|
Uruguaysuchidae
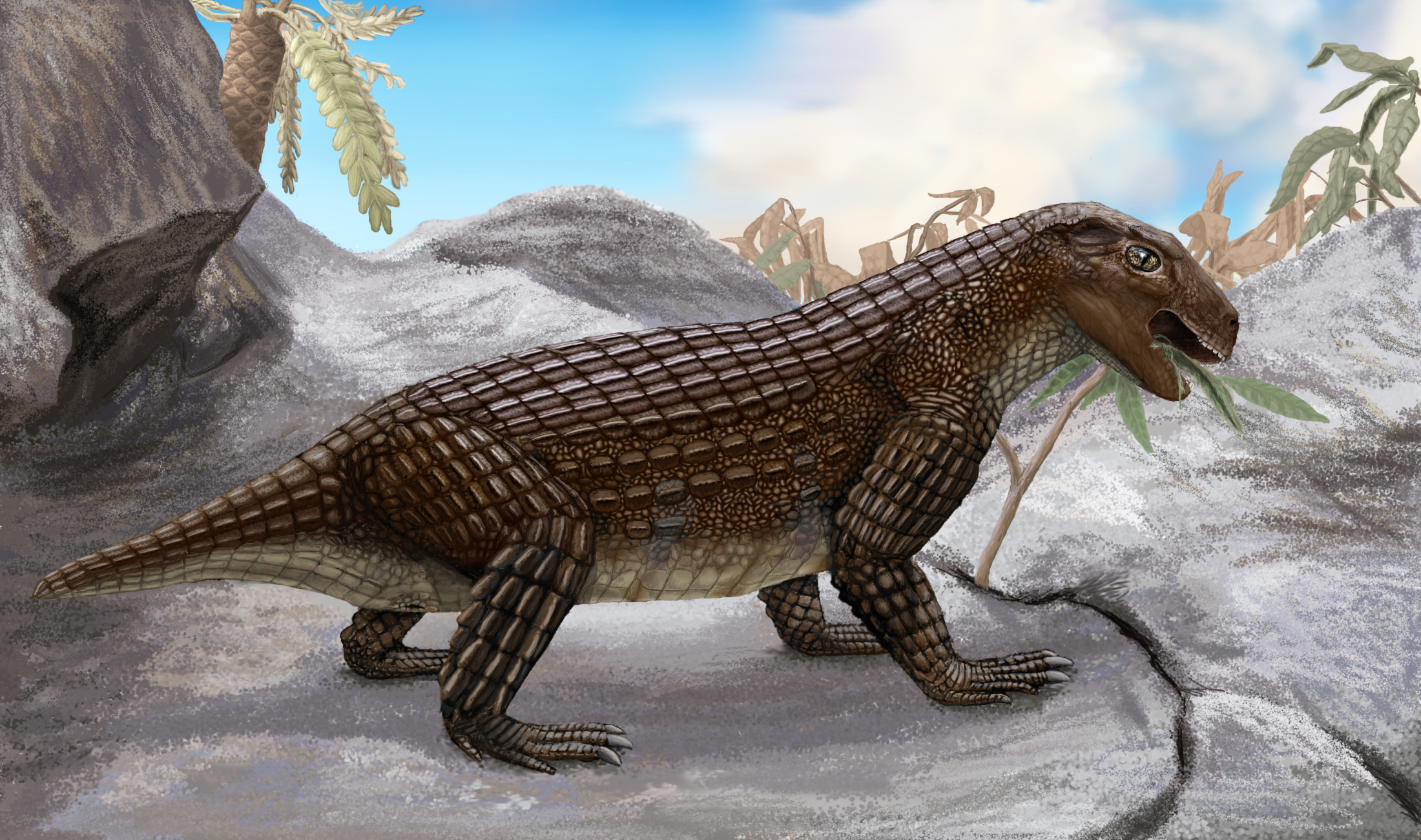
Uruguaysuchidae is a family of notosuchian crocodyliforms that lived in South America and Africa during the Cretaceous period. It includes the genera ''Araripesuchus ''Araripesuchus'' is a genus of extinct crocodyliform that existed during the Cretaceous period of the late Mesozoic era some 125 to 66 million years ago. Six species of ''Araripesuchus'' are currently known. They are generally considered to be ...'' and '' Uruguaysuchus''. Below is a cladogram from Soto ''et al.'' (2011): References Early Cretaceous crocodylomorphs Terrestrial crocodylomorphs Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs Early Cretaceous first appearances Late Cretaceous extinctions Prehistoric reptile families {{paleo-archosaur-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araripesuchus Wegeneri
''Araripesuchus'' is a genus of extinct crocodyliform that existed during the Cretaceous period of the late Mesozoic The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Creta ... era some 125 to 66 million years ago. Six species of ''Araripesuchus'' are currently known. They are generally considered to be notosuchians (belonging to the clade Mesoeucrocodylia), characterized by their varied teeth types and distinct skull elements. This genus consists of six species: ''A. buitreraensis'', discovered in Argentina, ''A. wegeneri'', discovered in Cameroon and Niger, ''A. rattoides'', discovered in Niger, ''A. tsangatsangana'', discovered in Madagascar, ''A. gomesii'' (the type species), discovered in Brazil and another species discovered in Argentina, ''A. patagonicus''. Description Its length w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araripesuchus
''Araripesuchus'' is a genus of extinct crocodyliform that existed during the Cretaceous period of the late Mesozoic era some 125 to 66 million years ago. Six species of ''Araripesuchus'' are currently known. They are generally considered to be notosuchians (belonging to the clade Mesoeucrocodylia), characterized by their varied teeth types and distinct skull elements. This genus consists of six species: ''A. buitreraensis'', discovered in Argentina, ''A. wegeneri'', discovered in Cameroon and Niger, ''A. rattoides'', discovered in Niger, ''A. tsangatsangana'', discovered in Madagascar, ''A. gomesii'' (the type species), discovered in Brazil and another species discovered in Argentina, ''A. patagonicus''. Description Its length was about with a weight of . ''Araripesuchus'' can be distinguished by their laterally bulged edges of the snout, with the bulge being the most prominent around the area of an enlarged maxillary tooth. The snout and premaxilla are also smoother than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notosuchia
Notosuchia is a suborder of primarily Gondwanan mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Some phylogenies recover Sebecosuchia as a clade within Notosuchia, others as a sister group (see below); if Sebecosuchia is included within Notosuchia its existence is pushed into the Middle Miocene, about 11 million years ago. Fossils have been found from South America, Africa, Asia, and Europe. Notosuchia was a clade of terrestrial crocodilians that evolved a range of feeding behaviours, including herbivory (''Chimaerasuchus''), omnivory ('' Simosuchus''), and terrestrial hypercarnivory ('' Baurusuchus''). It included many members with highly derived traits unusual for crocodylomorphs, including mammal-like teeth, flexible bands of shield-like body armor similar to those of armadillos (''Armadillosuchus''), and possibly fleshy cheeks and pig-like snouts (''Notosuchus''). The suborder was first named in 1971 by Zulma Gasparini and has since under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruguaysuchids
Uruguaysuchidae is a family of notosuchian crocodyliforms that lived in South America and Africa during the Cretaceous period. It includes the genera ''Araripesuchus ''Araripesuchus'' is a genus of extinct crocodyliform that existed during the Cretaceous period of the late Mesozoic era some 125 to 66 million years ago. Six species of ''Araripesuchus'' are currently known. They are generally considered to be ...'' and '' Uruguaysuchus''. Below is a cladogram from Soto ''et al.'' (2011): References Early Cretaceous crocodylomorphs Terrestrial crocodylomorphs Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs Early Cretaceous first appearances Late Cretaceous extinctions Prehistoric reptile families {{paleo-archosaur-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simosuchus
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about in length. The type species is ''Simosuchus clarki'', found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of ''S. clarki'' were shaped like maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs. In fact, these features have led many palaeontologists to consider it a herbivore. Description ''Simosuchus'' was small, about long based on the skeletons of mature individuals. In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, ''Simosuchus'' has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means "pug-nosed crocodile" in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatosuchus
''Anatosuchus'' ("duck crocodile", the name from the Latin ''anas'' ("duck") and the Greek language, Greek ''souchos'' ("crocodile"), for the broad, duck-like snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorph discovered in Gadoufaoua, Niger, and described by a team of palaeontologists led by the United States, American Paul C. Sereno, Paul Sereno in 2003, in the ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology''. Its duck-like snout coincidentally makes it resemble a crocoduck, an imagined hybrid animal with the head of a crocodile and the body of a duck. Discovery The type species of ''Anatosuchus'' is ''A. minor'', in reference to its small body size. The holotype material (MNN GDF603), is a nearly complete skull with articulated lower jaws, belonging to a juvenile. It was discovered from the upper portion of the Elrhaz Formation and lower portion of Echkar Formation, indicating an Early Cretaceous (Late Aptian or Early Albian) age. Another specimen was found later ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java- Manihiki- Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kergue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberosuchus
''Iberosuchus'' (meaning "Iberian crocodile") is a genus of extinct sebecosuchian mesoeucrocodylian found in Western Europe from the Eocene. Remains from Portugal was described in 1975 by Antunes as a sebecosuchian crocodilian. This genus has one species: ''I. macrodon'' (meaning "large toothed). ''Iberosuchus'' was a carnivore, unlike the crocodilians today, they are not aquatic and are instead terrestrial. The first of its fossils were cranial remains found in Portugal, and later more fossils were found in France and Spain. They are only known from very fragmentary fossils, elements of the skull, dentary, teeth and osteoderm. History and discovery Remains of a mesocrocodylian were found in Portugal, it was named ''Iberosuchus macrodon'' in 1975 by Antunes, and is assigned as the type species. It was reclassified as a baurusuchid by Robert Carroll in 1988. In 1996 Ortega and colleges extended their range to France, they analyzed the fragmentary fossils of ''Atacisaurus crassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notosuchus
''Notosuchus'' (; 'southern crocodile') is an extinct genus of South American notosuchian crocodylomorph. It was terrestrial, living approximately 85 million years ago in the Santonian stage of the Late Cretaceous. Description ''Notosuchus'' was relatively small, reaching in length and a weight of . Remains have been found in the Bajo de la Carpa Formation in Patagonia, Argentina. First named in 1896, ''Notosuchus'' was the first known notosuchian. The type species is ''N. terrestris''. A second species, ''N. lepidus'', was named in 1957. A paper published in 2008 by Fiorelli and Calvo described new remains of the type species ''N. terrestris''. In it, the authors suggested that the skull would have supported a short trunk, or "hog's snout" as well as fleshy upper and lower lips. The anteriorly directed nares and the absence of a bony nasal septum (which presumably indicates cartilaginous tissue serving its place) provide evidence for a trunk-like snout, while striations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comahuesuchus
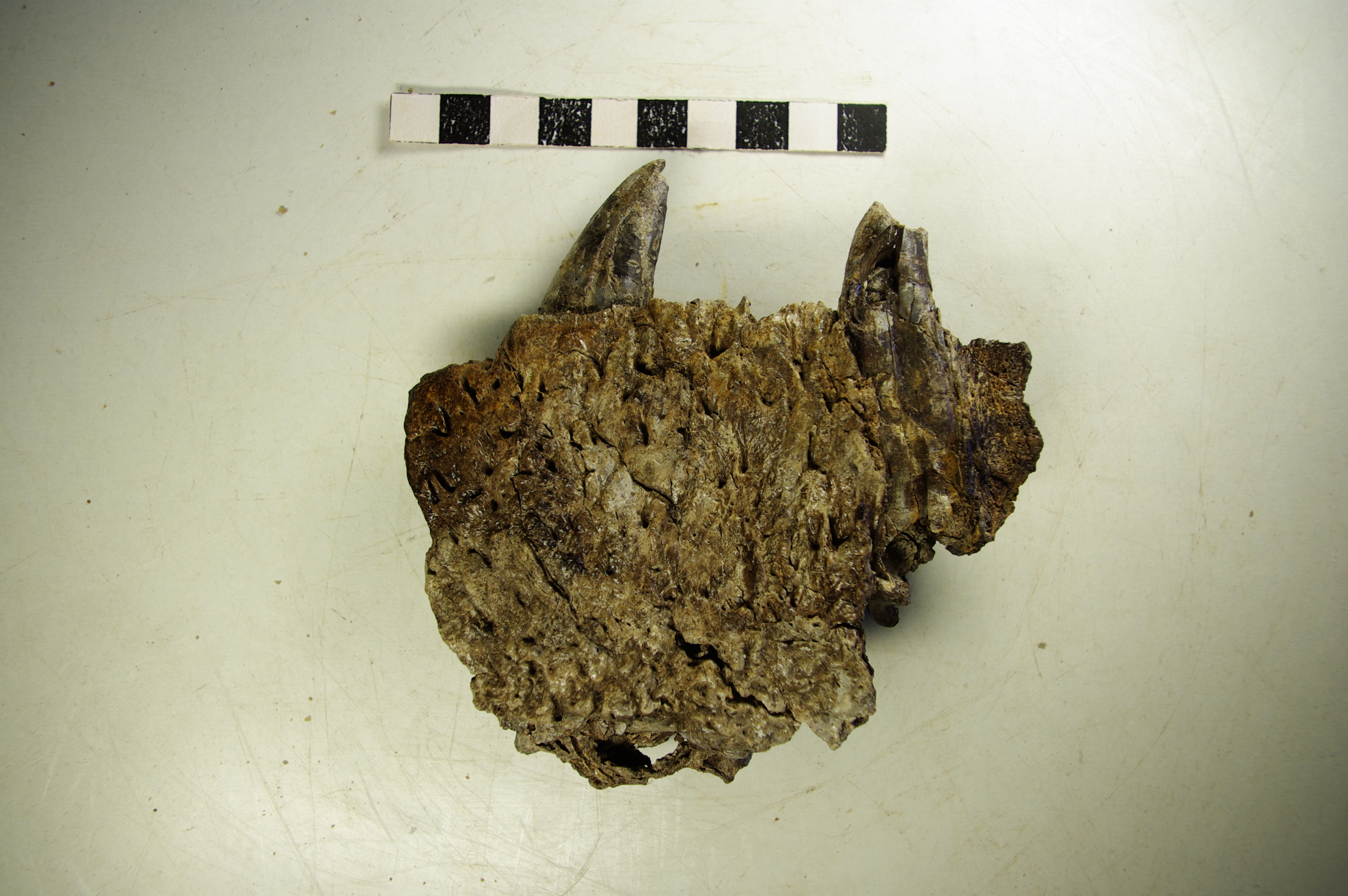
''Comahuesuchus'' is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Santonian Bajo de la Carpa Formation of Argentina. It was described by palaeontologist José Bonaparte in 1991. The type species is ''C. brachybuccalis''.''Comahuesuchus'' at .org Classification 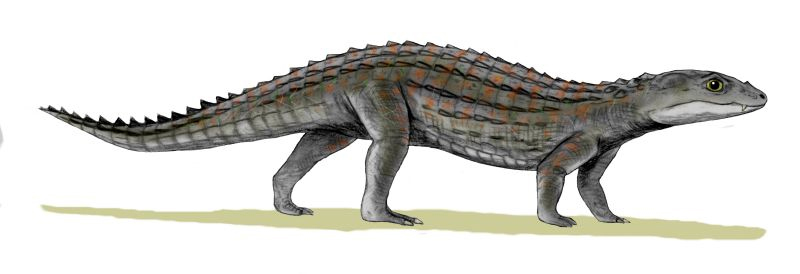 The of ''C. brachybuccalis'' is MUCPv-202. ''Comahuesuchus'' is ...
The of ''C. brachybuccalis'' is MUCPv-202. ''Comahuesuchus'' is ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Crocodylomorphs
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth. Terrestrial may also refer to: * Terrestrial animal, an animal that lives on land opposed to living in water, or sometimes an animal that lives on or near the ground, as opposed to arboreal life (in trees) ** A fishing fly that simulates the appearance of a land insect is referred to as a terrestrial fly. * Terrestrial ecoregion, land ecoregions, as distinct from freshwater ecoregions and marine ecoregions * Terrestrial ecosystem, an ecosystem found only on landforms * Terrestrial gamma-ray flash, a burst of gamma rays produced in Earth's atmosphere * Terrestrial locomotion, evolutionary adaptation from aquatic types of locomotion * Terrestrial plant, a plant that grows on land rather than in water or on rocks or trees * Terrestrial planet, a planet that is primarily composed of silicate rocks, and thus "Earth-like" * Terrestrial radio, radio signals received through a conventional aerial, as opposed to satellite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




