Upper Bari Doab Canal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Madhopur Headworks is a barrage on the
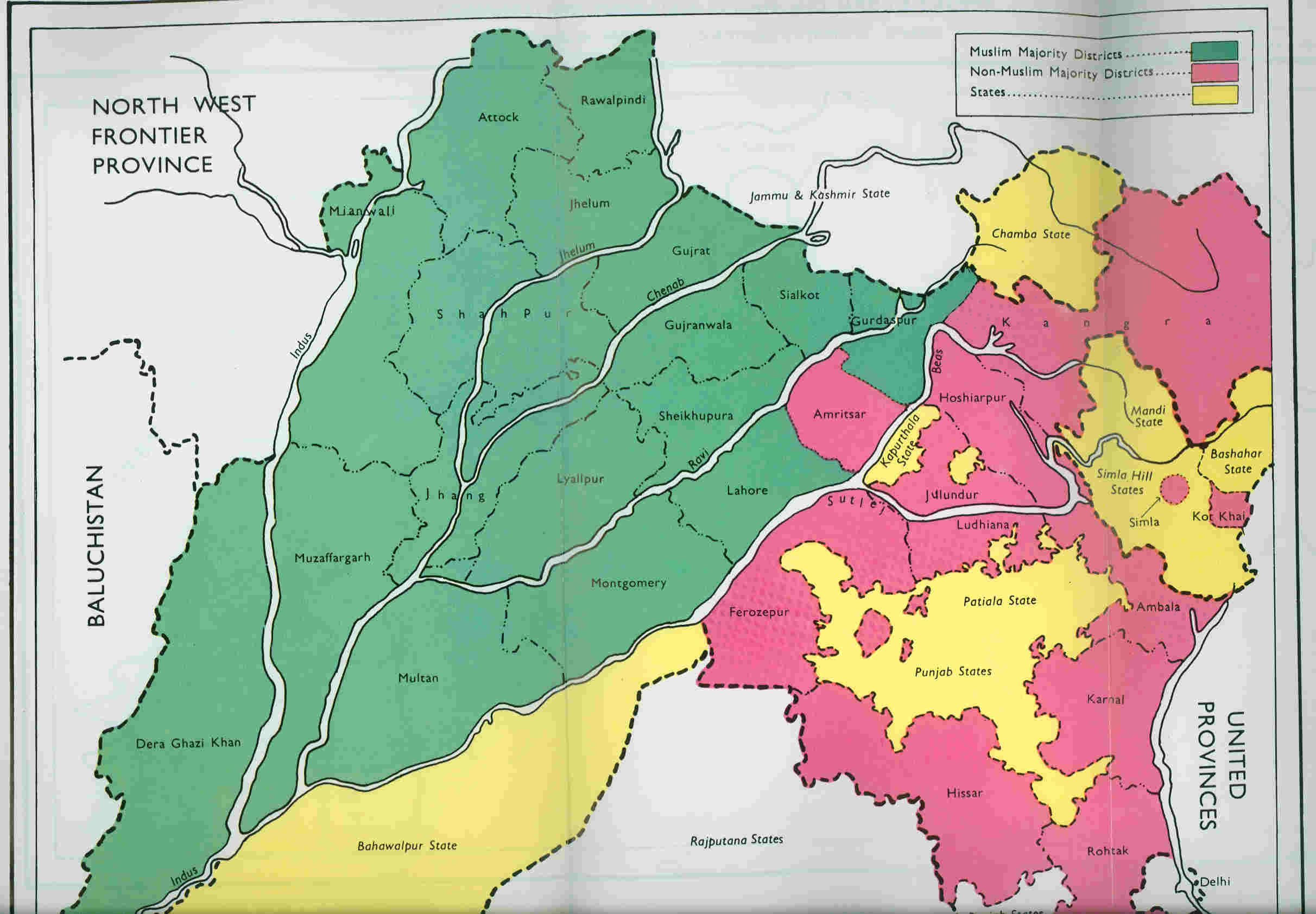 After conquering Punjab from the
After conquering Punjab from the
(watercolour painting 1865), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020. Modern commentators also note that the canal was constructed with an excessive slope of 0.05 m/km which caused erosion of its bed. The Madhopur headwork was added during 1875–1879. It consisted of a long weir across the Ravi river, with the crest varying from 3 feet to 6 feet above the bed of the river. The last 300 feet towards on the left (towards Punjab) held undersluices with 12 openings of 20 feet width and 3–4 feet height. They were operated by iron gates. Even though the canal system was capable of carrying flows of per second, the headwork supplied a maximum of per second. The main line of the canal ran to after which it divided into a main branch and a Kasur branch near the town of
Canal Administration Post-Independence
Department of Irrigation, Government of Punjab, retrieved 5 May 2020.
The UBDC canal network was remodelled during 2001–2005 after the construction of the
Department of Irrigation, Government of Punjab, retrieved 5 May 2020.
(watercolour painting 1865), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020.
(watercolour painting, 1869), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020. * Main branch – Bedian on OpenStreetMap
Indian sidePakistan side
* Lahore branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian sidePakistan side
* Kasur branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
* Sobraon branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
Map of the canal network on floodmap.net
Map of the canal network on Cartogiraffe.com
{{Hydrography of Punjab, India Dams in Punjab, India Buildings and structures in Gurdaspur district Gurdaspur district Dams on the Ravi River Pathankot district Upper Bari Doab Canal Upper Bari Doab Canal 1875 establishments in British India Dams completed in 1875
Ravi River
The Ravi River is a transboundary river in South Asia, flowing through northwestern India and eastern Pakistan, and is one of five major rivers of the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two oth ...
in Madhopur, just 14 km from Pathankot city in Pathankot district
Pathankot district, the northernmost district of Punjab, India, Punjab, India, was formed on July 27, 2011, after being carved out from Gurdaspur district. Pathankot serves as the district headquarters. The district shares its Border, borders ...
in the Indian state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. It is located on the border with Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory since 2019
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered by India as a state from 1952 to 2019
* Jammu and Kashmir (prin ...
. The Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) off-taking from Madhopur irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
and provides water to the cities of Pathankot
Pathankot () is a city and the district headquarters of the Pathankot district in Punjab, India. Pathankot is the sixth most populous city of Punjab, after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala and Bathinda. Its local government is a municipal ...
, Gurdaspur
Gurdaspur is a city in the Majha region of the Indian state of Punjab, between the rivers Beas and Ravi. It houses the administrative headquarters of Gurdaspur District and is in the geographical centre of the district, which shares a bord ...
, Batala
Batala is the eighth largest city in the state of Punjab, India in terms of population after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala, Bathinda, Mohali and Hoshiarpur. Batala ranks as the second-oldest city after Bathinda. It is a municipal cor ...
and Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
.
The headworks was one of the first irrigation projects constructed in Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
during the British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
, within 10 years of the conquest of Punjab. It provided irrigation in the lands of Gurdaspur, Amritsar and Lahore districts of the undivided Punjab. During the partition arrangements, Cyrill Radcliffe allocated three tehsils of Gurdaspur district
Gurdaspur district is a district in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. Gurdaspur is the district headquarters. It internationally borders Narowal District of Pakistani Punjab, and the districts of Amritsar, Pathankot, Kapurthala ...
to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
for maintaining the integrity of the canal system from Madhopur.
After independence, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
signed the Indus Waters Treaty
The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) is a water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan, arranged and negotiated by the World Bank, to use the water available in the Indus River and its tributaries. It was signed in Karachi on 19 September 196 ...
obtaining the exclusive use of waters from the Ravi River. Subsequently, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
rebuilt the Madhopur headwork as full barrage. Pakistan continues to use the UBDC canal network within its territory, replacing the Ravi waters by waters from Chenab
The Chenab River is a major river in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, the Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himac ...
via the BRB Canal
__NOTOC__
Bambanwala-Ravi-Bedian Canal (BRB Canal), also called Ichogil Canal (by Indian authors), is a manmade waterway in Pakistan that takes off from the Upper Chenab Canal near the Bambanwala village (to the west of Daska), runs southeast u ...
.
Antecedents
A canal by name Hasli canal was constructed during the reign of Mughal EmperorShah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
(), taking water from Madhopur to Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
. The canal plan was created by Ali Mardan Khan
Ali Mardan Khan (; died 2 April 1657) was a Kurdish military leader and administrator, serving under the Safavid kings Shah Abbas I and Shah Safi, and later the Mughal ruler Shah Jahan. He was the son of Ganj Ali Khan. After surrendering th ...
and built into construction by Mullah Ala'ul-Mul Tuni.
In the 19th century, the Sikh emperor Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia M ...
refurbished the canal and extended it with another branch going to Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
.
According to Scholar Ian Stone, these early canals were defective in many ways. The construction was made from weak masonry structures and easily gave way to floods. They were also prone to silt deposits and therefore had to be periodically refurbished.
British projects
 After conquering Punjab from the
After conquering Punjab from the Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
in 1849, the British East India Company rebuilt the canals under the name Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC). It was planned and carried out by engineers Joseph Henry Dyas and James Crofton. Providing employment to the disbanded Sikh soldiers via agriculture is said to have been the main motivation for its urgent construction. The new canals were opened in 1859 and irrigated agricultural lands in Gurdaspur
Gurdaspur is a city in the Majha region of the Indian state of Punjab, between the rivers Beas and Ravi. It houses the administrative headquarters of Gurdaspur District and is in the geographical centre of the district, which shares a bord ...
, Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
and Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
districts. No headworks were constructed at this time due to apprehensions that they would not be able to withstand the floods of the Ravi River. A side channel of the river with a weir
A weir or low-head dam is a barrier across the width of a river that alters the flow characteristics of water and usually results in a change in the height of the water level. Weirs are also used to control the flow of water for outlets of l ...
and falling shutters regulated the canal waters. A bridge with 23 arched openings 10 feet wide was constructed for this purpose.
The head of the Bari-Doab Canal, Madhopur(watercolour painting 1865), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020. Modern commentators also note that the canal was constructed with an excessive slope of 0.05 m/km which caused erosion of its bed. The Madhopur headwork was added during 1875–1879. It consisted of a long weir across the Ravi river, with the crest varying from 3 feet to 6 feet above the bed of the river. The last 300 feet towards on the left (towards Punjab) held undersluices with 12 openings of 20 feet width and 3–4 feet height. They were operated by iron gates. Even though the canal system was capable of carrying flows of per second, the headwork supplied a maximum of per second. The main line of the canal ran to after which it divided into a main branch and a Kasur branch near the town of
Gurdaspur
Gurdaspur is a city in the Majha region of the Indian state of Punjab, between the rivers Beas and Ravi. It houses the administrative headquarters of Gurdaspur District and is in the geographical centre of the district, which shares a bord ...
. The two branches had further subbranches leading to Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
and Sobraon
Sobraon () is a village in Punjab, India. It is located west to Harike village in Tarn Taran district. The Sutlej river is to the south of this village. The village is located at 31°10'39N 74°51'10E with an altitude of 192 metres (633 feet).
...
respectively.
* The main branch flowed past the towns of Batala
Batala is the eighth largest city in the state of Punjab, India in terms of population after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala, Bathinda, Mohali and Hoshiarpur. Batala ranks as the second-oldest city after Bathinda. It is a municipal cor ...
and Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
and headed towards the village of Bedian in the Lahore district. It continued in the Lahore district flowing past the villages of Raiwind
Raiwind ( Punjabi & ) is a town located within union council 149 (Dholanwal) in Allama Iqbal Town of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. The town serves as the headquarters of Tablighi Jamaat and hosts the annual Raiwind Markaz Ijtema. Raiwind is also ...
and Kot Radha Kishan. An escape to the channel of the Ravi River allowed any excess flood waters to drain back into the river.
* The Lahore branch took off the main branch near Batala and, flowing past Amritsar on its north, headed towards the city of Lahore.
* The Kasur branch ran south from Gurdaspur till the town of Kahnuwan and then turned southwest. Flowing past Batala and Tarn Taran Sahib
Tarn Taran Sahib is a city in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. It is the district headquarters and hosts the municipal council of Tarn Taran district. Gurdwara Sri Tarn Taran Sahib, a prominent Sikh shrine, is located in the c ...
, it entered the Kasur tehsil near the village of Patti (now in Tarn Taran district
Tarn Taran district is one of the districts in the Majha region of Punjab, India. The main cities are Tarn Taran Sahib, Bhikhiwind, Khadur Sahib and Patti. The City of Tarn Taran Sahib is a holy place for Sikhs. Tarn Taran's Sikh populatio ...
).
* The Sobraon branch continued south of Kahnuwan and turned southwest. Flowing parallel to the Sutlej River, it ended near Sobraon
Sobraon () is a village in Punjab, India. It is located west to Harike village in Tarn Taran district. The Sutlej river is to the south of this village. The village is located at 31°10'39N 74°51'10E with an altitude of 192 metres (633 feet).
...
(to its north).
Most of these areas were later scenes of conflict during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965.
Modern development
In 1955, a full barrage was constructed at Madhopur after the original weir of the Madhopur headwork got damaged in a flood. Over the next two years, a Madhopur–Beas Link canal was also added, to link the Ravi waters to the Beas River via the ''Chaki nalla''.Department of Irrigation, Government of Punjab, retrieved 5 May 2020.
Ranjit Sagar Dam
The Ranjit Sagar Dam, also known as the Thein Dam, is part of a hydroelectric project constructed by the Punjab Irrigation Department on the Ravi River on the border of Union Territory, Jammu and Kashmir and state Punjab. It is located upstrea ...
. It presently carries up to per second, distributing them to seven branches and 247 distributaries. The total length of the canal network is and cultivates of land.Canal AdministrationDepartment of Irrigation, Government of Punjab, retrieved 5 May 2020.
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
(watercolour painting 1865), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020.
(watercolour painting, 1869), British Library, retrieved 1 May 2020. * Main branch – Bedian on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
* Lahore branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
* Kasur branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
* Sobraon branch on OpenStreetMap
Indian side
Map of the canal network on floodmap.net
Map of the canal network on Cartogiraffe.com
{{Hydrography of Punjab, India Dams in Punjab, India Buildings and structures in Gurdaspur district Gurdaspur district Dams on the Ravi River Pathankot district Upper Bari Doab Canal Upper Bari Doab Canal 1875 establishments in British India Dams completed in 1875