Pomponius Mela on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known
 Little is known of Pomponius except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera (identified as Iulia Traducta) in southern
Little is known of Pomponius except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera (identified as Iulia Traducta) in southern
 His
His
Editions in the original Latin
in the
I
an
in Latin, digitised at ''The Latin Library'' ;Attribution {{DEFAULTSORT:Pomponius Mela 40s deaths Ancient Roman geographers 1st-century Romans Romans from Hispania Year of birth unknown 1st-century geographers Silver Age Latin writers
 Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest known Roman geographer
;Pre-Hellenistic Classical Greece
*Homer
*Anaximander (died )
*Hecataeus of Miletus (died )
*Massaliote Periplus (6th century BC)
*Scylax of Caryanda (6th century BC)
*Herodotus (died )
;Hellenistic period
*Pytheas (died )
*''Periplus of Pseudo- ...
. He was born at the end of the 1st century BC in Tingentera (now Algeciras
Algeciras () is a city and a municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, Andalusia. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, near the Strait of Gibraltar, it is the largest city on the Bay of G ...
) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less than one hundred pages of ordinary print, and is described by the ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
'' (1911) as "dry in style and deficient in method, but of pure Latinity, and occasionally relieved by pleasing word-pictures." Except for the geographical parts of Pliny's ''Historia naturalis'' (where Mela is cited as an important authority), the ''De situ orbis'' is the only formal treatise on the subject in Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It formed parallel to Vulgar Latin around 75 BC out of Old Latin ...
.
Biography
 Little is known of Pomponius except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera (identified as Iulia Traducta) in southern
Little is known of Pomponius except his name and birthplace—the small town of Tingentera or Cingentera (identified as Iulia Traducta) in southern Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, on Algeciras
Algeciras () is a city and a municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, Andalusia. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, near the Strait of Gibraltar, it is the largest city on the Bay of G ...
Bay (Mela ii. 6, § 96; but the text is here corrupt). The date of his writing may be approximately fixed by his allusion (iii. 6 § 49) to a proposed British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
expedition of the reigning emperor, almost certainly that of Claudius in AD 43. That this passage cannot refer to Julius Caesar is evidenced by several references to events of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
's reign; especially to certain new names given to Spanish towns. Mela, like the two Senecas, Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November AD 39 – 30 April AD 65), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba, Hispania Baetica (present-day Córdoba, Spain). He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imper ...
, Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman and Celtiberian poet born in Bilbilis, Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of '' Epigrams'', pu ...
, Quintilian
Marcus Fabius Quintilianus (; 35 – 100 AD) was a Roman educator and rhetorician born in Hispania, widely referred to in medieval schools of rhetoric and in Renaissance writing. In English translation, he is usually referred to as Quin ...
, Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
, Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
, were all part of Italic communities settled in various parts of Spain that eventually relocated in Rome. It has been conjectured that Pomponius Mela may have been related in some way to Marcus Annaeus Mela, son of Seneca the Elder
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Elder ( ; – c. AD 39), also known as Seneca the Rhetorician, was a Roman writer, born of a wealthy equestrian family of Corduba, Hispania. He wrote a collection of reminiscences about the Roman schools of rhetoric, ...
and father of Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November AD 39 – 30 April AD 65), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba, Hispania Baetica (present-day Córdoba, Spain). He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imper ...
.
Geographical knowledge
The general views of the ''De situ orbis'' mainly agree with those current amongGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
writers from Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
; the latter was probably unknown to Mela. But Pomponius is unique among ancient geographers in that, after dividing the Earth into five zones, of which two only were habitable, he asserts the existence of antichthones
Antichthones, in geography, are those peoples who inhabit the antipodes, regions on opposite sides of the Earth. The word is compounded of the Greek ''ὰντὶ'' ("opposed") and ''χθών'' ("earth").
Classical and Medieval Europe consider ...
, inhabiting the southern temperate zone inaccessible to the folk of the northern temperate regions from the unbearable heat of the intervening torrid belt. On the divisions and boundaries of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, he repeats Eratosthenes; like all classical geographers from Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
(except Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
) he regards the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
as an inlet of the Northern Ocean, corresponding to the Persian and Arabian (Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
) gulfs on the south.
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
n conceptions are inferior to those of some earlier Greek writers; he follows Eratosthenes in supposing that country to occupy the south-eastern angle of Asia, whence the coast trended northwards to Scythia, and then swept round westward to the Caspian Sea. As usual, he places the Riphean Mountains
In Greco-Roman geography, the Riphean Mountains (also Riphaean; ; '; Latin: ''Rhipaei'' or ''Riphaei montes'') were a supposed mountain range located in the far north of Eurasia. The name of the mountains is probably derived from ("wind gust") ...
and the Hyperboreans near the Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people.
Etymology
The names ...
n Ocean. In western Europe his knowledge (as was natural in a Spanish subject of Imperial Rome) was somewhat in advance of the Greek geographers. He defines the western coast-line of Spain and Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
and its indentation by the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay ( ) is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Point Penmarc'h to the Spanish border, and along the northern coast of Spain, extending westward ...
more accurately than Eratosthenes or Strabo, his ideas of the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
and their position are also clearer than his predecessors. He is the first to name the Orcades or Orkney Islands
Orkney (), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The plural name the Orkneys is also sometimes used, but locals now consider it outdated. Part of the Northern Isles along with Shetland ...
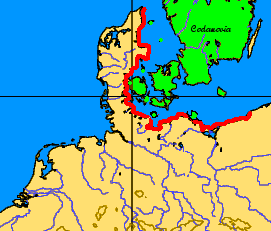
, which he defines and locates pretty correctly. Of northern Europe his knowledge was imperfect, but he speaks of a great bay (" Codanus sinus") to the north of Germany, among whose many islands was one, "Codanovia", of pre-eminent size; this name reappears in Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
's work as ''Scatinavia''. ''Codanovia'' and ''Scatinavia'' were both Latin renderings of the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
*''Skaðinawio'', the Germanic name for Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
.
Descriptive method
Mela's descriptive method follows ocean coasts, in the manner of aperiplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus wa ...
, probably because it was derived from the accounts of navigators. He begins at the Straits of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
, and describes the countries adjoining the south coast of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
; then he moves round by Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, and so returns to Spain along the north shore of the Euxine, Propontis, etc. After treating the Mediterranean islands, he next takes the ocean littoral
The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely i ...
—to west, north, east and south successively—from Spain and Gaul round to India, from India to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
; and so again works back to Spain. Like most classical geographers he conceives of the continent of Africa as surrounded by sea and not extending very far south.
Editions
The ''editio princeps
In Textual scholarship, textual and classical scholarship, the ''editio princeps'' (plural: ''editiones principes'') of a work is the first printed edition of the work, that previously had existed only in manuscripts. These had to be copied by han ...
'' of Mela was published at Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
in 1471; the first critical edition was by Joachim Vadian (Wien, 1518), superseded by those of Johann Heinrich Voss (1658), Johann Friedrich Gronovius (1685 and 1696), A. Gronovius (1722 and 1728), and Tzschucke (1806–1807), in seven parts (Leipzig; the most elaborate of all); G. Paithey's (Berlin, 1867) for its text. The English translation by Arthur Golding (1585) was celebrated.See also Edward Bunbury, ''Ancient Geography'', ii. 352–368, and D. Detlefsen, ''Quellen und Forschungen zur alten Gesch. und Geog.'' (1908).
A recent English translation is that of F. E. Romer, originally published in 1998.
*
References
Sources
*Editions in the original Latin
in the
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including web ...
*BookI
an
in Latin, digitised at ''The Latin Library'' ;Attribution {{DEFAULTSORT:Pomponius Mela 40s deaths Ancient Roman geographers 1st-century Romans Romans from Hispania Year of birth unknown 1st-century geographers Silver Age Latin writers