coprocessor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the

 The original
The original  Another coprocessor for the 8086/8088 central processor was the
Another coprocessor for the 8086/8088 central processor was the
 A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be ...
, graphics
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of data, as in design and manufacture ...
, signal processing, string processing
String functions are used in computer programming languages to manipulate a string or query information about a string (some do both).
Most programming languages that have a string datatype will have some string functions although there may ...
, cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adve ...
or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it.
Functionality
Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such asFPU FPU may stand for:
Universities
* Florida Polytechnic University, in Lakeland, Florida, United States
* Franklin Pierce University, in New Hampshire, United States
* Fresno Pacific University, in California, United States
* Fukui Prefectural Univ ...
s) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ' ...
focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these to be driven by direct memory access (DMA), with the host processor (a CPU) building a command list
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics.
For more general computer hardware terms, see glossary of computer hardware terms.
0–9
A
B
...
. The PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, and in Australia on 3 ...
's Emotion Engine contained an unusual DSP-like SIMD vector unit
Vector Unit is a video game developer founded in December 2007 by Ralf Knoesel and Matt Small. The company is best known for its title, ''Hydro Thunder Hurricane'', released on the Xbox 360 via Xbox Live Arcade in 2010.
History
Vector Unit was ...
capable of both modes of operation.
History
To make the best use ofmainframe computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterpris ...
processor time, input/output tasks were delegated to separate systems called Channel I/O
In computing, channel I/O is a high-performance input/output (I/O) architecture that is implemented in various forms on a number of computer architectures, especially on mainframe computers. In the past, channels were generally implemented with cus ...
. The mainframe would not require any I/O processing at all, instead would just set parameters for an input or output operation and then signal the channel processor to carry out the whole of the operation. By dedicating relatively simple sub-processors to handle time-consuming I/O formatting and processing, overall system performance was improved.
Coprocessors for floating-point arithmetic first appeared in desktop computer
A desktop computer (often abbreviated desktop) is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply ...
s in the 1970s and became common throughout the 1980s and into the early 1990s. Early 8-bit and 16-bit processors used software to carry out floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can b ...
arithmetic operations. Where a coprocessor was supported, floating-point calculations could be carried out many times faster. Math coprocessors were popular purchases for users of computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
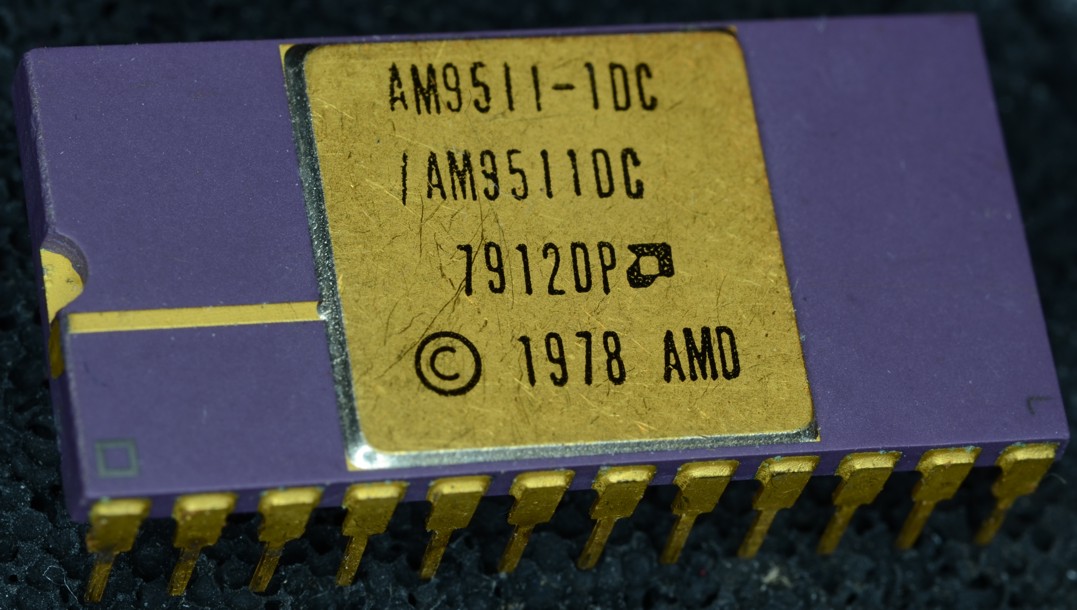
(CAD) software and scientific and engineering calculations. Some floating-point units, such as the AMD 9511, Intel 8231/8232
The Intel 8231 and 8232 were early designs of floating-point maths coprocessors (FPUs), marketed for use with their i8080 line of primary CPUs. They were licensed versions of AMD's Am9511 and Am9512 FPUs, from 1977 and 1979, themselves claimed by ...
and Weitek FPUs were treated as peripheral devices, while others such as the Intel 8087
The Intel 8087, announced in 1980, was the first x87 floating-point coprocessor for the 8086 line of microprocessors.
The purpose of the 8087 was to speed up computations for floating-point arithmetic, such as addition, subtraction, multiplicati ...
, Motorola 68881
The Motorola 68881 and Motorola 68882 are floating-point units (FPUs) used in some computer systems in conjunction with Motorola's 32-bit 68020 or 68030 microprocessors. These coprocessors are external chips, designed before floating point math bec ...
and National 32081
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
were more closely integrated with the CPU.
Another form of coprocessor was a video display coprocessor, as used in the Atari 8-bit family
The Atari 8-bit family is a series of 8-bit home computers introduced by Atari, Inc. in 1979 as the Atari 400 and Atari 800. The series was successively upgraded to Atari 1200XL , Atari 600XL, Atari 800XL, Atari 65XE, Atari 130XE, Atari 800XE, ...
, TI-99/4A, and MSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by Microsoft and ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, then vice-p ...
home computers, which were called " Video Display Controllers". The Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphi ...
custom chipset includes such a unit known as the Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
, as well as a blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to a ...
for accelerating bitmap manipulation in memory.
As microprocessors developed, the cost of integrating the floating point arithmetic functions into the processor declined. High processor speeds also made a closely integrated coprocessor difficult to implement. Separately packaged mathematics coprocessors are now uncommon in desktop computers. The demand for a dedicated graphics coprocessor has grown, however, particularly due to the increasing demand for realistic 3D graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the ...
in computer games
A personal computer game, also known as a PC game or computer game, is a type of video game played on a personal computer (PC) rather than a video game console or arcade machine. Its defining characteristics include: more diverse and user-deter ...
.
Intel
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
included a socket for the Intel 8087
The Intel 8087, announced in 1980, was the first x87 floating-point coprocessor for the 8086 line of microprocessors.
The purpose of the 8087 was to speed up computations for floating-point arithmetic, such as addition, subtraction, multiplicati ...
floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can b ...
coprocessor (aka FPU FPU may stand for:
Universities
* Florida Polytechnic University, in Lakeland, Florida, United States
* Franklin Pierce University, in New Hampshire, United States
* Fresno Pacific University, in California, United States
* Fukui Prefectural Univ ...
) which was a popular option for people using the PC for computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
or mathematics-intensive calculations. In that architecture, the coprocessor speeds up floating-point arithmetic on the order of fiftyfold. Users that only used the PC for word processing, for example, saved the high cost of the coprocessor, which would not have accelerated performance of text manipulation operations.
The 8087 was tightly integrated with the 8086/8088 and responded to floating-point machine code operation codes inserted in the 8088 instruction stream. An 8088 processor without an 8087 could not interpret these instructions, requiring separate versions of programs for FPU and non-FPU systems, or at least a test at run time to detect the FPU and select appropriate mathematical library functions.
8089
The Intel 8089 input/output coprocessor was available for use with the 8086/8088 central processor. It was announced in May 1979, but the price was not available at that time. It used the same programming technique as 8087 for input/output operat ...
input/output coprocessor. It used the same programming technique as 8087 for input/output operations, such as transfer of data from memory to a peripheral device, and so reducing the load on the CPU. But IBM didn't use it in IBM PC design and Intel stopped development of this type of coprocessor.
The Intel 80386 microprocessor used an optional "math" coprocessor (the 80387
x87 is a floating-point-related subset of the x86 architecture instruction set. It originated as an extension of the 8086 instruction set in the form of optional floating-point coprocessors that worked in tandem with corresponding x86 CPUs. Thes ...
) to perform floating point operations directly in hardware. The Intel 80486DX processor included floating-point hardware on the chip. Intel released a cost-reduced processor, the 80486SX, that had no floating point hardware, and also sold an 80487SX coprocessor that essentially disabled the main processor when installed, since the 80487SX was a complete 80486DX with a different set of pin connections.Scott Mueller, ''Upgrading and repairing PCs '' 15th edition, Que Publishing, 2003 , pages 108–110
Intel processors later than the 80486 integrated floating-point hardware on the main processor chip; the advances in integration eliminated the cost advantage of selling the floating point processor as an optional element. It would be very difficult to adapt circuit-board techniques adequate at 75 MHz processor speed to meet the time-delay, power consumption, and radio-frequency interference standards required at gigahertz-range clock speeds. These on-chip floating point processors are still referred to as coprocessors because they operate in parallel with the main CPU.
During the era of 8- and 16-bit desktop computers another common source of floating-point coprocessors was Weitek. These coprocessors had a different instruction set from the Intel coprocessors, and used a different socket, which not all motherboards supported. The Weitek processors did not provide transcendental mathematics functions (for example, trigonometric functions) like the Intel x87 family, and required specific software libraries to support their functions.Scott Mueller, ''Upgrading and Repairing PCs, Second Edition'', Que Publishing, 1992 , pp. 412-413
Motorola
TheMotorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector ...
family had the 68881/68882 coprocessors which provided similar floating-point speed acceleration as for the Intel processors. Computers using the 68000 family but not equipped with the hardware floating point processor could trap and emulate the floating-point instructions in software, which, although slower, allowed one binary version of the program to be distributed for both cases. The 68451 memory-management coprocessor was designed to work with the 68020 processor.William Ford, William R. Topp
''Assembly language and systems programming for the M68000 family'' Jones & Bartlett Learning, 1992 page 892 and ff.
Modern coprocessors
, dedicated Graphics Processing Units ( GPUs) in the form ofgraphics card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer moni ...
s are commonplace. Certain models of sound cards have been fitted with dedicated processors providing digital multichannel mixing and real-time DSP effects as early as 1990 to 1994 (the Gravis Ultrasound and Sound Blaster AWE32 being typical examples), while the Sound Blaster Audigy
Sound Blaster Audigy is a product line of sound cards from Creative Technology. The flagship model of the Audigy family used the EMU10K2 audio DSP, an improved version of the SB-Live's EMU10K1, while the value/SE editions were built with a less ...
and the Sound Blaster X-Fi are more recent examples.
In 2006, AGEIA announced an add-in card for computers that it called the PhysX PPU. PhysX was designed to perform complex physics computations so that the CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and ...
and GPU do not have to perform these time-consuming calculations. It was designed for video games, although other mathematical uses could theoretically be developed for it. In 2008, Nvidia purchased the company and phased out the PhysX card line; the functionality was added through software allowing their GPUs to render PhysX on cores normally used for graphics processing, using their Nvidia PhysX engine software.
In 2006, BigFoot Systems unveiled a PCI add-in card they christened the KillerNIC which ran its own special Linux kernel on a FreeScale PowerQUICC running at 400 MHz, calling the FreeScale chip a Network Processing Unit or NPU.
The SpursEngine
SpursEngine is a microprocessor from Toshiba built as a media oriented coprocessor, designed for 3D- and video processing in consumer electronics such as set-top boxes and computers. The SpursEngine processor is also known as the Quad Core HD pro ...
is a media-oriented add-in card with a coprocessor based on the Cell microarchitecture. The SPUs are themselves vector coprocessors.
In 2008, Khronos Group released the OpenCL with the aim to support general-purpose CPUs, ATI/AMD and Nvidia GPUs (and other accelerators) with a single common language for compute kernels.
In 2010s, some mobile computation devices had implemented the sensor hub as a coprocessor. Examples of coprocessors used for handling sensor integration in mobile devices include the Apple M7 and M8 motion coprocessors, the Qualcomm Snapdragon Sensor Core and Qualcomm Hexagon, and the Holographic Processing Unit
Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later re-constructed. Holography is best known as a method of generating real three-dimensional images, but it also has a wide range of other Holography#Applications, applic ...
for the Microsoft HoloLens.
In 2012, Intel announced the Intel Xeon Phi
Xeon Phi was a series of x86 manycore processors designed and made by Intel. It was intended for use in supercomputers, servers, and high-end workstations. Its architecture allowed use of standard programming languages and application programm ...
coprocessor.
, various companies are developing coprocessors aimed at accelerating artificial neural networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
An ANN is based on a collection of connected unit ...
for vision and other cognitive tasks (e.g. vision processing units, TrueNorth, and Zeroth), and as of 2018, such AI chips are in smartphones such as from Apple, and several Android phone vendors.
Other coprocessors
* The MIPS architecture supports up to four coprocessor units, used for memory management, floating-point arithmetic, and two undefined coprocessors for other tasks such as graphics accelerators. * UsingFPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware de ...
(field-programmable gate arrays), custom coprocessors can be created for acceleration of particular processing tasks such as digital signal processing (e.g. Zynq, combines ARM cores with FPGA on a single die).
* TLS/SSL accelerators, used on servers; such accelerators used to be cards, but in modern times are instructions for crypto in mainstream CPUs.
* Some multi-core
A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such a ...
chips can be programmed so that one of their processors is the primary processor, and the other processors are supporting coprocessors.
* China's Matrix 2000 128 core PCI-e coprocessor is a proprietary accelerator that requires a CPU to run it, and has been employed in an upgrade of the 17,792 node Tianhe-2 supercomputer (2 Intel Knights Bridge+ 2 Matrix 2000 each), now dubbed 2A, roughly doubling its speed at 95 petaflops, exceeding the world's fastest supercomputer.
* A range of coprocessors were available for Acorn BBC Micro computers. Rather than special-purpose graphics or arithmetic devices, these were general-purpose CPUs (such as 8086, Zilog Z80, or 6502) to which particular types of task were assigned by the operating system, off-loading them from the computer's main CPU and resulting in acceleration. In addition, a BBC Micro fitted with a coprocessor was able to run machine code software designed for other systems, such as CP/M and DOS which are written for 8086 processors.
Trends
Over time CPUs have tended to grow to absorb the functionality of the most popular coprocessors. FPUs are now considered an integral part of a processors' main pipeline; SIMD units gave multimedia its acceleration, taking over the role of various DSP accelerator cards; and even GPUs have become integrated on CPU dies. Nonetheless, specialized units remain popular away from desktop machines, and for additional power, and allow continued evolution independently of the main processor product lines.See also
*Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There ar ...
, the use of two or more CPUs within a single computer system
* Torrenza, an initiative to implement coprocessor support for AMD processors
* OpenCL framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous platforms
* Asymmetric multiprocessing
* AI accelerator
References
{{Authority control Central processing unit Heterogeneous computing OpenCL compute devices