|
Volksliste
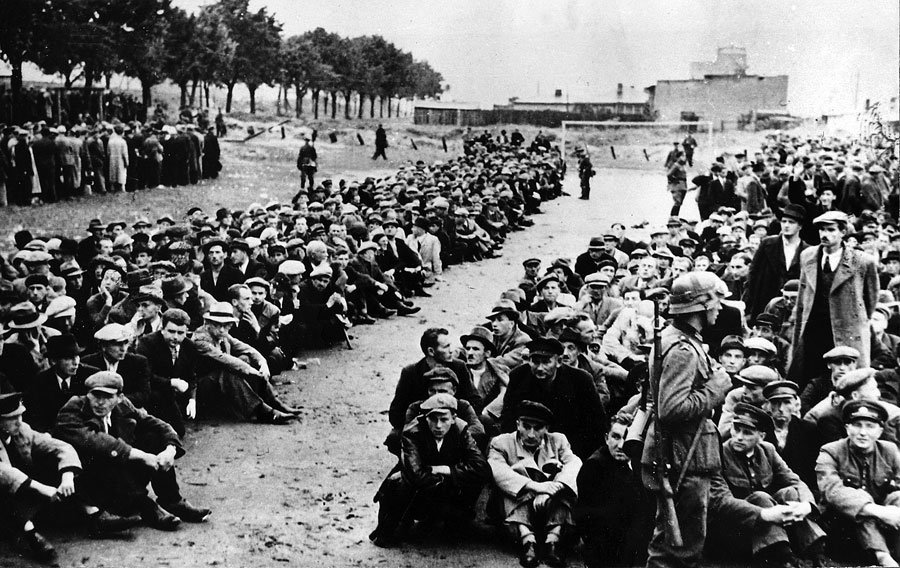
The Deutsche Volksliste (German People's List) was a Nazi Party institution that aimed to classify inhabitants of Nazi-occupied territories (1939–1945) into categories of desirability according to criteria systematised by ''Reichsführer-SS'' Heinrich Himmler. The institution originated in occupied western Poland (occupied 1939–1945). Similar schemes were subsequently developed in occupied France (1940–1944) and in the Reichskommissariat Ukraine (1941–1944). ''Volksdeutsche'' ( ethnic Germans) topped the list as a category. They comprised people without German citizenship but of German ancestry living outside Germany (unlike German expatriates). Though ''Volksdeutsche'' did not hold German citizenship, the strengthening and development of ethnic German communities throughout east-central Europe formed an integral part of the Nazi vision for the creation of Greater Germany (''Großdeutschland''). In some areas, such as Romania, Croatia, and Yugoslavia/Serbia, ethnic Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksdeutsche
In Nazi Germany, Nazi German terminology, () were "people whose language and culture had Germans, German origins but who did not hold German citizenship." The term is the nominalised plural of ''wikt:volksdeutsch, volksdeutsch'', with denoting a singular female, and , a singular male. The words ''Volk (German word), Volk'' and ''Völkisch movement, völkisch'' conveyed the meanings of "folk". Ethnic Germans living outside Germany shed their identity as ''Auslandsdeutsche'' (Germans abroad), and morphed into the in a process of self-radicalisation. This process gave the Nazi regime the nucleus around which the new Volksgemeinschaft was established across the German borders. were further divided into "racial" groupsminorities within a state minoritybased on special cultural, social, and historic criteria elaborated by the Nazis. Origin of the term ''Volksdeutsche'' According to the historian Doris Bergen, Adolf Hitler Neologism, coined the definition of which appeared in a 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazism And Race
The German Nazi Party adopted and developed several racial hierarchical categorizations as an important part of its racist ideology (Nazism) in order to justify enslavement, extermination, ethnic persecution and other atrocities against ethnicities which it deemed genetically or culturally inferior. The Aryan race is a pseudoscientific concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people who descend from the Proto-Indo-Europeans as a racial grouping and it was accepted by Nazi thinkers. The Nazis considered the putative "Aryan race" a superior "master race" with Germanic peoples as representative of Nordic race being best branch, and they considered Jews, mixed-race people, Slavs, Romani, Black People, and certain other ethnicities racially inferior subhumans, whose members were only suitable for slave labor and extermination. In these ethnicities, Jews were considered the most inferior. However, the Nazis considered Germanic peoples such as Germans to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
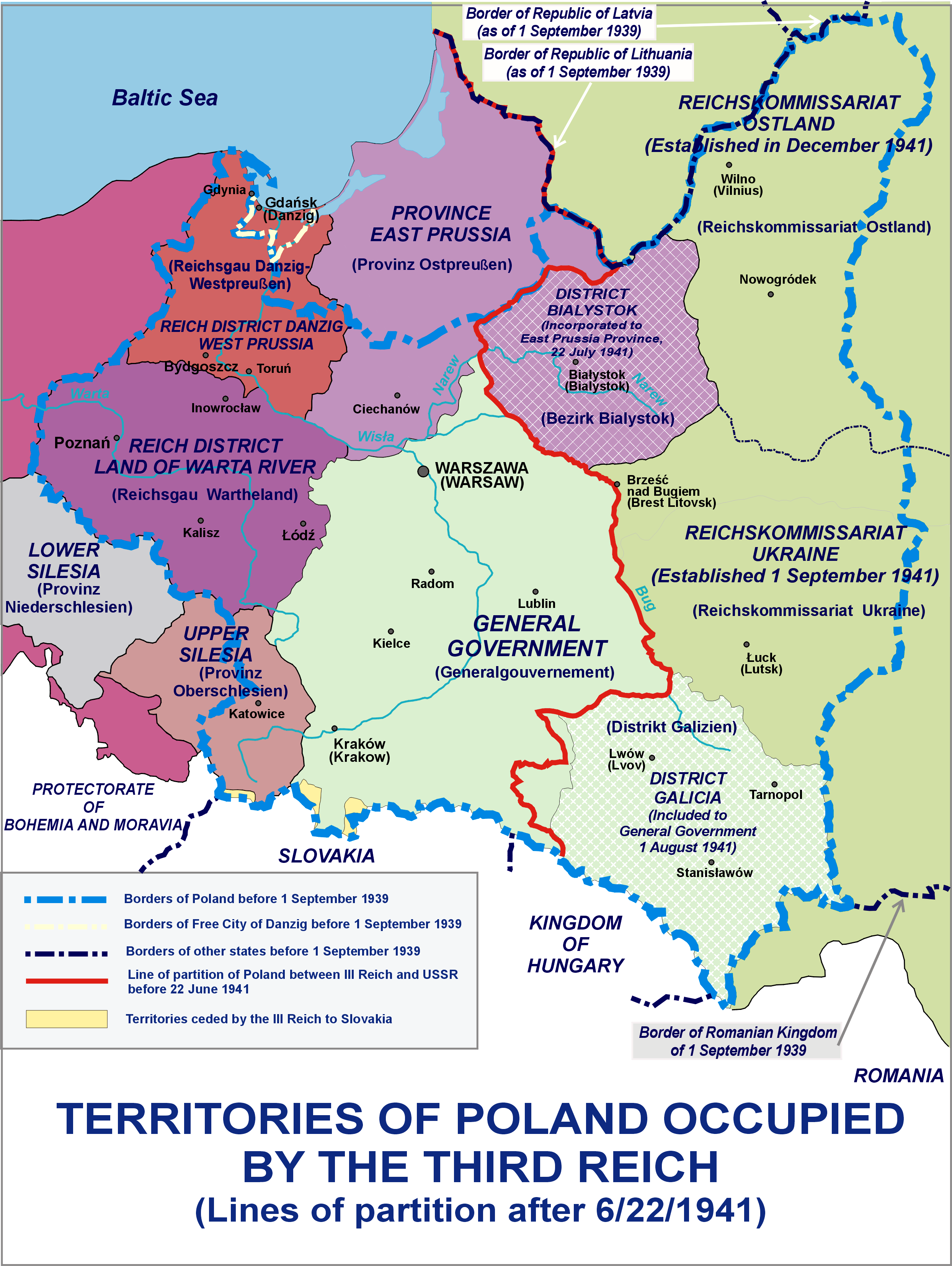
General Government
The General Government (, ; ; ), formally the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Operation Barbarossa, Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the General Government was the "Annexation Decree on the Administration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician and military leader who was the 4th of the (Protection Squadron; SS), a leading member of the Nazi Party, and one of the most powerful people in Nazi Germany. He is primarily known for being one of the main architects of the Holocaust. After serving in a reserve battalion during World War I without seeing combat, Himmler went on to join the Nazi Party in 1923. In 1925, he joined the SS, a small paramilitary arm of the Nazi Party that served as a bodyguard unit for Adolf Hitler. Subsequently, Himmler rose steadily through the SS's ranks to become by 1929. Under Himmler's leadership, the SS grew from a 290-man battalion into one of the most powerful institutions within Nazi Germany. Over the course of his career, Himmler acquired a reputation for good organisational skills as well as for selecting highly competent subordinates, such as Reinhard Heydrich. From 1943 onwards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Upper Silesia
East Upper Silesia (; ) is the easternmost extremity of Silesia, the eastern part of the Upper Silesian region around the city of Katowice ().Isabel Heinemann, ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": das Rasse- und Siedlungshauptamt der SS und die rassenpolitische Neuordnung Europas'' 2nd edition, Wallstein Verlag, 2003, p.229, The term is used primarily to denote those areas that became part of the Second Polish Republic on 20 June 1922, as a consequence of the post-World War I Treaty of Versailles. Prior to World War II, the Second Polish Republic administered the area as Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship. East Upper Silesia was also known as Polish (Upper) Silesia, and the German (Upper) Silesia was known as West Upper Silesia. Upper Silesia Plebiscite Consequently, to the end of World War I in 1918 various proposals emerged defining the division of Upper Silesia. At the Paris Peace Conference a commission for Polish affairs was created to prepare proposals for Polish borders. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgau
A (plural ) was an administrative subdivision created in a number of areas annexed by Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945. Overview The term was formed from the words (realm, empire) and , the latter a deliberately medieval-sounding word with a meaning approximately equivalent to ''shire''. The were an attempt to resolve the administrative chaos resulting from the mutually overlapping jurisdictions and different boundaries of the NSDAP Party , placed under a Party , and the list of historic states of Germany#States of the Weimar Republic, federal states, under a responsible to the Ministry of the Interior (Germany), Ministry of the Interior (in the Provinces of Prussia, Prussian provinces, the equivalent post was that of ). Interior Minister Wilhelm Frick had long desired to streamline the German administration, and the were the result: the borders of party and those of the federal states were to be identical, and the party also occupied the post of . Rival interests and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia () was an Reichsgau, administrative division of Nazi Germany created on 8 October 1939 from annexed territory of the Free City of Danzig, the Greater Pomeranian Voivodship (Polish Corridor), and the Marienwerder (region), ''Regierungsbezirk'' West Prussia of ''Gau (country subdivision), Gau'' East Prussia. Before 2 November 1939, the Reichsgau was called Reichsgau West Prussia. Though the name resembled that of the pre-1920 Provinces of Prussia, Prussian province of West Prussia, the territory was not identical. Unlike the former Prussian province, the ''Reichsgau'' included the Bromberg (Bydgoszcz) region in the south and lacked the ''Deutsch-Krone'' (Wałcz) region in the west. The province's capital was Danzig (Gdańsk), and its population without the city was (in 1939) 1,487,452. The province's area was 26,056 km2, 21,237 km2 of which was annexed Free City of Danzig, Danzig and Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919–1939), Pomeranian territory.P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsgau Wartheland
The Reichsgau Wartheland (initially Reichsgau Posen, also Warthegau) was a Nazi Germany, Nazi German ''Reichsgau'' formed from parts of Second Polish Republic, Polish territory Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed in 1939 during World War II. It comprised the region of Greater Poland and adjacent areas. Parts of ''Warthegau'' matched the similarly named Treaty of Versailles, pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen. The name was initially derived from the capital city, Poznań, Posen (Poznań), and later from the main river, Warta River, Warthe (Warta). During the Partitions of Poland from 1793, the bulk of the area had been annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia until 1807 as South Prussia. From 1815 to 1849, the territory was within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Posen, which was the Province of Posen until Second Polish Republic, Poland was re-established in 1918–1919 following World War I. The area is currently the Greater Poland Voivodeship. Establishment and administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiec Warszawskich VolksdeutschĂłw W Sali Roma
A ''veche'' was a popular assembly during the Middle Ages. The ''veche'' is mentioned during the times of Kievan Rus' and it later became a powerful institution in Russian cities such as Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod and Pskov, where the ''veche'' acquired great prominence and was broadly similar to the Norse Thing (assembly)#Viking and medieval society, ''thing'' or the Swiss ''Landsgemeinde''. The last ''veche'' meeting was held in Pskov before the institution was abolished in 1510. Etymology The word ''veche'' is a transliteration of the Russian (), which is in turn inherited from Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic (), which is also represented in the word ''soviet (council), soviet'', both ultimately deriving from the Proto-Slavic verbal stem of ). History Origins Procopius, Procopius of Caesarea mentioned Slavs gathering in popular assemblies in the 6th century: The ''veche'' is thought to have originated in the tribal assemblies of Eastern Europe, thus predating the stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zichenau (region)
''Regierungsbezirk Zichenau'' was a ''Regierungsbezirk'', or administrative region, of the Nazi German Province of East Prussia in 1939–45, established in German-occupied Polish territory during World War II. The regional capital was Zichenau (Ciechanów). It was also referred to under the designation of South East Prussia () which, however, was later sometimes also applied to Bialystok District, although the latter was not incorporated into, but merely attached to East Prussia. History The government region was created on 26 October 1939, out of Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany during World War II. The region had an area of 12,000 km2 and a population of approximately 895,000, including 800,000 Poles, 80,000 Jews, and 15,000 Germans. The Polish population was subjected to various crimes, including mass arrests, roundups, deportations to forced labour and concentration camps (including teenagers), executions, massacres (also as part of the ''Intelligenzaktion'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Lorenz
Werner Lorenz (2 October 1891 – 13 March 1974) was an SS functionary during the Nazi era. He was head of the ''Volksdeutsche Mittelstelle'' (VOMI) (Main Office for Ethnic Germans), an organization charged with resettling ethnic Germans in the "German Reich" from other parts of Europe, as well as colonising the occupied lands during World War II. After the war, Lorenz was sentenced to prison for crimes against humanity in 1948. He was released in 1954 and died in 1974. Early life He was born in Grünhof (now in Gmina Postomino, Sławno County) near Stolp, Pomerania. His father was a forest warden. In 1909 Lorenz went to Military school. He served in World War I first as a cavalry officer then as a pilot in the ''Luftstreitkräfte''. After the war he worked as a border guard and as farmer. He later acquired land and industrial property in Danzig. Through his daughter Rosemarie, Lorenz would become Axel Springer's father-in-law. Nazi Party and SS career In 1929 Lorenz joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |