|
Upper Bari Doab Canal
Madhopur Headworks is a barrage on the Ravi River in Madhopur, just 14 km from Pathankot city in Pathankot district in the Indian state of Punjab. It is located on the border with Jammu and Kashmir. The Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) off-taking from Madhopur irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab and provides water to the cities of Pathankot, Gurdaspur, Batala and Amritsar. The headworks was one of the first irrigation projects constructed in Punjab during the British Raj, within 10 years of the conquest of Punjab. It provided irrigation in the lands of Gurdaspur, Amritsar and Lahore districts of the undivided Punjab. During the partition arrangements, Cyrill Radcliffe allocated three tehsils of Gurdaspur district to India for maintaining the integrity of the canal system from Madhopur. After independence, India signed the Indus Waters Treaty obtaining the exclusive use of waters from the Ravi River. Subsequently, India rebuilt the Madhopur headwork as full barrage. Pakistan c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravi River
The Ravi River is a transboundary river in South Asia, flowing through northwestern India and eastern Pakistan, and is one of five major rivers of the Punjab region. Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers of the Punjab (Sutlej and Beas River) were allocated to India. Subsequently, the Indus Basin Project was developed in Pakistan, which transfers waters from western rivers of the Indus system to replenish the portion of the Ravi River lying in that country. Many inter-basin water transfers, irrigation, hydropower and multipurpose projects have been built in India. History According to ancient history traced to Vedas, the Ravi River was known as (). The Ravi was known as Purushni or Irawati to Indians in Vedic times and as Hydraotes () and Hyarotis (Ὑαρῶτις) to the Ancient Greeks. Part of the Battle of the Ten Kings was fought on a river, which according to Yaska (Nirukta 9.26) refers to the Ravi river at Punjab. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
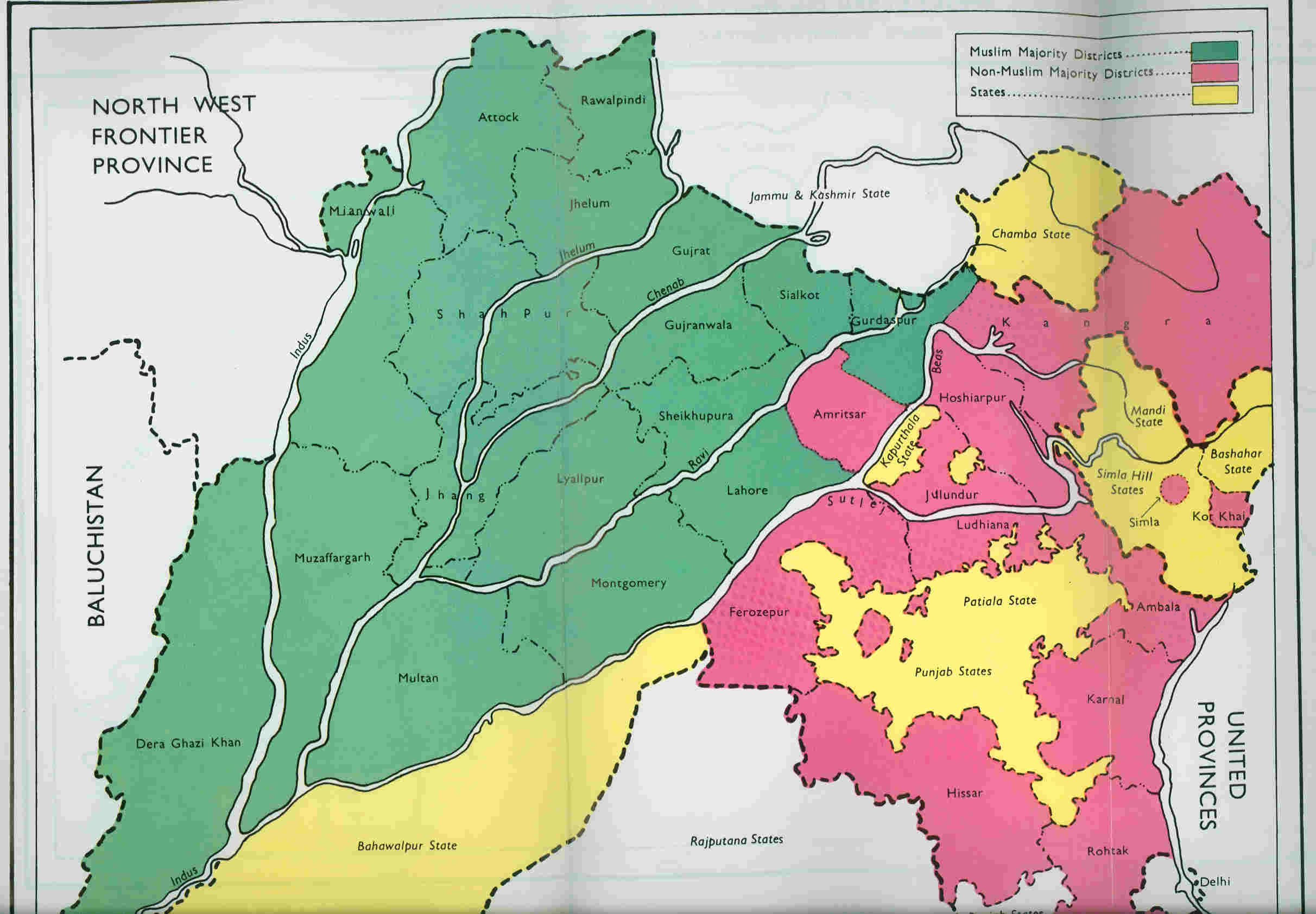
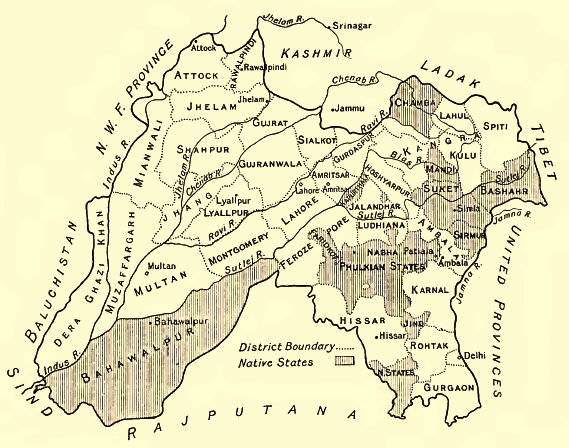
Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated by the two boundary commissions for the provinces of Punjab Province (British India), Punjab and Bengal Presidency, Bengal during the Partition of India. It is named after Cyril Radcliffe, 1st Viscount Radcliffe, Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissions, had the ultimate responsibility to equitably divide of territory with 88 million people. The term "Radcliffe Line" is also sometimes used for the entire boundary between India and Pakistan. However, outside of Punjab and Bengal, the boundary is made of existing provincial boundaries and had nothing to do with the Radcliffe commissions. The demarcation line was published on 17 August 1947, two days after the independence of Pakistan and India. Today, the Punjab part of the line is part of the India–Pakistan border while the Bengal part of the line serves as the Bangladesh–India border. Background Events leading up to the Radcliffe Boundary Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutlej River
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The combination of the Sutlej and Chenab rivers in the plains of Punjab forms the Panjnad, which finally flows into the Indus River at Mithankot. In India, the Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana. The waters of the Sutlej are allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan, and are mostly diverted to irrigation canals in India like the Sirhind Canal, Bhakra Main Line and the Rajasthan canal. The mean annual flow is 14 million acre feet (MAF) (roughly 1.727 × 1013 L) upstream of Ropar barrage, downstream of the Bhakra dam. It has several major hydroelectric points, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, British East India Company following the Second Anglo-Sikh War. At its peak in the mid-19th century the empire extended from Gilgit and Tibet under Qing rule, Tibet in the north to the Thar Desert, deserts of Sindh in the south and from the Khyber Pass in the west to the Sutlej in the east, and was divided into eight provinces. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 4.5 million in 1831 (making it the List of countries by population in 1800, 19th most populous state at the time), it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Raj, British Empire. In 1799, Ranjit Singh of Sukerchakia Misl captured Lahore from the Sikh triumvirate which had been ruling it Sikh period in Lahore#Sikh triumvirate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Bari Doab Canal (1911)
Madhopur Headworks is a barrage on the Ravi River in Madhopur, just 14 km from Pathankot city in Pathankot district in the Indian state of Punjab. It is located on the border with Jammu and Kashmir. The Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) off-taking from Madhopur irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab and provides water to the cities of Pathankot, Gurdaspur, Batala and Amritsar. The headworks was one of the first irrigation projects constructed in Punjab during the British Raj, within 10 years of the conquest of Punjab. It provided irrigation in the lands of Gurdaspur, Amritsar and Lahore districts of the undivided Punjab. During the partition arrangements, Cyrill Radcliffe allocated three tehsils of Gurdaspur district to India for maintaining the integrity of the canal system from Madhopur. After independence, India signed the Indus Waters Treaty obtaining the exclusive use of waters from the Ravi River. Subsequently, India rebuilt the Madhopur headwork as full barrage. Pakistan c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839. Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia Misl, Ranjit Singh survived smallpox in infancy but lost sight in his left eye. At the age of ten years old, he fought his first battle alongside his father. After his father died around Ranjit's early teenage years, he became leader of the Misl. Ranjit was the most prominent of the Sikh leaders who opposed Zaman Shah, the ruler of Durrani Empire, during his third invasion. After Zaman Shah's retreat in 1799, he captured Lahore from the Sikh triumvirate which had been ruling it since 1765. At the age of 21, he was formally crowned at Lahore. Before his rise, the Punjab had been fragmented into a number of warring Sikh (known as misls), Muslim and Hindu states. A large part of Punjab was under direct Durrani control. By 1813, Ranjit Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Mardan Khan
Ali Mardan Khan (; died 2 April 1657) was a Kurdish military leader and administrator, serving under the Safavid kings Shah Abbas I and Shah Safi, and later the Mughal ruler Shah Jahan. He was the son of Ganj Ali Khan. After surrendering the city of Qandahar, part of the easternmost territories of the Safavids to the Mughals in 1638, he served with distinction in the Mughal administration, earning the highest honors of the Mughal court. Career Ali Mardan Khan was a Kurd of the Zig tribe, and son of Safavid official Ganj Ali Khan. In 1624, Ali Mardan Khan inherited his father's position when he was appointed governor of Kerman, Sistan, and Qandahar by the Safavid emperor Shah Abbas. Like his father, Ali Mardan Khan governed from the city of Qandahar. In 1625, control of Kerman was handed over to Tahmasp Qoli Khan for administrative reasons. In 1632, Ali Mardan Khan began a series of correspondences with the Mughal court, culminating in the official surrender of his terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and 27th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a population of over 14 million. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial, educational and economic hubs. It has been the historic capital and cultural center of the wider Punjab region, and is one of Pakistan's most Social liberalism, socially liberal, Progressivism, progressive, and Cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities. Origins of Lahore, Lahore's origin dates back to antiquity. The city has been inhabited for around two millennia, although it rose to prominence in the late 10th century with the establishment of the Walled City of Lahore, Walled City, its fortified interior. Lahore served as the capital of several empires during the medieval era, including the Hindu Shahis, Gha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the zenith of Mughal architectural and cultural achievements. The third son of Jahangir (), Shah Jahan participated in the military campaigns against the Sisodia dynasty, Sisodia Rajputs of Mewar and the rebel Lodi (Pashtun tribe), Lodi nobles of the Deccan Plateau, Deccan. After Jahangir's death in October 1627, Shah Jahan defeated his youngest brother Shahryar Mirza and crowned himself emperor in the Agra Fort. In addition to Shahryar, Shah Jahan executed most of his rival claimants to the throne. He commissioned many monuments, including the Red Fort, Shah Jahan Mosque, Thatta, Shah Jahan Mosque and the Taj Mahal, where his favorite consort Mumtaz Mahal is entombed. In foreign affairs, Shah Jahan presided over the aggressive campaigns agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRB Canal
__NOTOC__ Bambanwala-Ravi-Bedian Canal (BRB Canal), also called Ichogil Canal (by Indian authors), is a manmade waterway in Pakistan that takes off from the Upper Chenab Canal near the Bambanwala village (to the west of Daska), runs southeast until reaching close to the India-Pakistan border and then runs south parallel to the border. It ends at the Sutlej near Kanganpur 100 km south of Lahore. It is the source of the Lahore Canal which runs westwards to the city of Lahore. History The canal was built by the citizens of Lahore in 1948 in response to an appeal by the Chief Minister of Punjab Iftikhar Hussein to safeguard the city from a possible Indian invasion in the future. As a result, common Pakistani nationals dug the whole 8km canal free of cost in a few days. Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 During the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, the Pakistani army blew up all except eight bridges crossing the canal and held back the invading Indian forces until the ceasefire wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |