|
Value-added
In business, total value added is calculated by tabulating the unit value added (measured by summing unit profit Price.html" ;"title="he difference between Price">sale price and production cost], unit depreciation cost, and unit Direct labor cost, labor cost) per each unit of product sold. Thus, total value added is equivalent to revenue minus intermediate consumption. Value added is a higher portion of revenue for integrated companies (e.g. manufacturing companies) and a lower portion of revenue for less integrated companies (e.g. retail companies); total value added is very closely approximated by compensation of employees, which represents a return to labor, plus earnings before taxes, representative of a return to capital. In economics, specifically macroeconomics, the term value added refers to the contribution of the factors of production (i.e. capital and labor) to raise the value of the product and increase the income of those who own the said factors. Therefore, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
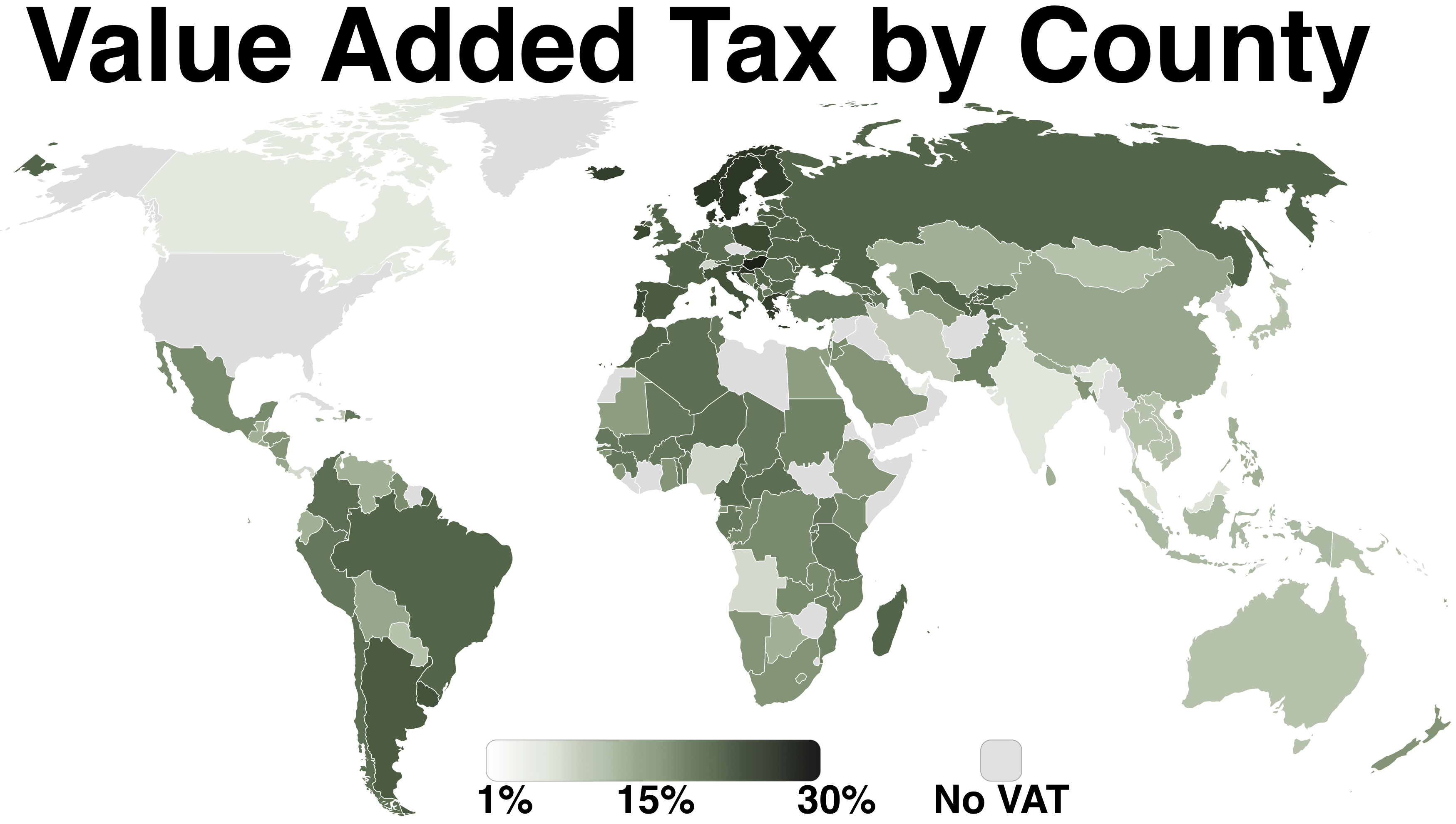
Value-added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities. Not all localities require VAT to be charged, and exports are often exempt. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. The terms VAT, GST, and the more general consumption tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Taxes
An indirect tax (such as sales tax, per unit tax, value added tax (VAT), or goods and services tax (GST), excise, consumption tax, tariff) is a tax that is levied upon goods and services before they reach the customer who ultimately pays the indirect tax as a part of market price of the good or service purchased. Alternatively, if the entity who pays taxes to the tax collecting authority does not suffer a corresponding reduction in income, i.e., impact and tax incidence are not on the same entity meaning that tax can be shifted or passed on, then the tax is indirect. An indirect tax is collected by an intermediary (such as a retail store) from the person (such as the consumer) who pays the tax included in the price of a purchased good. The intermediary later files a tax return and forwards the tax proceeds to government with the return. In this sense, the term indirect tax is contrasted with a direct tax, which is collected directly by government from the persons (legal or natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Consumption
Intermediate consumption (also called "intermediate expenditure") is an economic concept used in national accounts, such as the United Nations System of National Accounts (UNSNA), the US National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA) and the European System of Accounts (ESA). Conceptually, the aggregate "intermediate consumption" is equal to the amount of the difference between gross output (roughly, the total sales value) and net output (gross value added or GDP). In the US economy, total intermediate consumption represents about 45% of gross output. The services component in intermediate consumption has grown strongly in the US, from about 30% in the 1980s to more than 40% today. Thus, intermediate consumption is an accounting flow which consists of the total monetary value of goods and services ''consumed or used up as inputs in production'' by enterprises, including raw materials, services and various other operating expenses. Because this value must be subtracted from gross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Output
Net output is an accounting concept used in national accounts such as the United Nations System of National Accounts (UNSNA) and the NIPAs, and sometimes in corporate or government accounts. The concept was originally invented to measure the total net addition to a country's stock of wealth created by production during an accounting interval. The concept of net output is basically "gross revenue from production ''less'' the value of goods and services ''used up'' in that production". The idea is that if one deducts intermediate expenditures from the annual flow of income generated by production, one obtains a measure of the net new value in the new products created. Definition In national accounts, net output is equivalent to the gross value added during an accounting period when producing enterprises use inputs (labor and capital assets) to produce outputs. Gross value added is called "gross" because it includes depreciation charges or consumption of fixed capital. The calcu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measures Of National Income And Output
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income (NNI adjusted for natural resource depletion – also called as NNI at factor cost). All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by ''imputing'' monetary values to them. National accounts Arriving at a figure for the total production of goods and services in a large region like a country entails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Value Added
In economics, gross value added (GVA) is the measure of the value of goods and services produced in an area, industry or sector of an economy. "Gross value added is the value of output minus the value of intermediate consumption; it is a measure of the contribution to GDP made by an individual producer, industry or sector; gross value added is the source from which the primary incomes of the System of National Accounts (SNA) are generated and is therefore carried forward into the primary distribution of income account." Relationship to gross domestic product GVA is a very important measure, because it is used to determine gross domestic product (GDP). GDP is an indicator of the health of a national economy and economic growth. It represents the monetary value of all products and services produced in the country within a defined period of time. "In comparing GVA and GDP, we can say that GVA is a better measure for the economic welfare of the population, because it includes all pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxism
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, no single, definitive Marxist theory exists. In addition to the schools of thought which emphasize or modify elements of classical Marxism, various Marxian concepts have been incorporated and adapted into a diverse array of social theories leading to widely varying conclusions. Alongside Marx's critique of political economy, the defining characteristics of Marxism have often been described using the terms dialectical materialism and historical materialism, though these terms were coined after Marx's death and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
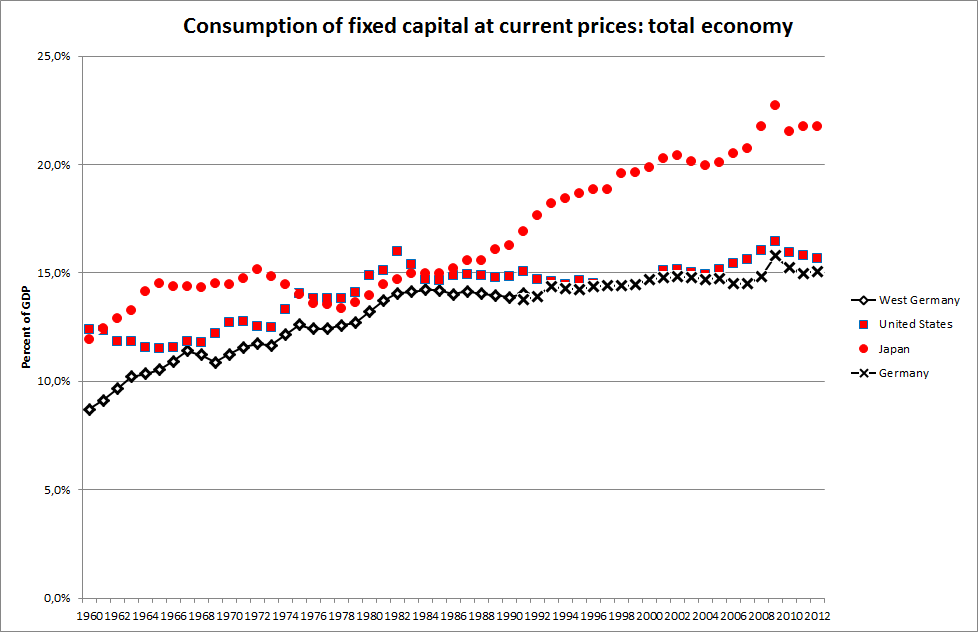
Consumption Of Fixed Capital
Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value (so-called "economic depreciation"); CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to ''producing'' enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets. CFC refers to a depreciation charge (or "write-off") against the gross income of a producing enterprise, which reflects the decline in value of fixed capital being operated with. Fixed assets will decline in value after they are purchased for use in production, due to wear and tear, changed market valuation and possibly market obsolescence. Thus, CFC represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wages
A wage is payment made by an employer to an employee for work done in a specific period of time. Some examples of wage payments include compensatory payments such as ''minimum wage'', '' prevailing wage'', and ''yearly bonuses,'' and remunerative payments such as ''prizes'' and ''tip payouts.'' Wages are part of the expenses that are involved in running a business. It is an obligation to the employee regardless of the profitability of the company. Payment by wage contrasts with salaried work, in which the employer pays an arranged amount at steady intervals (such as a week or month) regardless of hours worked, with commission which conditions pay on individual performance, and with compensation based on the performance of the company as a whole. Waged employees may also receive tips or gratuity paid directly by clients and employee benefits which are non-monetary forms of compensation. Since wage labour is the predominant form of work, the term "wage" sometimes refers to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Final Consumption Expenditure
Household final consumption expenditure (POES) is a transaction of the national account's use of income account representing consumer spending. It consists of the expenditure incurred bresidenthouseholds on individual consumption goods and services, including those sold at prices that are not economically significant. It also includes various kinds of imputed expenditure of which the imputed rent for services of owner-occupied housing ( imputed rents) is generally the most important one. The household sector covers not only those living in traditional households, but also those people living in communal establishments, such as retirement homes, boarding houses and prisons. The above given definition of HFCE includes expenditure by resident households on the domestic territory and expenditure by resident households abroad (outbound tourists), but excludes any non-resident households' expenditure on the domestic territory (inbound tourists). From this national definition of consum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation, inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing standard of living, living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the GDP per capita, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |