes of Madurai railway division, in addition to locos from Golden Rock. To provide space for electric locomotives, all the EMDs (WDG-4 and WDP-4D), WDM-3A and WDG-3A were transferred to Golden Rock. Currently no services are hauled by Erode diesels. As of June 2025, Diesel Loco Shed Erode only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
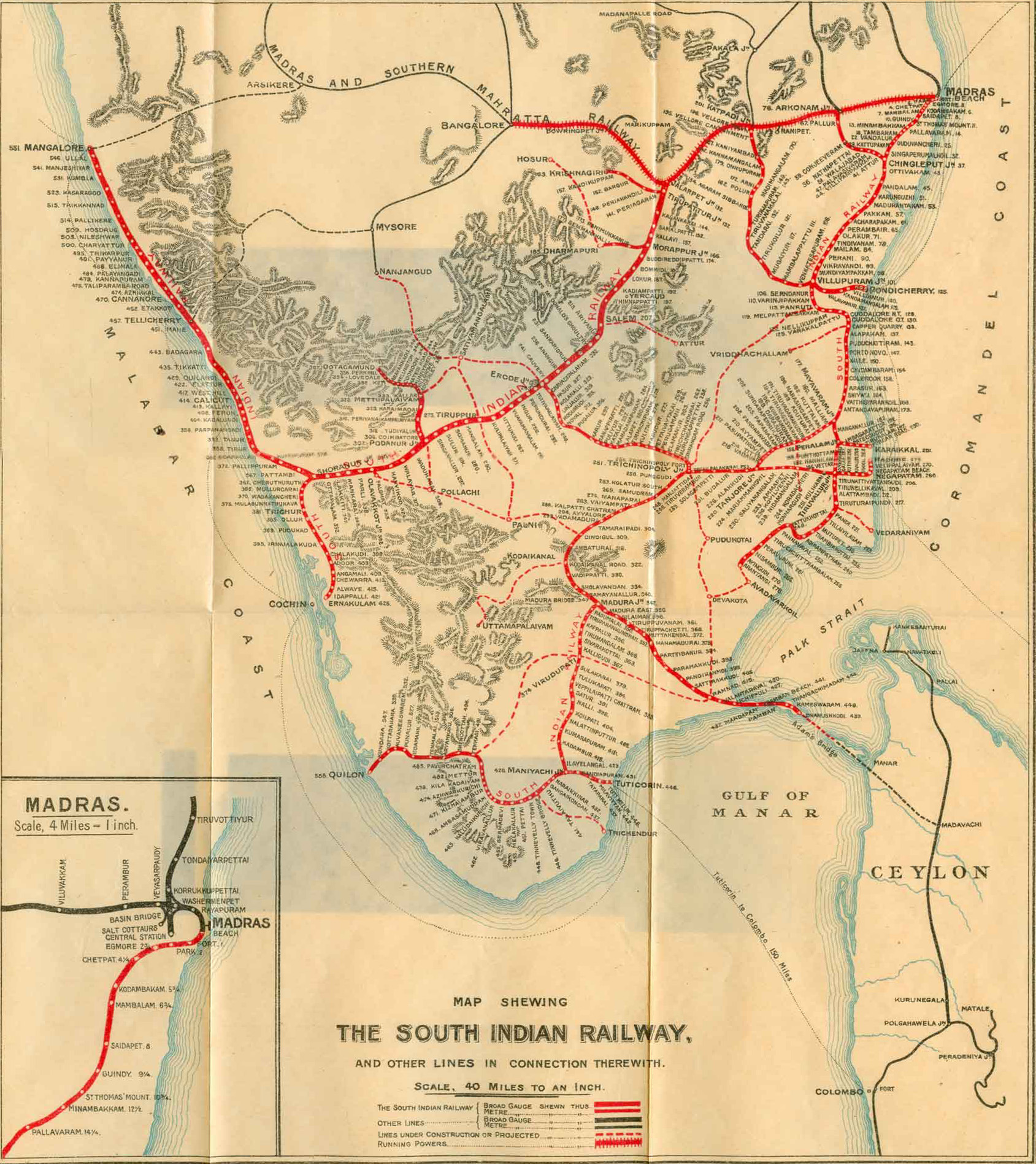
Southern Railway Zone
Southern Railway (SR) is one of the eighteen zones of Indian Railways. It is headquartered at Chennai and operates across the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and the union territory of Puducherry. The origin of the Southern Railway can be traced back to the Madras Railway formed in 1845. Southern Railway was created on 14 April 1951 by merging three state railways, namely, the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway, the South Indian Railway Company, and the Mysore State Railway and became the first railway zone created in newly formed India. Southern Railway maintains about of railway lines and operates 727 railway stations. It has the distinction of operating the first railway line in India, which opened for traffic from Redhills to Chindadripettai in Madras on 12 September 1836. History The history of the Southern Railway can be traced back to the Madras Railway. In 1832, the proposal to construct the first railway line in India at Madras was made by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izzatnagar Railway Station
Izzatnagar railway station is main railway station in Izzatnagar Bareilly district, Uttar Pradesh. Its code is IZN. It serves Izzatnagar city. The station consists of 4 platforms. Izzatnagar railway division is a part of North Eastern Railway zone of Indian Railways. This railway division was founded on 14 April 1952. Trains * Lucknow Junction–Kathgodam Express The Lucknow Junction–Kathgodam Express is an Express train belonging to North Eastern Railway zone that runs between and in India. It is currently being operated with 15043/15044 train numbers on a tri-weekly basis. Service The 15043/Lu ... * Purnagiri Jan Shatabdi Express Diesel Loco Shed, Izzatnagar Gallery Izzatnagar railway station, Bareilly 03.jpg, Izzatnagar railway station, Bareilly Izzatnagar station 05.jpg, Izzatnagar station in daylight Izzatnagar railway station 06.jpg, Izzatnagar railway station at night References External links Izzatnagar railway division Railway station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucknow
Lucknow () is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the largest city of the List of state and union territory capitals in India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Lucknow district, district and Lucknow division, division. Having a population of 2.8 million as per 2011 census, it is the List of cities in India by population, eleventh most populous city and List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, the twelfth-most populous urban agglomeration of India. Lucknow has always been a Multiculturalism, multicultural city that flourished as a North Indian cultural and artistic hub, and the seat of power of Nawabs in the 18th and 19th centuries. It continues to be an important centre of governance, administration, education, commerce, aerospace, finance, pharmaceuticals, information technology, design, culture, tourism, music, and poetry. Lucknow, along with Agra and Varanasi, is in the Uttar P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Railway Zone
The Northern Railway (NR) is one of the 17 Railway zones of India and the northernmost zone of the Indian Railways. It is headquartered at Baroda House in New Delhi. History Officially notified as a new railway zone on 14 April 1952, its origin goes back to 3 March 1859. On 14 April 1952, the Northern Railway zone was created by merging Jodhpur Railway, Bikaner Railway, Eastern Punjab Railway and three divisions of the East Indian Railway north-west of Mughalsarai (Uttar Pradesh). On 3 March 1859, Allahabad–Kanpur, the first passenger railway line in North India was opened, which falls under Northern Railway zone. In 1864, a broad-gauge track from Calcutta to Delhi was laid. In 1864, the railway line between Old Delhi and Meerut City railway station was constructed. Meerut Cantt railway station was established by British India government around 1865 after the sepoy mutiny of 1857. In 1866, through trains started running on the East Indian Railway Company's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Locomotive Class WCP-1
The Indian locomotive class WCP-1 (originally classified as EA/1) is a class of 1.5 Volt, kV Direct current, DC electric locomotives that were developed in late 1920s by Swiss Locomotive and Machine Works (SLM) for the Great Indian Peninsula Railway to handle passenger trains. A total of 22 WCP-1s were built in England between 1928 and 1929, and entered service in 1930. The WCP-1 served passenger trains for nearly 50 years until its withdrawal in the early 1980s. Only one locomotive, GIPR 4006, is preserved at the National Rail Museum, New Delhi, National Rail Museum, with the remainder of the units being scrapped. History The electrification of the Great Indian Peninsula Railway began in 1922, and powerful locomotives were required to haul express trains on over the Western Ghats. They also had to be able to reach speeds of 85 miles an hour (137 km/h) - a very high speed at that time, which was not even the case with the E 501 and 502 of the Compagnie du chemin de fer de Pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Indian Peninsula Railway
The Great Indian Peninsula Railway (reporting mark GIPR) was a predecessor of the Central Railway (and by extension, the current state-owned Indian Railways), whose headquarters was at the Boree Bunder in Mumbai (later, the Victoria Terminus and presently the Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus). The Great Indian Peninsula Railway Company was incorporated on 1 August 1849 by the ( 12 & 13 Vict. c. lxxxiii) of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It had a share capital of 50,000 pounds. On 21 August 1847 it entered into a formal contract with the East India Company for the construction and operation of a railway line, 56 km long, to form part of a trunk line connecting Bombay with Khandesh and Berar and generally with the other presidencies of India. The Court of Directors of the East India Company appointed James John Berkeley as Chief Resident Engineer and Charles Buchanan Ker and Robert Wilfred Graham as his assistants. It was India's first passenger railway, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |