|
Ulrich Kampffmeyer
Ulrich () is a Germanic given name derived from Old High German ''Uodalrich'', ''Odalric''. It is composed of the elements '' uodal-'' meaning "heritage" and ''-rih'' meaning "king, ruler". Attested from the 8th century as the name of Alamannic nobility, the name is popularly given from the high medieval period in reference to Saint Ulrich of Augsburg (canonized 993). Ulrich is also a surname. It is most prevalent in Germany and has the highest density in Switzerland. This last name was found in the United States in the year 1727 when Christof Ulrich landed in Pennsylvania. Most Americans with the last name were concentrated in Pennsylvania, which was home to many German immigrant communities. Nowadays in the United States, the name is distributed largely in the Pennsylvania-Ohio region. History Documents record the Old High German name ''Oadalrich'' or ''Uodalrich'' from the later 8th century in Alamannia. The related name ''Adalric'' (Anglo-Saxon cognate '' Æthelric'') is attes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Given Name
Germanic languages, Germanic given names are traditionally wikt:dithematic, dithematic; that is, they are formed from two elements (word stem, stems), by joining a prefix and a suffix. For example, Æthelred the Unready, King Æþelred's name was derived from ', meaning "noble", and ', meaning "counsel". The individual elements in dithematic names do not necessarily have any semantic relationship to each other and the combination does not usually carry a compound word, compound meaning. Dithematic names are found in a variety of Indo-European languages and are thought to derive from formulaic epithets of heroic praise. There are also names dating from an early time which seem to be monothematic, consisting only of a single element. These are sometimes explained as hypocorisms, short forms of originally dithematic names, but in many cases the etymology of the supposed original name cannot be recovered. The oldest known Germanic names date to the Roman Empire period, such as those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Bregenz
The county of Bregenz is recorded as part of the Holy Roman Empire between 1043 and 1160. It was in possession of the Udalriching family, who took the titles of counts of Bregenz. After 1160, Bregenz fell to the counts of Montfort-Bregenz (1160 to 1338), a cadet branch of the counts of Montfort (Swabia), counts of Montfort, Montfort-Tettnang-Bregenz (1354 to 1451). After 1451 the title of count of Bregenz was held by the House of Habsburg and Bregenz was incorporated into the duchy of Austria. The nominal title of count of Bregenz was kept as part of the grand title of the Emperor of Austria until 1918. Counts of Bregenz Counts of Bregenz (Udalriching): * Ulrich VI, Count of Bregenz, Ulrich VI, d. 950/957, count in Bregenz, count in Raetia * Ulrich IX, Count of Bregenz, Ulrich IX, d. before 1079, count of Bregenz, count in Argengau and Nibelgau * Ulrich X, Count of Bregenz, Ulrich X, d. 1097, count of Bregenz * Rudolf I, Count of Bregenz, Rudolf I, d. 1160, count of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulrich Hugwald
Ulrich Hugwald (''Udalricus Hugualdus'', ''Huldaricus Mutius Hugwaldus''; 1496–1571) was a Swiss humanist scholar and Reformer. Born in Wilen near Bischofszell, county of Thurgau, he was enrolled in the theological faculty in Basel University from 1519. He published critical pamphlets with Basel printer Adam Petri from 1520. He was in correspondence with a number of reformers, such as Vadianus, Michael Stifel, Jacques Lefèvre d'Étaples and Guillaume Farel. He also opened a private school of rhetorics in Basel. In 1524, he debated with Oecolampadius and Thomas Müntzer on the topic of believer's baptism. He joined the Basel Anabaptists in 1525, and was consequently imprisoned. He retired to his native Thurgau, working as a craftsman and farmer for some time. On his return to Basel, he distanced himself from the Anabaptists and was no longer active in religious debate. He taught at the Basel gymnasium from 1535, becoming rector in 1540, and he was professor for lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huldricus (other)
Huldricus (also ''Huldaricus'', ''Huldrych'', ''Huldreich'') is a variant of the given name Ulrich first introduced by Zwingli in the early 16th century and occasionally used as a variant of the name since. * Huldrych Zwingli (1484–1531), leader of the Swiss Reformation *''Huldaricus Mutius'', latinized name of Ulrich Hugwald Ulrich Hugwald (''Udalricus Hugualdus'', ''Huldaricus Mutius Hugwaldus''; 1496–1571) was a Swiss humanist scholar and Reformer. Born in Wilen near Bischofszell, county of Thurgau, he was enrolled in the theological faculty in Basel Universi ... (1496–1571) *'' Fridericus Huldaricus'', latinized name of Frederick Ulrich, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1591–1634) * Huldaricus Schönberger (Johann Ulrich Schönberger, 1601–1649), German blind organist, organ builder and polymath * Huldreich Georg Früh (1903–1945), Swiss composer * Jakob Huldreich Bachmann (1843–1915), Swiss politician See also * {{human name disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulrich Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenaries, Swiss mercenary system, he attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus. During his tenures at Basel and Einsiedeln, Zwingli began to familiarize himself with many criticisms Christian institutions were facing regarding their reform guidance and garnered scripture which aimed to address such criticisms. IIn 1519, Zwingli became the (people's priest) of the Grossmünster in Zurich where he began to preach ideas on reform of the Catholic Church. In his first public controversy in 1522, he attacked the Fasting and abstinence in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
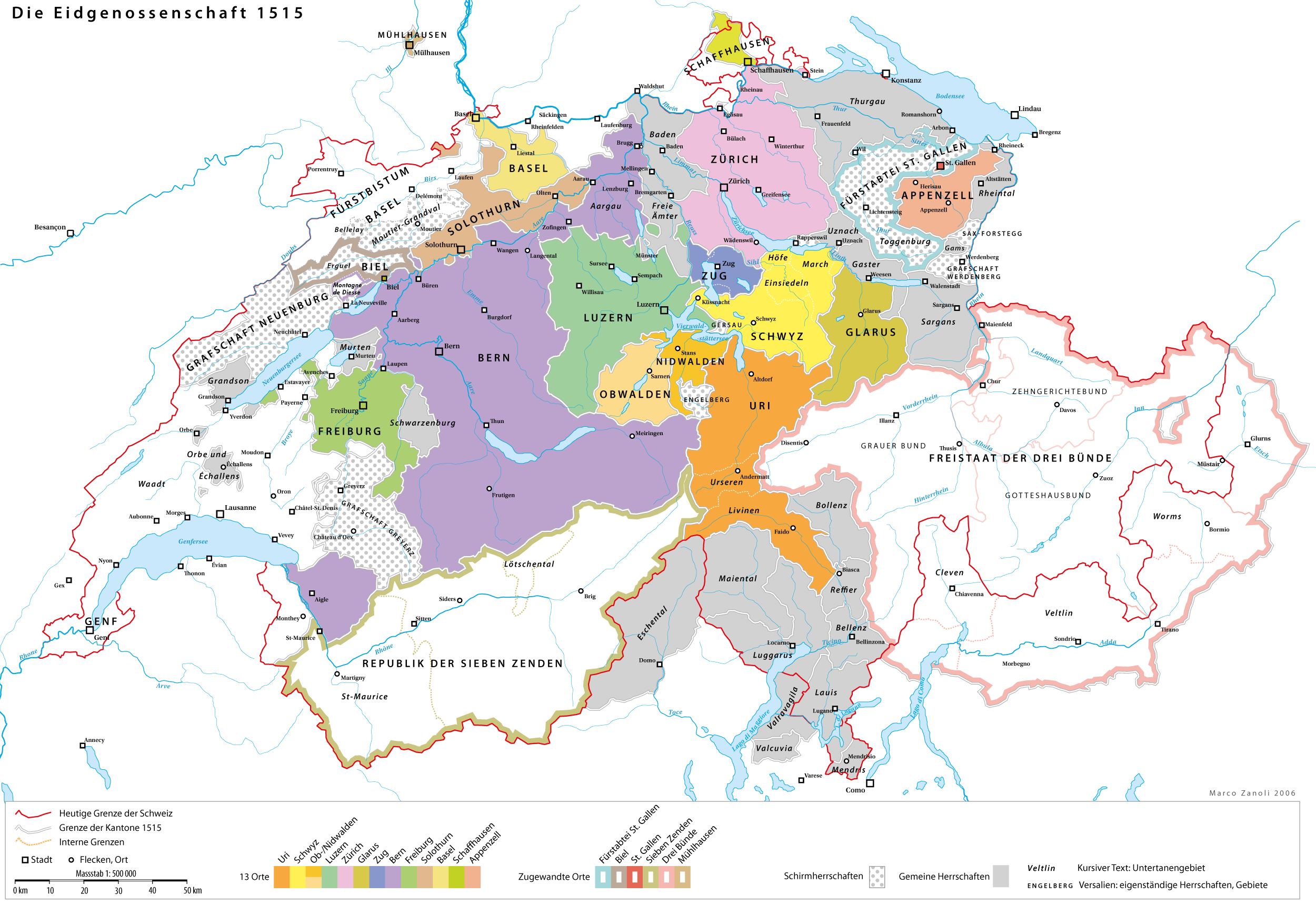
Swiss Reformation
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other cantons of Switzerland, cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Seven cantons remained Catholic, however, which led to intercantonal wars known as the Wars of Kappel. After the victory of the Catholic cantons in 1531, they proceeded to institute Counter-Reformation policies in some regions. The schism and distrust between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons defined their interior politics and paralysed any common foreign policy until well into the 18th century. Despite their religious differences and an exclusively Catholic defence alliance of the seven cantons (''Goldener Bund''), no other major armed conflicts directly between the cantons occurred. Soldiers from both sides fought in the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |