|
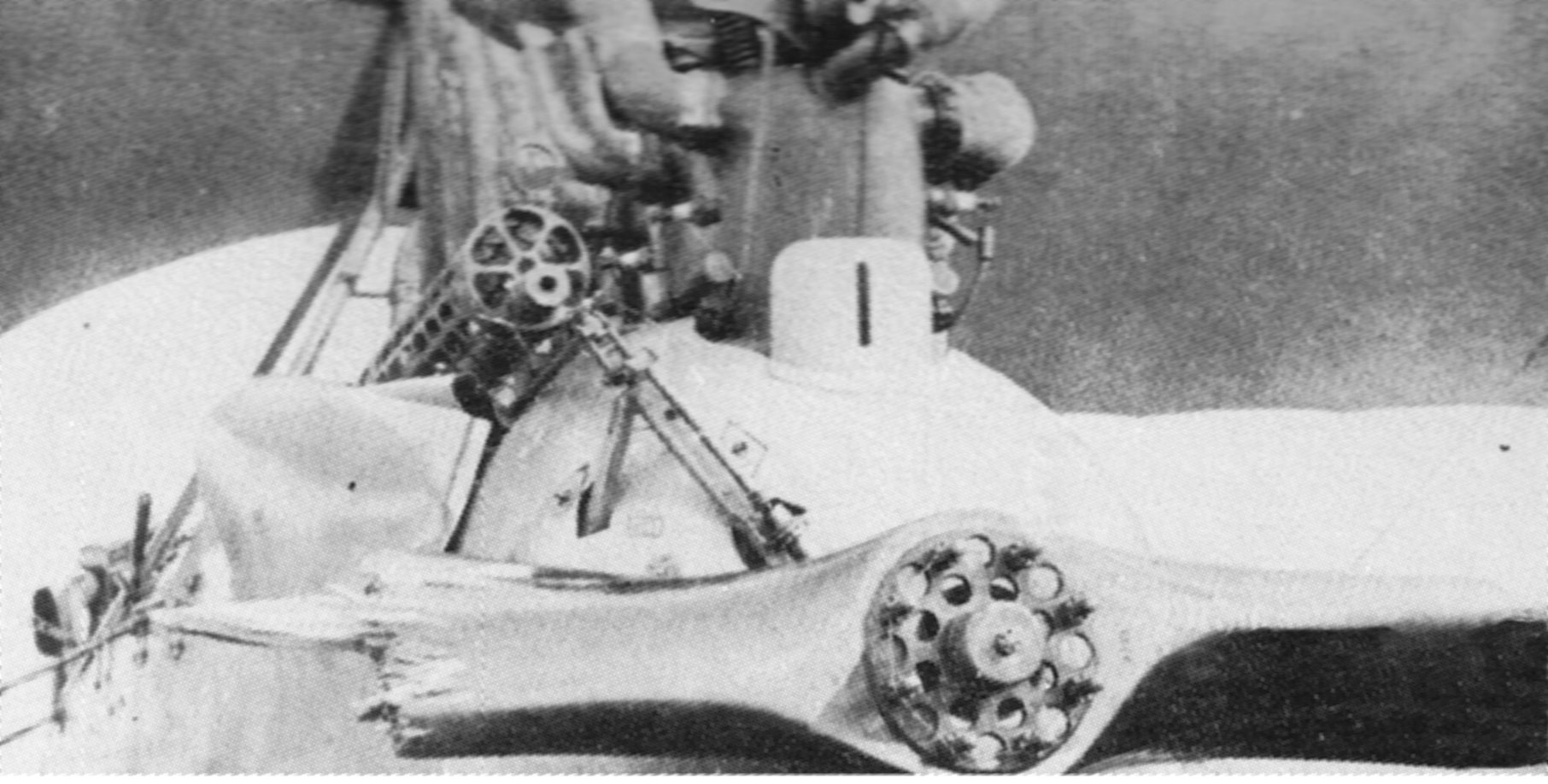
Vought XSO2U-1
The Vought XSO2U was an American observation floatplane developed by Vought-Sikorsky for the United States Navy during the late 1930s. Intended to replace the Curtiss SOC Seagull in service as a scout aboard cruisers, it proved superior to the Curtiss SO3C in evaluation, but failed to win a production contract due to Vought's lack of manufacturing capacity. Design and development In the late 1930s the United States Navy developed a set of specifications for a new scout-observation aircraft to operate from its cruisers in the reconnaissance and gunnery spotting roles. Intended to replace the Curtiss SOC biplane, the requirements included that the aircraft should have folding wings, have a superior range and speed to that of the SOC, and that the new type should be powered by the Ranger V-770 inline engine.Adcock 1991, p.44. Designs were submitted in response to the Navy's specifications by Vought-Sikorsky and Curtiss-Wright. The Vought design, designated Model 403 by the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple wings. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization Gear
A synchronization gear (also known as a gun synchronizer or interrupter gear) was a device enabling a single-engine tractor configuration aircraft to fire its forward-firing armament through the arc of its spinning Propeller (aeronautics), propeller without bullets striking the blades. This allowed the aircraft, rather than the gun, to be aimed at the target. There were many practical problems, mostly arising from the inherently imprecise nature of an automatic gun's firing, the great (and varying) velocity of the blades of a spinning propeller, and the very high speed at which any gear synchronizing the two had to operate. In practice, all known gears worked on the principle of actively triggering each shot, in the manner of a semi-automatic weapon. Design and experimentation with gun synchronization had been underway in French Third Republic, France and German Empire, Germany in 1913–1914, following the ideas of August Euler, who seems to have been the first to suggest mounti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M2 Browning Machine Gun
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50-caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed near the end of World War I by John Browning. While similar to Browning's M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge, the M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It has been used against infantry, light armored vehicles, watercraft, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO countries and has been used by man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in the older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are typically carried out to protect friendly shipping and coastal facilities from submarine attacks and to overcome blockades. Successful ASW operations typically involve a combination of sensor and weapon technologies, along with effective deployment strategies and sufficiently trained personnel. Typically, sophisticated sonar equipment is used for first detecting, then classifying, locating, and tracking a target submarine. Sensors are therefore a key element of ASW. Common weapons for attacking submarines include torpedoes and naval mines, which can both be launched from an array of air, surface, and underwater platforms. ASW capabilities are often considered of significant strategic importance, particularly following provocative instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardpoint
A hardpoint is an attachment location on a structural frame designed to transfer force and carry an external or internal structural load, load. The term is usually used to refer to the mounting points (more formally known as a weapon station or station) on the airframe of military aircraft that carry list of aircraft weapons, weapons (e.g. gun pods and rocket pods), aircraft ordnance, ordnances (aerial bomb, bombs and guided missile, missiles) and support equipment (e.g. flare (countermeasure), flares and electronic countermeasure, countermeasures, targeting pods or drop tanks), and also include hardpoints (also known as pylons) on the wings or fuselage of a military transport aircraft, commercial airliner or private jet where external turbofan jet engines are often mounted. Aircraft In aeronautics, the term ''station'' is used to refer to a point of carriage on the frame of an aircraft. A station is usually rated to carry a certain amount of payload. It is a design number whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon designed to destroy submarine A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...s by detonating in the water near the target and subjecting it to a destructive shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use high explosives with a fuze set to detonate the charge, typically at a specific depth from the surface. Depth charges can be dropped by ships (typically fast, agile surface combatants such as destroyers or frigates), patrol aircraft and helicopters. Depth charges were developed during World War I, and were one of the first viable methods of attacking a submarine underwater. They were widely used in World War I and World War II, and remained part of the anti-submarine arsenals of many navies during the Cold War, duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dive Bombing
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact throughout the bomb run. This allows attacks on point targets and ships, which were difficult to attack with conventional level bombers, even ''en masse''. Dive bombing was especially effective against vehicles when integrated into early instances of Blitzkrieg. After World War II, the rise of precision-guided munitions and improved anti-aircraft defences—both fixed gunnery positions and fighter interception—led to a fundamental change in dive bombing. New weapons, such as rockets, allowed for better accuracy from smaller dive angles and from greater distances. They could be fitted to almost any aircraft, including fighters, improving their effectiveness without the inherent vulnerabilities of dive bombers, which needed air superiority to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Bomber
A torpedo bomber is a military aircraft designed primarily to attack ships with aerial torpedoes. Torpedo bombers came into existence just before the World War I, First World War almost as soon as aircraft were built that were capable of carrying the weight of a torpedo, and remained an important aircraft type until they were rendered obsolete by anti-ship missiles. They were an important element in many famous World War II, Second World War battles, notably the United Kingdom, British Battle of Taranto, attack at Taranto, the sinking of the German battleship German battleship Bismarck, ''Bismarck'', the sinking of the British battleship ''HMS Prince of Wales (53), HMS Prince Of Wales'' and the British battlecruiser ''HMS Repulse (1916), HMS Repulse'' and the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Types Torpedo bombers first appeared immediately prior to the First World War. Generally, they carried torpedo, torpedoes specifically designed for air launch, which were smaller and lighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grumman TBF Avenger
The Grumman TBF Avenger (designated TBM for aircraft manufactured by General Motors) is an American World War II-era torpedo bomber developed initially for the United States Navy and Marine Corps, and eventually used by several air and naval aviation services around the world. The Avenger entered U.S. service in 1942, and first saw action during the Battle of Midway. Despite the loss of five of the six Avengers on its combat debut, it survived in service to become the most effective submarine killer and most widely-used torpedo bomber of World War II, sharing credit for sinking the super-battleships and and being credited for sinking 30 submarines. Greatly modified after the war, it remained in use until the 1960s.Wheeler 1992, p. 53. From 1942-on, production of the Avenger (in fact nearly three quarters of its the total production) was subcontracted to a purposely established division of General Motors: the Eastern Aircraft Division. Design and development The Dougl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Control Surfaces
Flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude. The primary function of these is to control the aircraft's movement along the three axes of rotation. Flight control surfaces are generally operated by dedicated aircraft flight control systems. Development of an effective set of flight control surfaces was a critical advance in the history of development of aircraft. Early efforts at fixed-wing aircraft design succeeded in generating sufficient lift to get the aircraft off the ground, however with limited control. The development of effective flight controls allowed stable flight. A conventional fixed-wing aircraft uses three primary flight control surfaces– aileron, rudder and elevator to control the roll, yaw, and pitch respectively. Secondary flight control surfaces might include spoiler, flaps, and slats on the wings. The main control surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft are attached to the airfram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |