|
Venetiko
Venetiko (), is a small uninhabited Greek island off the southern coast of the Peloponnese, south of the Cape Akritas. It belongs to the cluster of the Messenian Oinousses. It is administratively part of the municipality of Pylos-Nestor, in Messenia. During the ancient times, it was called Theganoussa () and it is mentioned by the Pomponius Mela, Pliny the Elder, Pausanias and Ptolemaeus. Though Pausanias calls it an uninhabited island, archaeological evidence suggests that it was once occupied. It is included in the Natura 2000 Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectiv .... References Ionian Islands Landforms of Messenia Pylos-Nestor {{Peloponnese-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenian Oinousses
Messenian Oinousses () is a Greek island complex in the southwest coasts of Peloponnese, in Ionian Sea. It is located to the south of Messenian peninsula, opposite Methoni and Foinikounda. The archipelago comprises the islands Schiza and Sapientza and the islets and rocks Venetiko, Agia Mariani, Avgo, Dyo Aderfia and Boba. The largest island is Schiza, whereas the only populated island is Sapientza. To the southwest of Oinousses is the deepest point of the Mediterranean Sea, the Calypso Deep, also known as the Oinousses Deep or the Vavilov Deep. Oinousses has been included in the environmental program Natura 2000. The islands belong to Pylos-Nestor Pylos-Nestoras () is a municipality in the Messenia regional unit, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Pylos. The municipality has an area of 554.265 km2. Municipality The municipality Pylos-Nestora ... municipality. Main islands References {{Ionian Islands Archipelagoes of Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a prefecture (''nomos'') covering the same territory. The capital and largest city of Messenia is Kalamata. Geography Physical Messenia borders on Elis to the north, Arcadia to the northeast, and Laconia to the southeast. The Ionian Sea lies to the west, and the Gulf of Messinia to the south. The most important mountain ranges are the Taygetus in the east, the Kyparissia mountains in the northwest and the Lykodimo in the southwest. The main rivers are the Neda in the north and the Pamisos in central Messenia. Off the south coast of the southwesternmost point of Messenia lie the Messinian Oinousses islands. The largest of these are Sapientza, Schiza and Venetiko. The small island Sphacteria closes off the bay of Pylos. All these islands are virtua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccation, desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
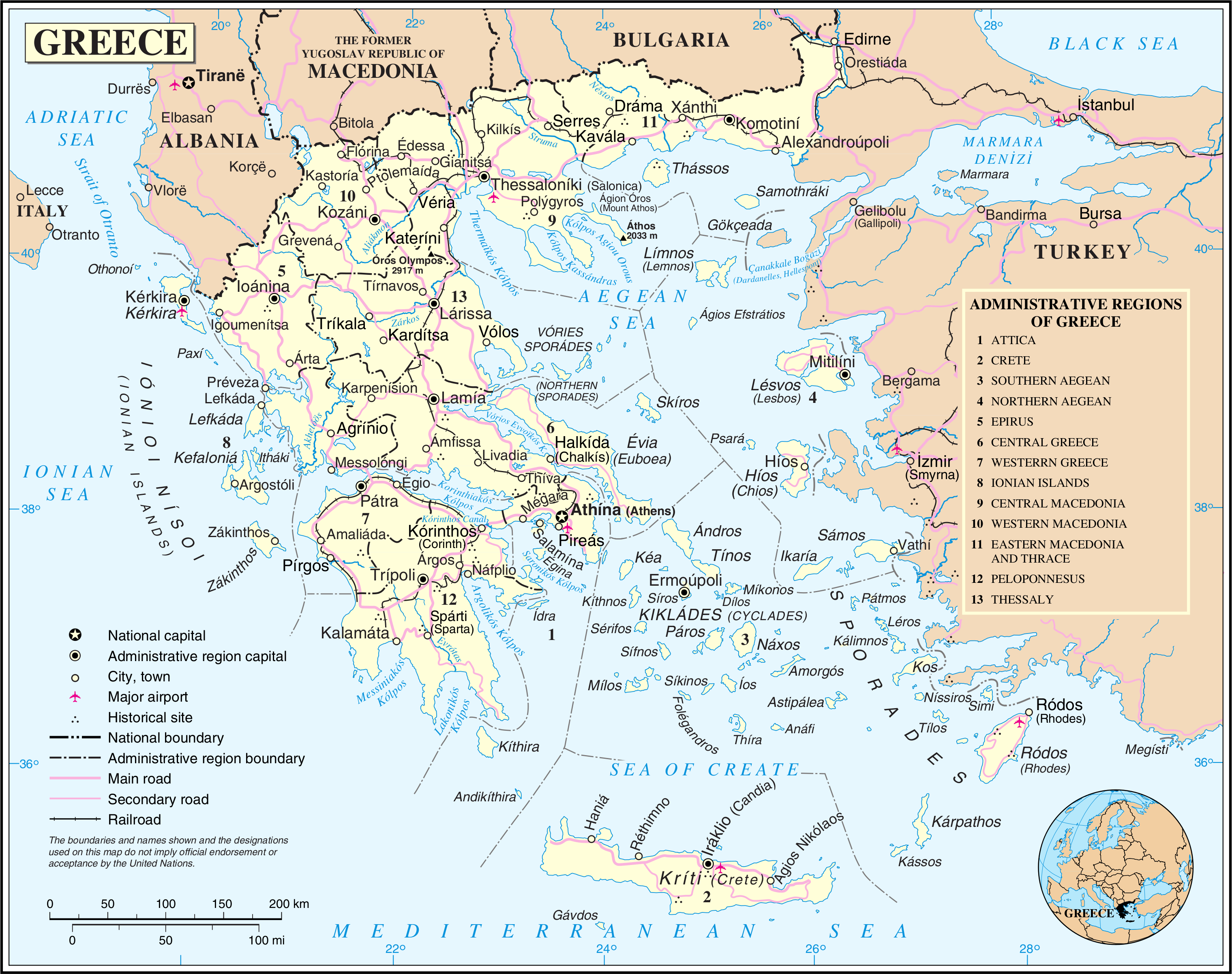
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece (, ; singular , ) are the country's third-level administrative units (counting decentralized administrations as first-level). They are subdivisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality' .... They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, on the mainland, coterminous with the "pre-Kallikratis" prefectures of Greece. List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communities And Municipalities Of Greece
The municipalities of Greece ( , in singular case ) are the lowest level of government within the organizational structure of the state. As of 2021, there are 332 municipalities, further divided into 1036 municipal units and 6136 communities. Thirteen administrative regions form the second-level unit of government. The regions consist of 74 regional units, which mostly correspond to the old prefectures. Regional units are then divided into municipalities. The new municipalities may be subdivided into municipal units (δημοτικές ενότητες, ''dimotikés enótites''), consisting of the pre-Kallikratis municipalities. These were further subdivided into municipal communities (δημοτικές κοινότητες, ''dimotikés koinótites'') and local communities (τοπικές κοινότητες, ''topikés koinótites'') according to population, but are simply named communities (κοινότητες, ''koinótites'') since the entry into force of the Kleisth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylos-Nestor
Pylos-Nestoras () is a municipality in the Messenia regional unit, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Pylos. The municipality has an area of 554.265 km2. Municipality The municipality Pylos-Nestoras was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 6 former municipalities, that became municipal units: *Chiliochoria *Koroni *Methoni, Messenia, Methoni *Nestoras *Papaflessas, Messenia, Papaflessas *Pylos References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known Roman geographer. He was born at the end of the 1st century BC in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45. His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less than one hundred pages of ordinary print, and is described by the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (1911) as "dry in style and deficient in method, but of pure Latinity, and occasionally relieved by pleasing word-pictures." Except for the geographical parts of Pliny the Elder, Pliny's ''Historia naturalis'' (where Mela is cited as an important authority), the ''De situ orbis'' is the only formal treatise on the subject in Classical Latin. Biography Little is known of Pomponius except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera (identified as Iulia Traducta) in southern Spain, on Algeciras Bay (Mela ii. 6, § 96; but the text is here corrupt). The date of his writing may be appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( ; ; ) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his '' Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology, which is providing evidence of the sites and cultural details he mentions although knowledge of their existence may have become lost or relegated to myth or legend. Biography Nothing is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is probable that he was born into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From until his death around 180, Pausanias travelled throughout the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing his '' Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemaeus
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Solar System, and unlike most Greek mathematicians, Ptolemy's writings (foremost the ''Almagest'') never ceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |