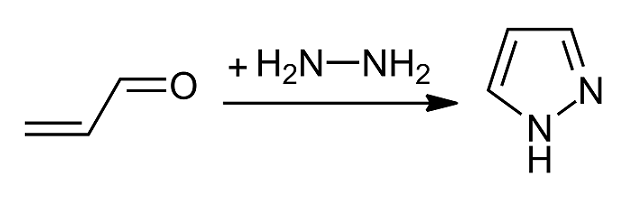|
Vebreltinib
Vebreltinib (also known as bozitinib) is a pharmaceutical drug used for the treatment of cancer. Vebreltinib selectively binds to c-Met, preventing its phosphorylation and thereby disrupting c-Met signal transduction pathways. In China, it is approved for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitiv ... (NSCLC) with MET exon 14 skipping mutations. References Antineoplastic and immunomodulating drugs Kinase inhibitors Indazoles Cyclopropyl compounds Pyrazoles Fluoroarenes {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Met
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGF receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MET'' gene. The protein possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. HGF receptor is a single pass tyrosine kinase receptor essential for embryonic development, organogenesis and wound healing. Hepatocyte growth factor/Scatter Factor (HGF/SF) and its splicing isoform (NK1, NK2) are the only known ligands of the HGF receptor. MET is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin, while expression of HGF/SF is restricted to cells of mesenchymal origin. When HGF/SF binds its cognate receptor MET it induces its dimerization through a not yet completely understood mechanism leading to its activation. Sometimes MET is misunderstood as of an abbreviation of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition. It is incorrect. The three letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols: : This equation can be written in several ways that are nearly equivalent that describe the behaviors of various protonated states of ATP, ADP, and the phosphorylated product. As is clear from the equation, a phosphate group per se is not transferred, but a phosphoryl group (PO3-). Phosphoryl is an electrophile. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. During respiration Phosphorylation is essential to the processes of both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, which involve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "high-energy" exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand (biochemistry), ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a Cell signaling#Signaling pathways, signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription (biology), transcription or translation (biology), translation of genes, and post-translational modification, post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-small-cell Lung Cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively ( neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively ( adjuvant chemotherapy). Types The most common types of NSCLC are squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but several other types occur less frequently. A few of the less common types are pleomorphic, carcinoid tumor, salivary gland carcinoma, and unclassified carcinoma. All types can occur in unusual histologic variants and as mixed cell-type combinations. Non-squamous-cell carcinoma almost occupies the half of NSCLC. In the tissue classification, the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase Inhibitors
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whether it be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indazoles
Indazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole. Indazole is an amphoteric molecule which can be protonated to an indazolium cation or deprotonated to an indazolate anion. The corresponding ''pKa'' values are 1.04 for the equilibrium between indazolium cation and indazole and 13.86 for the equilibrium between indazole and indazolate anion. Indazole derivatives display a broad variety of biological activities. Indazoles are rare in nature. The alkaloids nigellicine, nigeglanine, and nigellidine are indazoles. Nigellicine was isolated from the widely distributed plant '' Nigella sativa'' L. (black cumin). Nigeglanine was isolated from extracts of '' Nigella glandulifera''. The Davis–Beirut reaction can generate 2''H''-indazoles. Indazole, C7H6N2, was obtained by E. Fischer (''Ann.'' 1883, 221, p. 280) by heating ortho-hydrazine cinnamic acid, : Drugs made from Indazole B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropyl Compounds
A cyclopropyl group is a chemical structure derived from cyclopropane; it is typically produced in a cyclopropanation reaction. The group has an empirical formula of C3H5 and chemical bonds from each of the three carbons to both of the other two. Structure and bonding Due to the unfavoured bond angles (60°), cyclopropyl groups are highly strained. Two orbital models were proposed to describe the bonding situation. The Coulson-Moffit model uses bent bonds. The C-C bonds are formed by overlap of two sp-hybrid orbitals. To adapt to the small bond angle, there is some rehybridization resulting in sp~5-hybrids for the ring bonds and sp~2 for the C-H bonds. This model resembles the banana bond model for C=C double bonds (τ bonds). Alternatively the structure can be explained with the Walsh model. Here the two sp-hybrids forming the ring bond are separated into one sp2-hybrid and one pure p-orbital. This corresponds to the π bond description of C=C double bonds. Cyclopropyl grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazoles
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula . It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest. Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib (celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol. Properties Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). According to X-ray crystallography, the compound is planar. The two C-N distances are similar, both near 1.33 Å History The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German Chemist Ludwig Knorr in 1883. In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and diazomethane. Preparation Pyrazoles are syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |