|
Volitive Modality
Volitive modality (abbreviated ) is a linguistic modality that indicates the desires, wishes or fears of the speaker. It is classified as a subcategory of deontic modality. Realisation in speech Volitive moods are a category of grammatical moods that are used to express volitive modality. Examples are the optative, desiderative and imprecative moods. However, many languages (like English) have other ways to express volitive modality, for example modal verbs ("''Wish'' that you were here!", "''May'' he live forever!"). Esperanto Esperanto has a volitive verb form that is formed by adding a to the verb stem and used to indicate that an action or state is desired, requested, ordered, or aimed for. The verb form is formally called volitive, but in practice, it can be seen as a broader deontic form, rather than a pure volitive form, since it is also used to express orders and commands besides wishes and desires. Examples: * ― "Come." (a request or command) * ― "Give it to me." (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing Rules, Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or uncommon. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically indicating direction downward b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Linguistic Modality
In linguistics and philosophy, modality refers to the ways language can express various relationships to reality or truth. For instance, a modal expression may convey that something is likely, desirable, or permissible. Quintessential modal expressions include modal auxiliaries such as "could", "should", or "must"; modal adverbs such as "possibly" or "necessarily"; and modal adjectives such as "conceivable" or "probable". However, modal components have been identified in the meanings of countless natural language expressions, including counterfactuals, propositional attitudes, evidentials, habituals, and generics. Modality has been intensely studied from a variety of perspectives. Within linguistics, typological studies have traced crosslinguistic variation in the strategies used to mark modality, with a particular focus on its interaction with tense–aspect–mood marking. Theoretical linguists have sought to analyze both the propositional content and discourse effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Deontic Modality
Deontic modality (abbreviated ) is a linguistic modality that indicates how the world ought to be according to certain norms, expectations, speaker desires, etc. In other words, a deontic expression indicates that the state of the world (where 'world' is loosely defined here in terms of the surrounding circumstances) does not meet some standard or ideal, whether that standard be social (such as laws), personal (desires), etc. The sentence containing the deontic modal generally indicates some action that would change the world so that it becomes closer to the standard or ideal. This category includes the following subcategories: *Commissive modality (the speaker's commitment to do something, like a promise or threat; alethic logic or temporal logic would apply): "I shall help you." * Directive modality (commands, requests, etc.; deontic logic would apply): "Come!", "Let's go!", "You've got to taste this curry!" * Volitive modality (wishes, desires, etc.; boulomaic logic would app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Grammatical Moods
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences. In theoretical linguistics, a speaker's judgement on the well-formedness of a linguistic 'string'—called a grammaticality judgement—is based on whether the sentence is interpreted in accordance with the rules and constraints of the relevant grammar. If the rules and constraints of the particular lect are followed, then the sentence is judged to be grammatical. In contrast, an ungrammatical sentence is one that violates the rules of the given language variety. Linguists use grammaticality judgements to investigate the syntactic structure of sentences. Generative linguists are la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Optative Mood
The optative mood ( or ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood that indicates a wish or hope regarding a given action. It is a superset of the cohortative mood and is closely related to the subjunctive mood but is distinct from the desiderative mood. English has no morphological optative, but various constructions impute an optative meaning. Examples of languages with a morphological optative mood are Ancient Greek, Albanian, Armenian, Georgian, Friulian, Kazakh, Kurdish, Navajo, Old Prussian, Old Persian, Sanskrit, Turkish, and Yup'ik. English Although English has no morphological optative, analogous constructions impute an optative meaning, including the use of certain modal verbs: *''May you have a long life!'' *''Would that I were younger.'' Periphrastic constructions include ''if only'' together with a subjunctive complement: *''If only I were rich!'' *''I would sing if only I weren't tone deaf.'' The optative mood can also be expressed elliptically: *''(May) G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Desiderative Mood
In linguistics, a desiderative (abbreviated or ) form is one that has the meaning of "wanting to X". Desiderative forms are often verbs, derived from a more basic verb through a process of morphological derivation. Desiderative mood is a kind of volitive mood. Sanskrit In Sanskrit, the desiderative is formed through the suffixing of /sa/ and the prefixing of a reduplicative syllable, consisting of the first consonant of the root (sometimes modified) and a vowel, usually /i/ but /u/ if the root has an /u/ in it. Changes to the root vowel sometimes happen, as well. The acute accent, which indicates high pitch in Vedic, is usually placed at the first vowel. For example: Meadow Mari In Meadow Mari, the desiderative mood is marked by the suffix -не ''-ne''. Positive present Negative present Japanese In Japanese, the desiderative takes two main forms: () and (). Both forms conjugate for tense and positivity, but in different ways: with the ending, the verb becomes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Imprecative Mood
Some languages distinguish between the optative mood and an imprecative mood (abbreviated An abbreviation () is a shortened form of a word or phrase, by any method including shortening, contraction, initialism (which includes acronym), or crasis. An abbreviation may be a shortened form of a word, usually ended with a trailing per ... ). In these languages, the imprecative mood is used to wish misfortune upon others, whereas the optative mood is used for wishes in general. In such a language, "May he lose the race" is in imprecative mood, whereas "May I win the race" would be in optative mood. A commonly given example of a language with an imprecative mood is Turkish, which uses an otherwise obsolete future-tense suffix ''-esi'' solely in the third person for curses: Imprecative retorts in English While not a mood in English, expressions like ''like hell it is'' or ''the fuck you are'' are imprecative retorts. These consist of an expletive + a personal pronoun subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Modal Verb
A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a ''likelihood'', ''ability'', ''permission'', ''request'', ''capacity'', ''suggestion'', ''order'', ''obligation'', ''necessity'', ''possibility'' or ''advice''. Modal verbs generally accompany the base (infinitive) form of another verb having semantic content. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are ''can'', ''could'', ''may'', ''might'', ''must'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''would'', and ''ought''. Function Modal verbs have a wide variety of communicative functions, but these functions can generally be related to a scale ranging from possibility ("may") to necessity ("must"), in terms of one of the following types of modality: *epistemic modality, concerned with the theoretical ''possibility of propositions being true or not true'' (including likelihood and certainty) * deontic modality, concerned with ''possibility and necessity in terms of freedom to act'' (including permission and dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Esperanto
Esperanto (, ) is the world's most widely spoken Constructed language, constructed international auxiliary language. Created by L. L. Zamenhof in 1887 to be 'the International Language' (), it is intended to be a universal second language for international communication. He described the language in ''Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as 'one who hopes'. Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''Constructed language#A priori and a posteriori languages, a priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European group. A substantial majority of its vocabulary (approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Universal Esperanto Association
The Universal Esperanto Association (, UEA), also known as the World Esperanto Association, is the largest international organization of Esperanto speakers, with 5,501 individual members in 121 countries and 9,215 through national associations (in 2015) in 214 countries. In addition to individual members, 70 national Esperanto organizations are affiliated with UEA. Its current president is Prof. Duncan Charters. The magazine ''Esperanto (magazine), Esperanto'' is the main publication to inform UEA members about everything happening in the Esperanto community. The UEA was founded in 1908 by the Swiss journalist Hector Hodler and others and is now headquartered in Rotterdam, Netherlands. The organization has official relations with the United Nations and has an office at the Headquarters of the United Nations, United Nations headquarters in New York City. Structure and affiliated organizations According to its 1980 statutes (Statuto de UEA), the Universal Esperanto Association ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lernu!
''lernu!'' is a multilingual, web-based free project for promoting and teaching Esperanto. The name ''Lernu'' comes from the imperative form of the Esperanto verb ''lerni'', meaning "to learn". The site is run by E@I, an international youth organization, which started as a working group of the World Esperanto Youth Organization. The site's content includes various tools for learning Esperanto, such as exercises, games, dictionaries, grammatical overviews, an examination system and a multimedia library with books, music, voice-narrated stories and videos. The site also provides communication services such as an instant messenger, discussion forums on various topics, and news about Esperanto events. Esperantists and Esperanto organizations can advertise their activities and services on the website. History The ''lernu!'' project was first proposed at the first Esperanto@Interreto (now E@I) seminar in Stockholm, Sweden in April 2000, and was developed in October 2001 at the seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
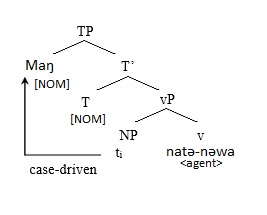 |
Volition (linguistics)
In linguistics, volition is a concept that distinguishes whether the subject, or agent of a particular sentence intended an action or not. Simply, it is the intentional or unintentional nature of an action.Tournadre, Nicolas. The Rhetorical Use of the Tibetan Ergative. 1991. Web. Volition concerns the idea of control and for the purposes outside of psychology and cognitive science Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary, scientific study of the mind and its processes. It examines the nature, the tasks, and the functions of cognition (in a broad sense). Mental faculties of concern to cognitive scientists include percep ..., is considered the same as intention in linguistics. Volition can then be expressed in a given language using a variety of possible methods. These sentence forms usually indicate that a given action has been done intentionally, or willingly. There are various ways of marking volition cross-linguistically. When using verbs of volition in English, like "w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |