|
Vulval
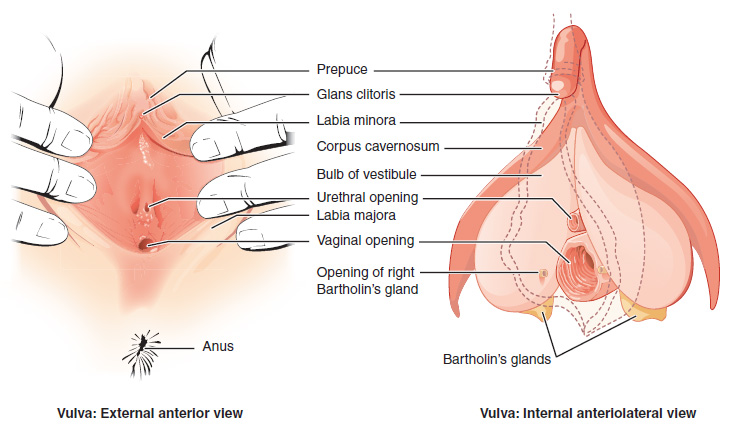
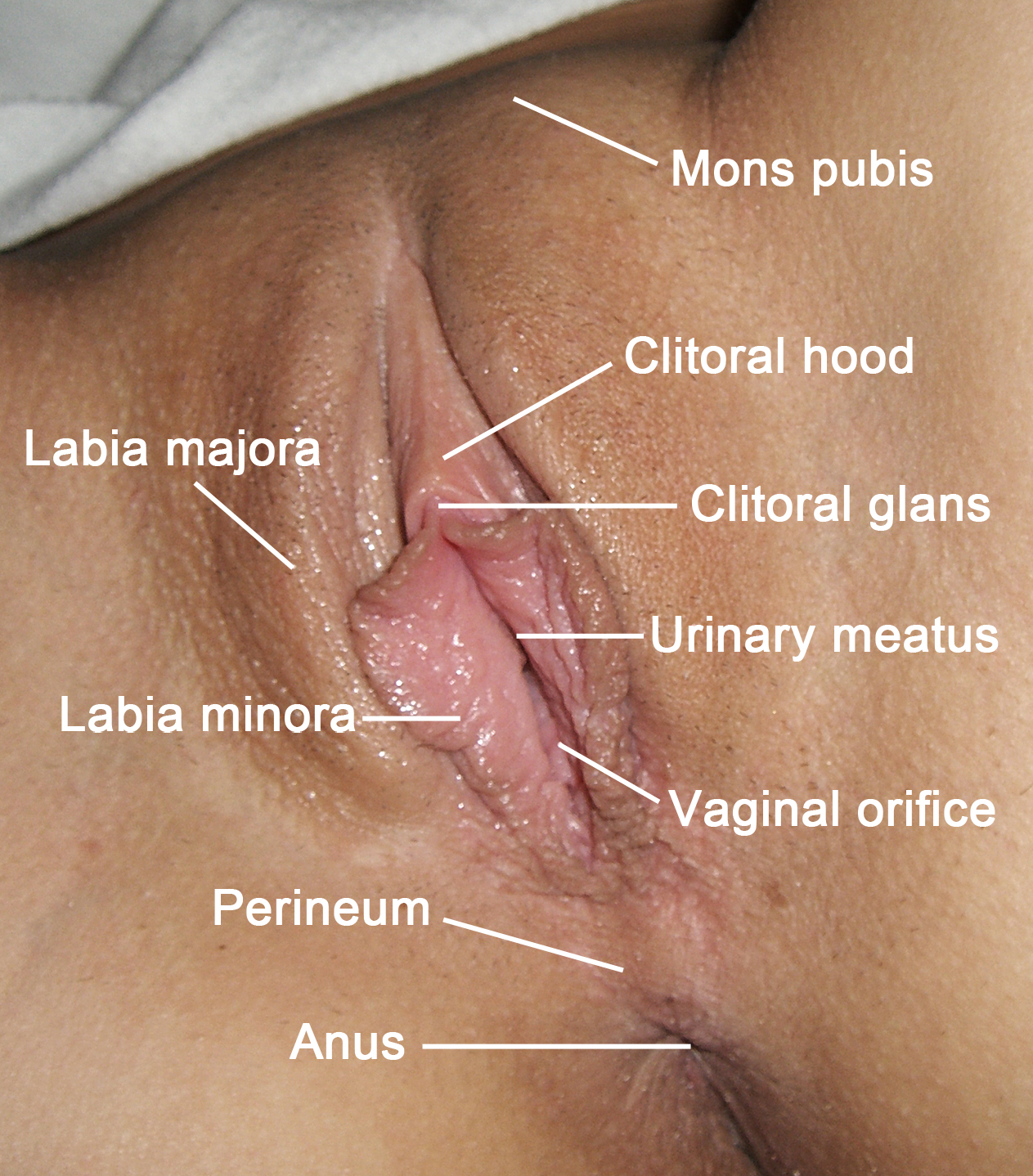
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Afferent lymph vesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', singular: ''labium minus'', 'smaller lip'), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips or nymphae are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening in the vulva, situated between the labia majora (Latin for 'larger lips'; also called outer labia, or outer lips). The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual. The labia minora are homologous to the male urethral surface of the penis. Structure and functioning The labia minora extend from the clitoris obliquely downward, laterally, and backward on either side of the vulval vestibule, ending between the bottom of the vulval vestibule and the labia majora. The posterior ends (bottom) of the labia minora are usually joined across the middle line by a flap of skin, named the frenulum of labia minora or fourchette. On the front, each lip forks dividing into two portions surrounding the clitoris. The upper part of each lip p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulval Vestibule
The vulval vestibule (or vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is a part of the vulva between the labia minora into which the urinary meatus (urethral opening) and the vaginal opening open. Its edge is marked by Hart's line. It represents the distal end of the urogenital sinus of the embryo.Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1–16. . Structure Structures opening in the vulval vestibule are the urethra, vagina, Bartholin's glands, and Skene's ducts. The external urethral orifice is placed about 25–30 millimetres (1–1.2 in) behind the clitoris and immediately in front of that of the vagina; it usually assumes the form of a short, sagittal cleft with slightly raised margins. Nearby are the openings of the Skene's ducts. The vaginal orifice is a median slit below and behind the opening of the urethra; its size varies inversely with that of the hymen. To the left and right of the vulval vestibule are the labia minora. Anterior to it are the clitoral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
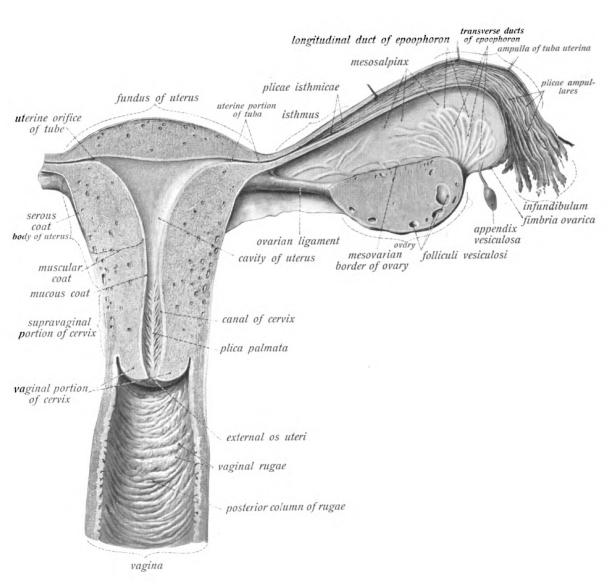
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Meatus
The urinary meatus, (, ) also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in both sexes and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. The meatus is located on the glans of the penis or in the vulval vestibule. In human males The male external urethral orifice is the external opening or urinary meatus, normally located at the tip of the glans penis, at its junction with the frenular delta. It presents as a vertical slit, possibly bounded on either side by two small labia-like projections, and continues longitudinally along the front aspect of the glans, which facilitates the flow of urine micturition. In some cases, the opening may be more rounded. This can occur naturally or may also occur as a side effect of excessive skin removal during circumcision. The meatus is a sensitive part of the male reproductive system. In human females The female exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons Pubis
In human anatomy, and in mammals in general, the ''mons pubis'' or pubic mound (also known simply as the mons, and known specifically in females as the ''mons Venus'' or ''mons veneris'') is a rounded mass of fatty tissue found over the pubic symphysis of the pubic bones. Anatomy For females, the ''mons pubis'' forms the anterior portion of the vulva. It divides into the labia majora (literally "larger lips"), on either side of the furrow known as the pudendal cleft, that surrounds the labia minora, clitoris, urethra, vaginal opening, and other structures of the vulval vestibule. Although present in both men and women, the ''mons pubis'' tends to be larger in women. Its fatty tissue is sensitive to estrogen, causing a distinct mound to form with the onset of female puberty. This pushes the forward portion of the labia majora out and away from the pubic bone. The mound also becomes covered with pubic hair. It often becomes less prominent with the decrease in bodily estrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips; the singular is ''labium majus.'' The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of female external genitals (vulva)—labia majora and labia minora. Labia majora are commonly known as the outer lips, while labia minora (Latin for ''small lips''), which run alongside between them, are referred to as the inner lips. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the labia of female genitals were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymen
The hymen is a thin piece of mucosal tissue that surrounds or partially covers the external vaginal opening. It forms part of the vulva, or external genitalia, and is similar in structure to the vagina. In children, a common appearance of the hymen is crescent-shaped, although many shapes are possible. During puberty, estrogen causes the hymen to change in appearance and become very elastic. Normal variations of the post-pubertal hymen range from thin and stretchy to thick and somewhat rigid. Very rarely, it may be completely absent. The hymen can rip or tear during first penetrative intercourse, which usually results in pain and, sometimes, mild temporary bleeding or spotting. Sources differ on how common tearing or bleeding after first intercourse are. The state of the hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity, though " virginity testing" remains a common practice in some cultures, sometimes accompanied by surgical restoration of hymen to give the appearance of virgin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartholin's Gland
The Bartholin's glands (named after Caspar Bartholin the Younger; also called Bartholin glands or greater vestibular glands) are two pea sized compound alveolar glandsManual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina. They are homologous to bulbourethral glands in males. However, while Bartholin's glands are located in the superficial perineal pouch in females, bulbourethral glands are located in the deep perineal pouch in males. Their duct length is 1.5 to 2.0 cm and they open into navicular fossa. The ducts are paired and they open on the surface of the vulva. History Bartholin's glands were first described in the 17th century by the Danish anatomist Caspar Bartholin the Younger (1655–1738). Some sources mistakenly ascribe their discovery to his grandfather, theologian and anatomist Caspar Bartholin the Elder (1585–1629). Function Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Triangle
The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vagina and associated parts of the internal genitalia. Structure The urogenital triangle is the area bound by a triangle with one vertex at the pubic symphysis and the two other vertices at the iliac tuberosities of the pelvic bone. Components As might be expected, the contents of the urogenital triangle differ greatly between the male and the female. Some of the components include:Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . * Posterior scrotal nerves / Posterior labial nerves * Urethra * Vagina * Bulbourethral gland / Bartholin's gland * Muscles ** Superficial transverse perineal muscle ** Ischiocavernosus muscle ** Bulbospongiosus muscle * Crus penis / Clitoral crura * Bulb of penis / vestibular bulb * Urogenital diaphragm * Muscular perineal body * Superficial and Deep perineal pouch * Blood vessels and lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |