|
Consumption Of Fixed Capital
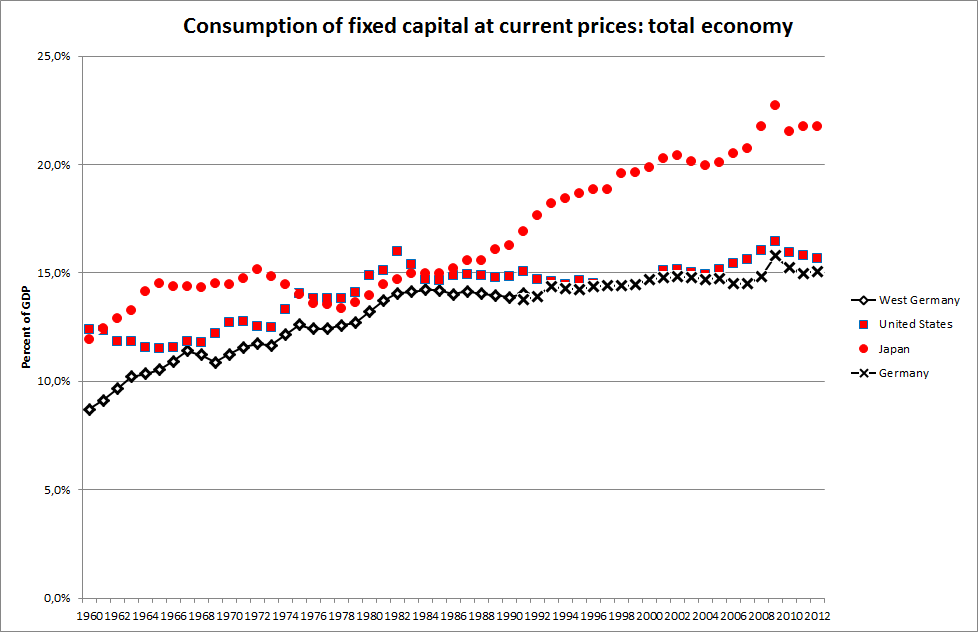
Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value (so-called "economic depreciation"); CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to ''producing'' enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets. CFC refers to a depreciation charge (or "write-off") against the gross income of a producing enterprise, which reflects the decline in value of fixed capital being operated with. Fixed assets will decline in value after they are purchased for use in production, due to wear and tear, changed market valuation and possibly market obsolescence. Thus, CFC represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Consumption
Intermediate consumption (also called "intermediate expenditure") is an economic concept used in national accounts, such as the United Nations System of National Accounts (UNSNA), the US National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA) and the European System of Accounts (ESA). Conceptually, the aggregate "intermediate consumption" is equal to the amount of the difference between gross output (roughly, the total sales value) and net output (gross value added or GDP). In the US economy, total intermediate consumption represents about 45% of gross output. The services component in intermediate consumption has grown strongly in the US, from about 30% in the 1980s to more than 40% today. Thus, intermediate consumption is an accounting flow which consists of the total monetary value of goods and services ''consumed or used up as inputs in production'' by enterprises, including raw materials, services and various other operating expenses. Because this value must be subtracted from gros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Product
Value or values may refer to: Ethics and social sciences * Value (ethics), concept which may be construed as treating actions themselves as abstract objects, associating value to them ** Axiology, interdisciplinary study of values, including ethical values * Social imaginary, set of morals, institutions, laws, and symbols common to a particular social group * Religious values, beliefs and practices which a religious adherent partakes in Economics * Value (economics), a measure of the benefit that may be gained from goods or service ** Theory of value (economics), the study of the concept of economic value ** Value (marketing), the difference between a customer's evaluation of benefits and costs ** Value investing, an investment paradigm * Values (heritage), the measure by which the cultural significance of heritage items is assessed * Present value, value of an expected income stream as of the date of valuation * Present value of benefits, discounted sum of a stream o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Added
Value added is a term in economics for calculating the difference between market value of a product or service, and the sum value of its constituents. It is relatively expressed by the supply-demand curve for specific units of sale. Value added is distinguished from the accounting term added value which measures only the financial profits earned upon transformational processes for specific items of sale that are available on the market. In business, ''total value added'' is calculated by tabulating the ''unit value added'' (measured by summing unit profit — the difference between sale price and production cost, unit depreciation cost, and unit labor cost) per each unit sold. Thus, total value added is equivalent to revenue minus intermediate consumption. Value added is a higher portion of revenue for integrated companies (e.g. manufacturing companies) and a lower portion of revenue for less integrated companies (e.g. retail companies); total value added is very nearly ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Output
In economics, gross output (GO) is a measure of the value of production of new goods and services during an accounting period. Gross output represents the total value of ''sales'' by producing enterprises (their gross revenue or turnover) in an accounting period (a quarter or a year), before subtracting the value of intermediate goods used up in production from the value of sales. Gross output can also be defined as the value of net output (the gross value-added or GDP) ''plus'' the value of intermediate consumption. Gross output is therefore a broader measure of the value of production than gross domestic product (GDP), which measures only the net value of final output (finished goods and services). , for example, the Bureau of Economic Analysis estimated gross output in the United States to be $50.9 trillion, compared to $29.3 trillion for GDP. Gross output and net output are complementary measures of the value of production. The components of gross output provide extra in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Capital
In accounting, fixed capital is any kind of real, physical asset that is used repeatedly in the production of a product. In economics, fixed capital is a type of capital good that as a real, physical asset is used as a means of production which is durable or isn't fully consumed in a single time period.Varri P. (1987) Fixed Capital. In: Durlauf S., Blume L. (eds) The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. "fixed capital", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', 1st Editio/ref> It contrasts with circulating capital such as raw materials, operating expenses etc. The concept was first theoretically analyzed in some depth by the economist Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) and by David Ricardo in On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1821). Ricardo studied the use of machines in place of labor and concluded that workers' fear of technology replacing them might be justified. Thus fixed capital is that portion of the total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, an actual reduction in the fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wears, and second, the allocation in accounting statements of the original cost of the assets to periods in which the assets are used (depreciation with the matching principle). Depreciation is thus the decrease in the value of assets and the method used to reallocate, or "write down" the cost of a tangible asset (such as equipment) over its useful life span. Businesses depreciate long-term assets for both accounting and tax purposes. The decrease in value of the asset affects the balance sheet of a business or entity, and the method of depreciating the asset, accounting-wise, affects the net income, and thus the income statement that they report. Generally, the cost is allocated as depreciation expense among the periods in which the asset is expected to be used. Account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Consumption Allowance
Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value (so-called "economic depreciation"); CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to ''producing'' enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets. CFC refers to a depreciation charge (or "write-off") against the gross income of a producing enterprise, which reflects the decline in value of fixed capital being operated with. Fixed assets will decline in value after they are purchased for use in production, due to wear and tear, changed market valuation and possibly market obsolescence. Thus, CFC represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surplus Value
In Marxian economics, surplus value is the difference between the amount raised through a sale of a product and the amount it cost to manufacture it: i.e. the amount raised through sale of the product minus the cost of the materials, plant and labour power. The concept originated in Ricardian socialism, with the term "surplus value" itself being coined by William Thompson (philosopher), William Thompson in 1824; however, it was not consistently distinguished from the related concepts of surplus labor and surplus product. The concept was subsequently developed and popularized by Karl Marx. Marx's formulation is the standard sense and the primary basis for further developments, though how much of Marx's concept is original and distinct from the Ricardian concept is disputed (see ). Marx's term is the German word "''Mehrwert''", which simply means value added (sales revenue minus the cost of materials used up), and is cognate to English "more worth". It is a major concept in Karl M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faux Frais Of Production
Faux frais of production is a concept used by classical political economists and by Karl Marx in his critique of political economy. It refers to "incidental operating expenses" incurred in the productive investment of capital, which do not themselves add new value to output. In Marx's social accounting, the faux frais are a component of constant capital, or alternately are funded by a fraction of the new surplus value. When owners of capital invest in production, they do not just invest in labor power, materials, buildings and equipment (or means of production). They must also meet a range of other operating expenses. These can include all kinds of things like bookkeeping, training, catering, cleaning & repairs, advertising, insurance, security services, bribes, taxes & levies etc. Marx has in mind mainly those circulation costs directly necessary and indispensable to keep production going, not "fringe benefits". In modern medium-sized to large-sized business, fixed capital asse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Capital
Constant or The Constant may refer to: Mathematics * Constant (mathematics), a non-varying value * Mathematical constant, a special number that arises naturally in mathematics, such as or Other concepts * Control variable or scientific constant, in experimentation the unchanging or constant variable * Physical constant, a physical quantity generally believed to be universal and unchanging * Constant (computer programming), a value that, unlike a variable, cannot be reassociated with a different value * Logical constant, a symbol in symbolic logic that has the same meaning in all models, such as the symbol "=" for "equals" People * Constant (given name) * Constant (surname) * John, Elector of Saxony (1468–1532), known as John the Constant * Constant Nieuwenhuys (1920-2005), better known as Constant Places * Constant, Barbados, a populated place Arts and entertainment * " The Constant", a 2008 episode of the television show ''Lost'' * ''The Constant'' (Story of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxian Economics
Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl Marx's critique of political economy. However, unlike critics of political economy, Marxian economists tend to accept the concept of the economy prima facie. Marxian economics comprises several different theories and includes multiple schools of thought, which are sometimes opposed to each other; in many cases Marxian analysis is used to complement, or to supplement, other economic approaches. An example can be found in the works of Soviet economists like Lev Gatovsky, who sought to apply Marxist economic theory to the objectives, needs, and political conditions of the socialist construction in the Soviet Union, contributing to the development of Soviet political economy. Marxian economics concerns itself variously with the analysis of crisis in capitalism, the role and distribution of the surplus product and surplus value in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |