 |
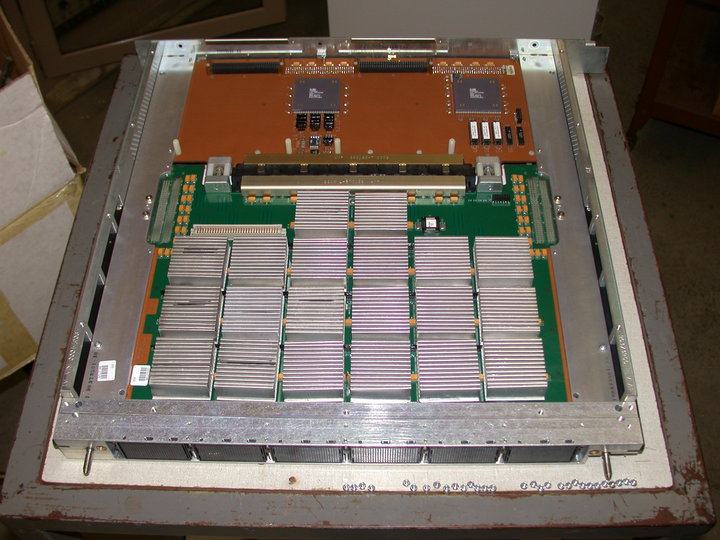
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SIMD within a register (SWAR) Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation, compression and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
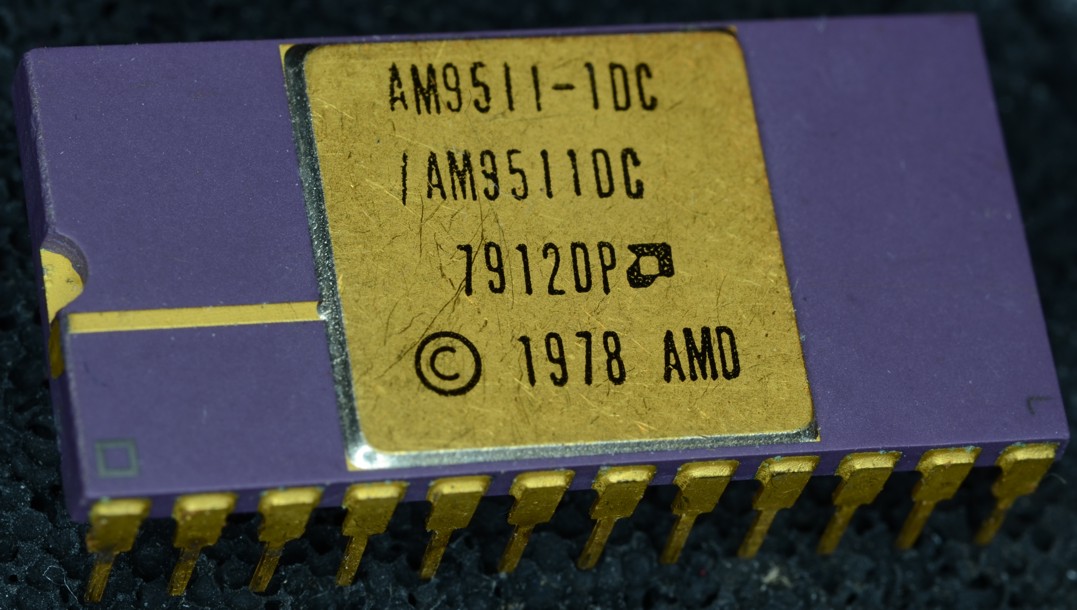 |
Coprocessor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it. Functionality Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such as FPUs) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Computer For Operations With Functions
Within computer engineering and computer science, a computer for operations with (mathematical) functions (unlike the usual computer) operates with functions at the hardware level (i.e. without programming these operations).see also here http://www.sigcis.org/files/SIGCISMC2010_001.pdf and english version here(see alshere in Russian (see alshere in Russian History A computing machine for operations with functions was presented and developed by Mikhail Kartsev in 1967. Among the operations of this computing machine were the functions addition, subtraction and multiplication, functions comparison, the same operations between a function and a number, finding the function maximum, computing indefinite integral, computing definite integral of derivative of two functions, derivative of two functions, shift of a function along the X-axis etc. By its architecture this computing machine was (using the modern terminology) a vector processor or ''array processor'', a central processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Distributed Array Processor
The Distributed Array Processor (DAP) produced by International Computers Limited (ICL) was the world's first commercial massively parallel computer. The original paper study was complete in 1972 and building of the prototype began in 1974. The first machine was delivered to Queen Mary College in 1979. Development The initial Pilot DAP was designed and implemented by Dr Stewart F Reddaway with the aid of David J Hunt and Peter M Flanders at the ICL Stevenage Labs. Their manager and a major contributor was John K Iliffe, designer of the Basic Language Machine and known for Iliffe vectors. The pilot implementation had a 32×32 processing element arrangement. The ICL DAP had 64×64 single bit processing elements (PEs) with 4096 bits of storage per PE. It was attached to an ICL mainframe and its memory was mapped into the mainframe's memory. Programs for the DAP were written in DAP FORTRAN which was FORTRAN extended with 64×64 matrix and 64 element vector primitives. DAP Fortran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
International Computers Limited
International Computers Limited (ICL) was a British computer hardware, computer software and computer services company that operated from 1968 until 2002. It was formed through a merger of International Computers and Tabulators (ICT), English Electric Computers (EEC) and Elliott Automation in 1968. The company's most successful product line was the ICL 2900 Series range of mainframe computers. In later years, ICL diversified its product line but the bulk of its profits always came from its mainframe customers. New ventures included marketing a range of powerful IBM clones made by Fujitsu, various minicomputer and personal computer ranges and (more successfully) a range of retail point-of-sale equipment and back-office software. Although it had significant sales overseas, ICL's mainframe business was dominated by large contracts from the UK public sector, including Post Office Ltd, the Inland Revenue, the Department for Work and Pensions and the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Single Instruction, Multiple Threads
Single instruction, multiple threads (SIMT) is an execution model used in parallel computing where single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is combined with zero-overhead multithreading, i.e. multithreading where the hardware is capable of switching between threads on a cycle-by-cycle basis. There are two models of multithreading involved. In addition to the zero-overhead multithreading mentioned, the SIMD execution hardware is virtualized to represent a multiprocessor, but is inferior to a SPMD processor in that instructions in all "threads" are executed in lock-step in the lanes of the SIMD processor which can only execute the same instruction in a given cycle across all lanes. The SIMT execution model has been implemented on several GPUs and is relevant for general-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU), e.g. some supercomputer A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Massively Parallel
Massively parallel is the term for using a large number of computer processors (or separate computers) to simultaneously perform a set of coordinated computations in parallel. GPUs are massively parallel architecture with tens of thousands of threads. One approach is grid computing, where the processing power of many computers in distributed, diverse administrative domains is opportunistically used whenever a computer is available.''Grid computing: experiment management, tool integration, and scientific workflows'' by Radu Prodan, Thomas Fahringer 2007 pages 1–4 An example is BOINC, a volunteer-based, opportunistic grid system, whereby the grid provides power only on a best effort basis.''Parallel and Distributed Computational Intelligence'' by Francisco Fernández de Vega 2010 pages 65–68 Another approach is grouping many processors in close proximity to each other, as in a computer cluster. In such a centralized system the speed and flexibility of the interconnect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid dynamics, fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid (liquids and gases) with surfaces defined by Boundary value problem#Boundary value conditions, boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulence, turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed Closed-form solution, analytical or Empirical research, empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
GFLOPS
Floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate measure than measuring instructions per second. Floating-point arithmetic Floating-point arithmetic is needed for very large or very small real numbers, or computations that require a large dynamic range. Floating-point representation is similar to scientific notation, except computers use base two (with rare exceptions), rather than base ten. The encoding scheme stores the sign, the exponent (in base two for Cray and VAX, base two or ten for IEEE floating point formats, and base 16 for IBM Floating Point Architecture) and the significand (number after the radix point). While several similar formats are in use, the most common is ANSI/IEEE Std. 754-1985. This standard defines the format for 32-bit numbers called ''single precision'', as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
ILLIAC IV
The ILLIAC IV was the first massively parallel computer. The system was originally designed to have 256 64-bit floating-point units (FPUs) and four central processing units (CPUs) able to process 1 billion operations per second. Due to budget constraints, only a single "quadrant" with 64 FPUs and a single CPU was built. Since the FPUs all processed the same instruction — etc. — in modern terminology, the design would be considered to be single instruction, multiple data, or SIMD. The concept of building a computer using an array of processors came to Daniel Slotnick while working as a programmer on the IAS machine in 1952. A formal design did not start until 1960, when Slotnick was working at Westinghouse Electric Corporation and arranged development funding under a United States Air Force contract. When that funding ended in 1964, Slotnick moved to the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and joined the Illinois Automatic Computer (ILLIAC) team. With funding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
University Of Illinois At Urbana–Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United States. Established in 1867, it is the founding campus and flagship institution of the University of Illinois System. With over 59,000 students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the United States. The university contains 16 schools and colleges and offers more than 150 undergraduate and over 100 graduate programs of study. The university holds 651 buildings on and its annual operating budget in 2016 was over $2 billion. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign also operates a research park home to innovation centers for over 90 start-up companies and multinational corporations. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Data Set
A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more table (database), database tables, where every column (database), column of a table represents a particular Variable (computer science), variable, and each row (database), row corresponds to a given Record (computer science), record of the data set in question. The data set lists values for each of the variables, such as for example height and weight of an object, for each member of the data set. Data sets can also consist of a collection of documents or files. In the open data discipline, a dataset is a unit used to measure the amount of information released in a public open data repository. The European data.europa.eu portal aggregates more than a million data sets. Properties Several characteristics define a data set's structure and properties. These include the number and types of the attributes or variables, and various statistical measures applicable to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |