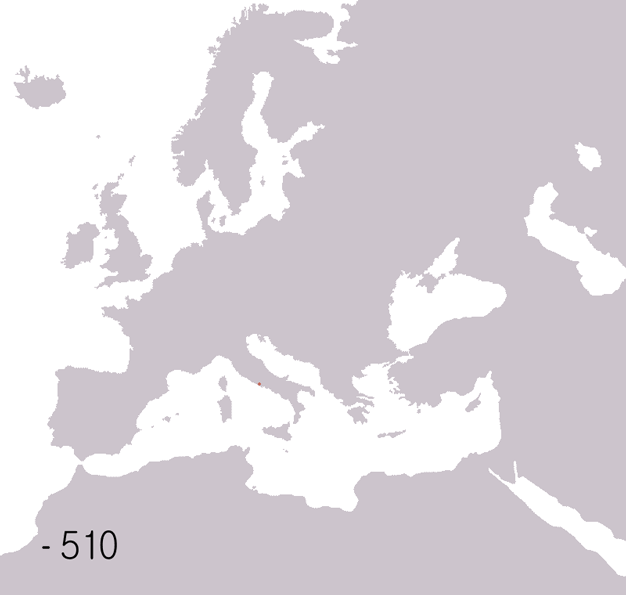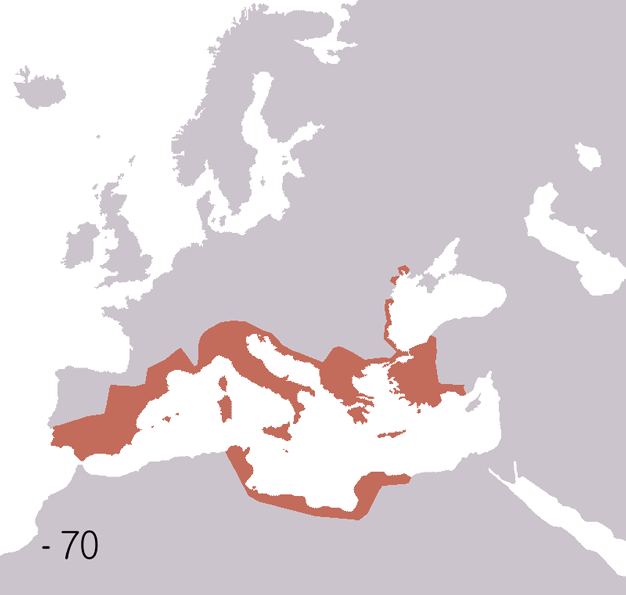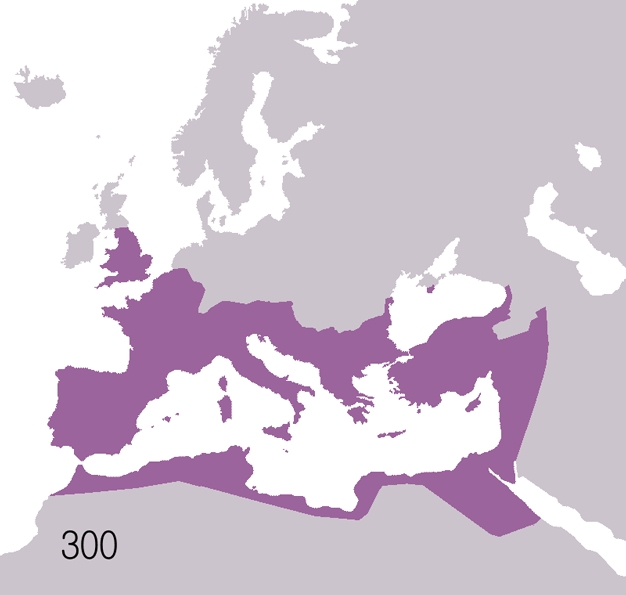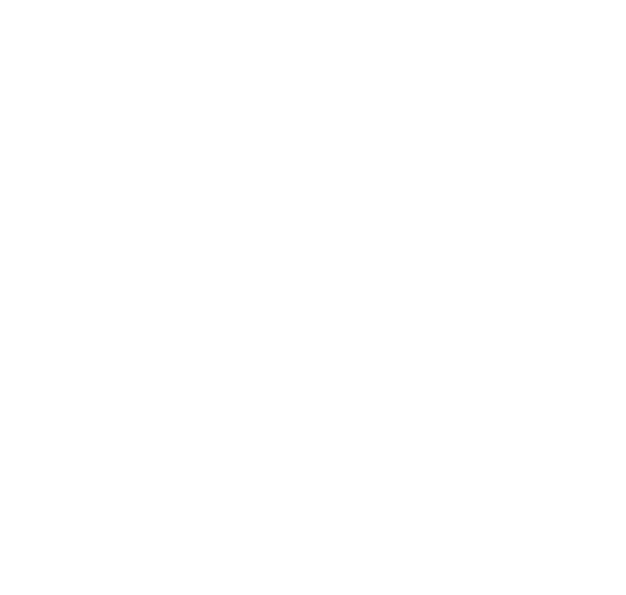
|
Vendel Period
In Scandinavian prehistory, sometimes specifically Swedish prehistory, the Vendel Period, or Vendel Age (; ) appears between the Migration Period and the Viking Age. The name is taken from the rich boat inhumation cemetery at Vendel parish church, Uppland. Unlike the preceding and succeeding eras, the Vendel Period left very few precious metal artifacts or runic inscriptions. Instead, it is extremely rich in animal art on copper-alloy objects. It is also known for '' guldgubbar'', tiny embossed gold foil images, and elaborate helmets with embossed decoration similar to the one found at Sutton Hoo in England. During the period, Swedish expeditions began to explore the waterways of territories which later became Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. The Elder Futhark writing system was abandoned in favor of the Younger Futhark, virtually simultaneously over the whole of Scandinavia. Some runestones survive, most notably those at Rök and Sparlösa, both from . Other written so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
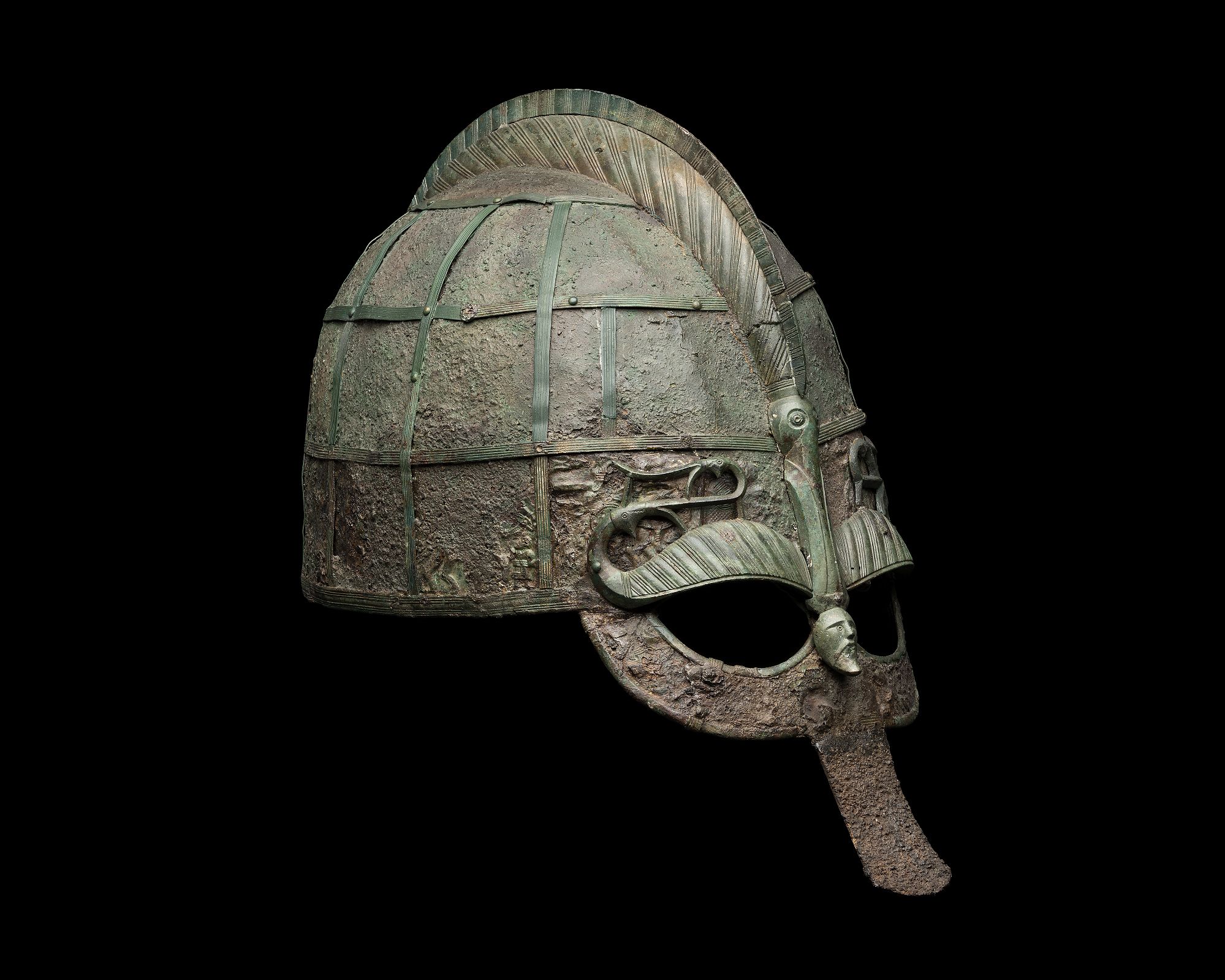
Vendel I Helmet 456059
Vendel is a village at Tierp Municipality in Uppland, Sweden. The village overlooks Vendelsjön, a long inland stretch of water near the Vendel river which has its confluence with the river Fyris. Vendel was the site of an ancient royal estate, part of '' Uppsala öd'', a network of royal estates meant to provide income for the medieval Swedish kings. A large number of archaeological finds have been found here, which have given their name to the Vendel Period. Vendel Church (''Vendels kyrka'') was probably begun to be built in Romanesque style during the latter half of the 13th century. Around 1450, the church was vaulted with brick vaults. The church is most noted for its murals by Johannes Iwan who worked in Uppland during the 15th century. Archaeological research In 1881 to 1883, several excavations by Swedish archaeologist Hjalmar Stolpe (1841–1905) revealed 14 graves in and just beyond the south-east corner of the churchyard. Several of the burials were contained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runestone
A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic alphabet, runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition of erecting runestones as a memorial to dead men began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but the majority of the extant runestones date from the late Viking Age. While most of these are located in Scandinavia, particularly Sweden, there are also scattered runestones in locations that were visited by Norsemen. Runestones were usually brightly coloured when erected, though this is no longer evident as the colour has worn off. History The tradition of raising stones that had runic inscriptions first appeared in the 4th and 5th century, in Norway and Sweden, and these early runestones were usually placed next to graves, though their precise function as commemorative monuments has been questioned. The earliest Danish runestones appeared in the 8th and 9th centuries, and there are about 50 runest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries. In the late 4th century, the lands of the Goths in present-day Ukraine were overwhelmed by a significant westward movement of Alans and Huns from the east. Large numbers of Goths subsequently concentrated upon the Roman border at the Lower Danube, seeking refuge inside the Roman Empire. After they entered the Empire, violence broke out, and Goth-led forces inflicted a devastating defeat upon the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late antiquity.Norman A. Stillman ''The Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khosrau I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; ), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ("the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 531 to 579. He was the son and successor of Kavad I (). Inheriting a reinvigorated empire at war with the Byzantines, Khosrow I signed a peace treaty with them in 532, known as the Perpetual Peace, in which the Byzantine emperor Justinian I paid 11,000 pounds of gold to the Sasanians. Khosrow then focused on consolidating his power, executing conspirators, including his uncle Bawi. Dissatisfied with the actions of the Byzantine clients and vassals, the Ghassanids, and encouraged by Ostrogoth envoys from Italy, Khosrow violated the peace treaty and declared war against the Byzantines in 540. He sacked the major city of Antioch and deported its population to Persia. In 541, he invaded Lazica and made it an Iranian protectorate, thus initiating the Lazic War. In 545, the two empires agreed to halt the wars in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eternal Peace (532)
The Perpetual Peace or the Treaty of Eternal Peace (), signed in 532 between the East Roman (Byzantine) Empire and Sassanid Persia, was a peace treaty of indefinite duration, which concluded the Iberian War (527–531) between the two powers. It heralded a period of relatively cordial relations, but lasted only until 540, when hostilities resumed over the control of Lazica. History The Iberian War, which had been provoked by the uprising of the Iberians against the Persians in 524/5, had been largely indecisive: the Persians swiftly crushed the revolt, but were unable to make any gains in Byzantine territory except for two forts, Scanda and Sarapanis, in Lazica. The Byzantines had recovered from some early reversals to inflict two major defeats on the Persians in 530 at Dara and Satala. In their aftermath, they gained the two border forts of Bolum and Pharangium in Persarmenia, but were in turn defeated at Callinicum in 531. Throughout these conflicts, periods of truce and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Wars
The Gothic Wars were a long series of conflicts between the Goths and the Roman Empire between the years 249 and 554. The main wars are detailed below. History Crisis of the Third Century During the Crisis of the Third Century, Goths under Cniva fought against the Roman Empire between 248 and 253. The War was probably instigated after emperor Decius's predecessor Philip the Arab had refused to continue payments of annual subsidies to the tribes of the region initiated by Emperor Maximinus Thrax in 238 while they were starving. The Goths were led by King Cniva who had crossed the Danube in 249 or 250 with a number of units, however, the exact number is unknown. Cniva's main column of 70,000 unsuccessfully attacked Novae and were then defeated by Decius at the Battle of Nicopolis ad Istrum before moving on to Augusta Traiana pursued by Decius where at the Battle of Beroe they defeated him and looted the city. Decius was forced to withdraw his army north to Oescus leaving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars (Caucasus), Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774. The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili,: "From Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/winnaną, winna-'', meaning "to fight, win" who dwelt in northern Germany before migrating to seek new lands. Earlier Roman-era historians wrote of the Lombards in the first century AD as being one of the Suebian peoples, also from what is now northern Germany, near the Elbe river. They migrated south, and by the end of the fifth century, the Lombards had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria and Slovakia north of the Danube. Here they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepids. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid leader Thuris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading peoples outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gallo-Romans under their rule. They conquered most of Gaul, defeating the Visigoths (507) and the Burgundians (534), and also extended their rule into Raetia (537). In Germania, the Alemanni, Bavarii and Saxons accepted their lordship. The Merovingian realm was the largest and most powerful of the states of western Europe following the breakup of the empire of Theodoric the Great. The dynastic name, medieval Latin or ("sons of Merovech"), derives from an unattested Frankish language, Frankish form, akin to the attested Old English , with the final -''ing'' being a typical Germanic languages, Germanic patronymic suffix. The name derives from Salian Franks, Salian King Merovech, who is at the center of many legends. Unl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |