|
Vanbrugh Castle
Vanbrugh Castle is a house designed and built by John Vanbrugh around 1719 for his own family. It is located on Maze Hill on the eastern edge of Greenwich Park in London, to the north of Blackheath, London, Blackheath, with views to the west past the Old Royal Naval College at Greenwich down to the Thames reaching as far as the Houses of Parliament. History Vanbrugh years The castle was designed and built after Vanbrugh had been the architect of the baroque houses at Castle Howard and Blenheim Palace, and shortly after Vanbrugh succeeded his architectural mentor Christopher Wren as Surveyor to the Royal Naval Hospital in 1716. Vanbrugh took a lease of a 12-acre triangular site of the Westcombe Park, Westcombe estate from Sir Michael Biddulph, 2nd Baronet in 1718, now known as Vanbrugh Fields. In contrast to the baroque style used for his professional commissions, he chose a more medieval, almost gothic architecture, gothic, style for his own house. Built on the southwestern cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half of the 19th century, mostly in England. Increasingly serious and learned admirers sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic Revival had become the pre-eminent architectural style in the Western world, only to begin to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. For some in England, the Gothic Revival movement had roots that were intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Cathol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Duckham
Alexander Duckham (11 March 1877 – 1 February 1945) was an English chemist and businessman, best known for the development of machine lubricants. The son of an engineer, after university he specialised in lubrication, working briefly for Fleming's Oil Company before founding his own company, Alexander Duckham & Co, in Millwall in 1899. By the outbreak of World War I, he was an authority on technological problems relating to lubrication, and the company went public in about 1920, relocating from Millwall to Hammersmith. By the time he died in 1945, Duckhams had assumed a dominant position for the supply of lubricants and corrosion inhibitors to the motor industry in Britain and other markets. A new manufacturing plant was opened in Staffordshire in 1968, and soon thereafter the company was taken over by BP. Early career Duckham was born in Blackheath, London, the second eldest son (his elder brother was Frederick and younger brother Sir Arthur Duckham) of a Falmouth-born mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence Holker Potts
Laurence Holker Potts (18 April 1789 – 23 March 1850) was an English inventor and physician. Biography Potts son of Cuthbert Potts, surgeon, and Ethelinda Margaret Thorpe, daughter of John Thorpe, M.D., F.S.A. He was born in Pall Mall, London, on 18 April 1789. He was educated at Westminster School and at a school in Northamptonshire, and in 1805 he was apprenticed to Mr. Birch, surgeon, of Warwick. In 1810 he was entered at St. George's Hospital and became a house-pupil of Sir Benjamin Brodie; William Frederick Chambers and (Sir) Charles Locock were house-pupils at the same time. He passed the College of Surgeons in 1812, and graduated M.D. at Aberdeen in 1825. In 1812 he was appointed surgeon to the Royal Devon and Cornwall miners militia, then quartered in Ireland. The regiment returned to Truro in 1814, and was subsequently disbanded, Potts starting in practice in the town. He had always taken much interest in scientific pursuits, and in 1818 took an active part in foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Anna Needell
Mary Anna Needell (née Lupton, 1830–1922), was a popular English novelist, who usually wrote as Mrs. J. H. Needell. She was born at Vanbrugh Castle, Blackheath, Kent, now divided between the London boroughs of Greenwich and Lewisham. Little has been discovered about her personal background or life.John Sutherland: ''Longman Companion to Victorian Literature'', 2nd e. (Abingdon, Oxon./New York: Routledge, 2009), p. 463. Retrieved 2 March 2015./ref> Married life Mary Anna Lupton's father was John Lupton, described on her marriage certificate as a merchant. She was married at All Hallows, Bread Street on 4 May 1854 to John Hodder Needell ( Netherbury, Dorset, 16 September 1814 – Beaminster, July 1881) of Allington, Dorset, son of Thomas Wallace Needell, also described as a merchant. J. H. Needell's business affairs seem to have been sporadic and unsuccessful. His calico printing and warehousing partnership with a certain William Gregory Langdon in London, Cheapside, is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Vanbrugh
Charles Vanbrugh (c. 1680 – 2 November 1740) was an officer of the Royal Navy and member of parliament for Plymouth. Born in Chester, Charles Vanbrugh was baptised at Holy Trinity, Chester on 27 February 1679/1680. In June 1721 he married Ann Burt of Knightsbridge.History of Parliament Online The History of Parliament: the House of Commons 1715-1754, ed. R. Sedgwick, 1970 They had three or more children but only one recorded surviving son, Edward Vanbrugh (1722 – 1802). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
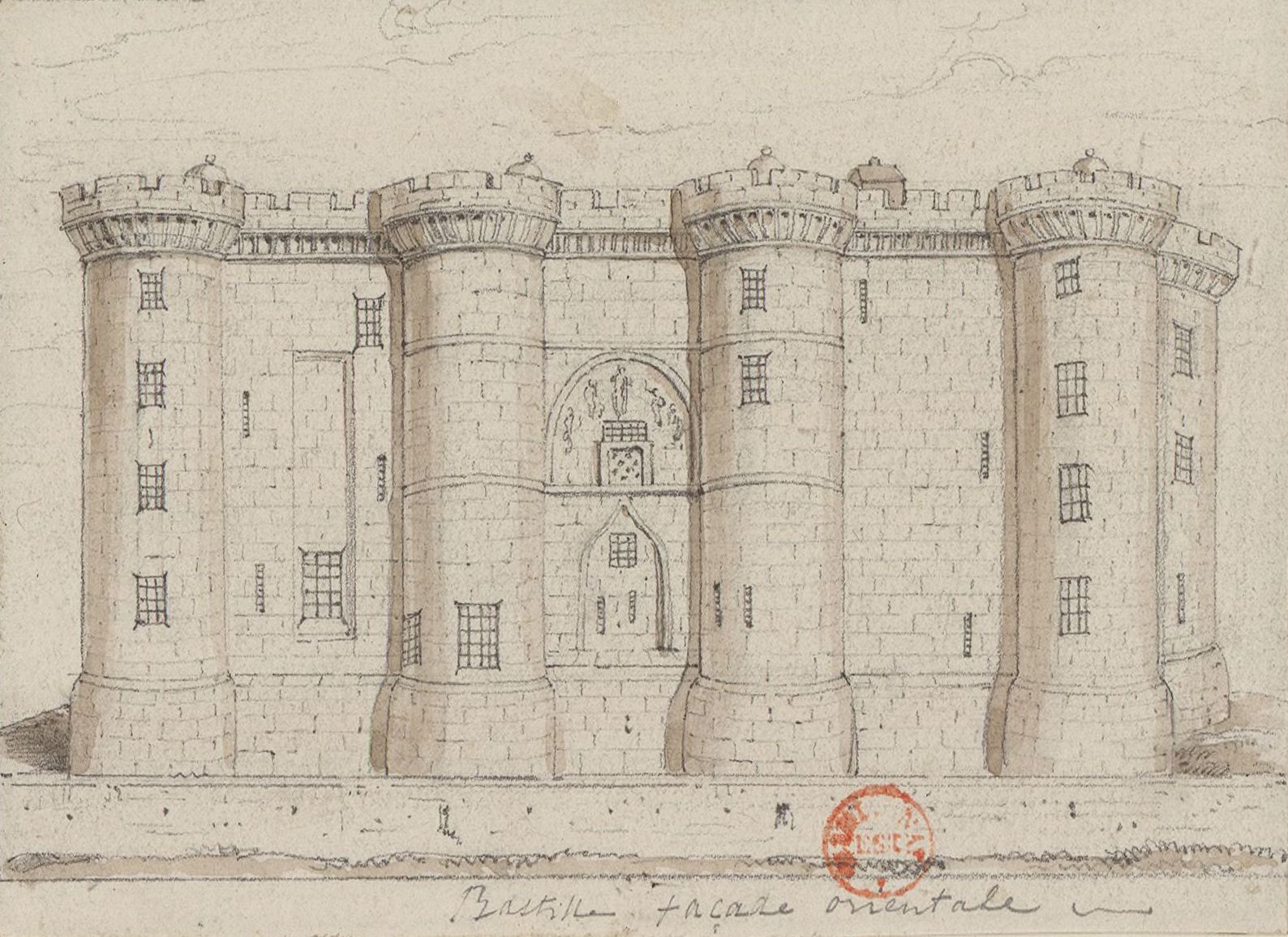
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions of the Bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirburn Castle
Shirburn Castle is a Grade I listed building, Grade I listed, moated castle located at the village of Shirburn, near Watlington, Oxfordshire, Watlington, Oxfordshire. Originally constructed in the fourteenth century, it was renovated and remodelled in the Georgian era by Thomas Parker, 1st Earl of Macclesfield, Thomas Parker, the first Earl of Macclesfield who made it his family seat, and altered further in the early nineteenth century. The Earls of Macclesfield remained in residence until 2004, and the castle is still (2022) owned by the Macclesfield family company. It formerly contained an important, early eighteenth century library which, along with valuable paintings, sculptures, and other artifacts including furniture, remained in the ownership of the 9th Earl and were largely dispersed at auction following his departure from the property; notable among these items were George Stubbs's 1768 painting "Brood Mares and Foals", a record setter for the artist at auction in 2010, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimbolton Castle
Kimbolton Castle is a country house in Kimbolton, Cambridgeshire, England. It was the final home of King Henry VIII's first wife, Catherine of Aragon. Originally a medieval castle but converted into a stately palace, it was the family seat of the Earls and Dukes of Manchester from 1615 until 1950. It now houses Kimbolton School. History The castle was built by Geoffrey Fitz Peter, 1st Earl of Essex, in the late 12th century. The inner court was rebuilt by Anne, Duchess of Buckingham, in the late 15th century. The castle was acquired by Sir Richard Wingfield in 1522 but after his death in 1525, was inherited by his eldest son, Charles. The Wingfield family reconstructed the medieval castle as a Tudor manor house, parts of which survive to this present day. Catherine of Aragon was sent here in April 1534 for refusing to give up her status or deny the validity of her marriage. In July 1534, a fool in the retinue of the diplomat Eustache Chapuys tried to swim the moat, dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancet Window
A lancet window is a tall, narrow window with a sharp pointed arch at its top. This arch may or may not be a steep lancet arch (in which the compass centres for drawing the arch fall outside the opening). It acquired the "lancet" name from its resemblance to a lance. Instances of this architectural element are typical of Gothic church edifices of the earliest period. Lancet windows may occur singly, or paired under a single moulding, or grouped in an odd number with the tallest window at the centre. The lancet window first appeared in the early French Gothic period (c. 1140–1200), and later in the Early English period of Gothic architecture (1200–1275). So common was the lancet window feature that this era is sometimes known as the "Lancet Period". The term ''lancet window'' is properly applied to single-light windows of austere form, without tracery. Paired windows were sometimes surmounted by a simple opening such as a quatrefoil cut in plate tracery. This form gave way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrowslit
An arrowslit (often also referred to as an arrow loop, loophole or loop hole, and sometimes a balistraria) is a narrow vertical aperture in a fortification through which an archer can launch arrows or a crossbowman can launch Crossbow bolt, bolts. The interior walls behind an arrow loop are often cut away at an oblique angle so that the archer has a wide field of view and field of fire (weaponry), field of fire. Arrow slits come in a variety of forms. A common one is the cross, accommodating the use of both the longbow and the crossbow. The narrow vertical aperture permits the archer large degrees of freedom to vary the elevation (ballistics), elevation and direction of their bowshot but makes it difficult for attackers to harm the archer since there is only a small target at which to aim. Balistraria, plural ''balistrariae'' (from balister, crossbowman), can often be found in the Curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls of medieval battlements beneath the crenellations. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |