|
Ube Halaya
''Ube halaya'' or ''halayang ube'' (also spelled ''halea'', ''haleya''; ) is a Filipino cuisine, Filipino dessert made from boiled and mashed purple yam (''Dioscorea alata'', locally known as ''ube''). Ube halaya is the main base in ube/purple yam flavored-pastries and ube ice cream. It can also be incorporated in other desserts such as ''halo-halo''. It is also commonly anglicized as ube jam, or called by its original native name, ''nilupak na ube''. History The Philippines shows the highest phenotype, phenotypic diversity of ube (''Dioscorea alata''), making it one of the likely Vavilov center, centers of origin of ube plant domestication, domestication. Remains of ube have been recovered from the Ille Cave archaeological site of Palawan (c. 11,000 BP). Preparation The main ingredient is peeled and boiled Dioscorea alata, purple yam which is grated and mashed. The mashed yam, with condensed milk (originally sweetened coconut milk), are added to a saucepan where butter or mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in Island groups of the Philippines, three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. With a population of over 110 million, it is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, twelfth-most-populous country. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It has Ethnic groups in the Philippines, diverse ethnicities and Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latik
''Latík'' () refers to two different coconut-based ingredients in Filipino cuisine. In the Visayan region it refers to a syrupy caramelized coconut cream (coconut caramel) used as a dessert sauce. In the northern Philippines, it refers to solid by-products of coconut oil production (coconut curds), used as garnishing for a variety of desserts. Visayan ''Latik'' ''Latík'' in its original sense in the Visayan languages literally means 'syrup' (equivalent to ''arnibal'' in Hiligaynon). It can refer to any type of thick sweetened liquids including jam. In the most common usage, however, ''latik'' means a syrupy condiment derived from reducing coconut milk and sugar. It is used much in the same way as syrup, in dishes like ''kalamay'' and '' suman''. It is usually Anglicized as "coconut caramel." A commercial version of the Visayan ''latik'' is marketed internationally as coconut syrup, although it should not be confused with coconut sugar derived from coconut sap. Tagalog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
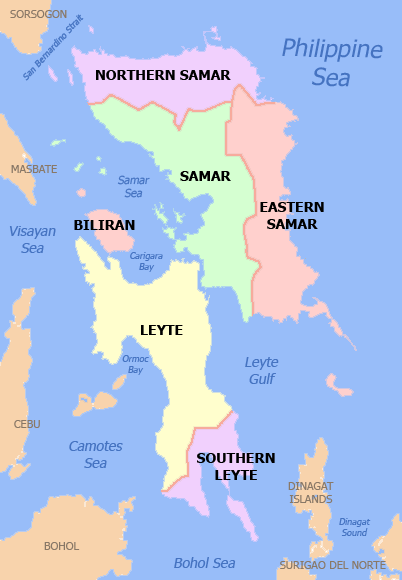
Eastern Visayas
Eastern Visayas (; ; ; ) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region VIII. It consists of three main islands: Samar, Leyte, and Biliran. The region has six provinces: Biliran, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar, Eastern Samar, Southern Leyte, one independent city, Ormoc, and one highly urbanized city, Tacloban (its regional center and largest city). The highly urbanized city of Tacloban is the sole regional center. These provinces and cities occupy the easternmost islands of the Visayas group of islands, hence the region's name. Some historians believe that the oldest ancient kingdom in the Philippines is found in this region, the Lakanate of Lawan, which plays a significant role in the Polynesian and Austronesian intermigration. Eastern Visayas faces the Philippine Sea to the east. The region's most famous landmark is the San Juanico Bridge, which links the islands of Samar and Leyte. As of 2020, the Eastern Visayas region has a population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binagol
''Binagol'' is a Filipino sweet steamed delicacy of the Waray people made from mashed giant taro corms, condensed milk, sugar, coconut milk, and egg yolks. It is distinctively placed in half of a coconut shell and then wrapped in banana leaves and twine. The name means "placed in a coconut shell", from the Visayan ''bagol'' (coconut shell). ''Binagol'' traditionally uses the corms of the giant taro (locally known as ''talyan'' or ''talian''); however, the corms of the taro (known in Tagalog as ''gabi'' and in Eastern Visayas, where the delicacy originates, as ''gaway'') is also alternatively used. It is a type of '' nilupak''. See also * Kalamay * Moron (food) * Ube halaya ''Ube halaya'' or ''halayang ube'' (also spelled ''halea'', ''haleya''; ) is a Filipino cuisine, Filipino dessert made from boiled and mashed purple yam (''Dioscorea alata'', locally known as ''ube''). Ube halaya is the main base in ube/purple ... References {{Philippine cuisine Foods containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ube Cake
Ube cake is a traditional Filipino chiffon cake or sponge cake made with ube halaya (mashed purple yam). It is distinctively vividly purple in color, like most dishes made with ube in the Philippines. Preparation Ube cake is generally prepared identically to mamón (chiffon cakes and sponge cakes in Filipino cuisine), but with the addition of mashed purple yam to the ingredients. It is typically made with flour, eggs, sugar, a dash of salt, baking powder, vanilla, oil, milk, and cream of tartar. The resulting cake is pink to purple in color (depending on the amount of ube used) and slightly denser and moister than regular chiffon cakes. Ube cake typically has a whipped cream, cream cheese, or buttercream frosting, which may also be flavored with ube or coconut. Variations Like mamón, ube cake can be modified readily into other recipes. Ube macapuno cake The combination of ube and macapuno (coconut sport) is a traditional one for ube halaya in Filipino cuisine, and it also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ube Macapuno
Buko salad, usually anglicized as young coconut salad, is a Filipino fruit salad dessert made from strips of fresh young coconut (''buko'') with sweetened milk or cream and various other ingredients. It is one of the most popular and ubiquitous Filipino desserts served during celebrations and '' fiestas''. By changing the ratio of milk, ''buko salad'' desserts can also become beverages (usually chilled or with shaved ice), known generally as ''samalamig''. A frozen dessert version of the dish is known as ice buko. Variants Buko salad can have many variations as it can incorporate numerous other ingredients ranging from fruits, ''gulaman'' (agar) jellies, sago, kaong, tapioca pearls, ''nata de coco'', macapuno, and others. Some versions however are popular enough to be considered as distinct subtypes. They include: Buko halo Buko halo or buko halo-halo is a combination of buko salad and '' halo-halo'' desserts, usually served directly on a coconut shell. It differs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macapuno
Macapuno, also called coconut sport, is a naturally occurring coconut cultivar that has an abnormal development of the endosperm. The result of this abnormal development is a soft translucent jelly-like flesh that fills almost the entire central cavity of coconut seeds, with little to no coconut water. Macapuno was first described scientifically from wild specimens in 1931 by Edwin Copeland. They were cultivated commercially in the Philippines after the development of the "embryo rescue" ''in vitro'' culture technology in the 1960s by Emerita V. De Guzman. Although called coconut sport, this mutation is not necessarily a sport in the botanical sense of a mutation arising in part of an adult plant; it may have arisen originally in a seed. It has become an important crop in coconut-producing countries and is now widely used in the cuisines of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. Name The name ''macapuno'' (also spelled ''makapuno'') is derived from Tagalog , the local name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalamay Ube
''Kalamay'' (also spelled ''calamay'', literally "sugar") is a sticky sweet delicacy that is popular in many regions of the Philippines. It is made of coconut milk, brown sugar, and ground glutinous rice. It can also be flavored with margarine, peanut butter, or vanilla. ''Kalamay'' can be eaten alone, but is usually used as a sweetener for a number of Filipino desserts and beverages. It is related to the Chamorro dessert called kalamai. Preparation ''Kalamay'' is made by extracting coconut milk from grated coconuts twice. Glutinous rice is added to the first batch of coconut milk and the mixture is ground into a paste. Brown sugar is added to the second batch of coconut milk and boiled for several hours to make '' latík''. The mixture of ground glutinous rice and coconut milk is then poured into the ''latík'' and stirred until the consistency becomes very thick. It can be served hot or at room temperature especially when eaten with other dishes. Viscous ''kalamay'' are of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Culture of Africa, African, Oceania, Oceanic, East Asian, Southeast Asian and South Asian cultures (similar to Yam (vegetable), yams). Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Common names The English term '':wikt:taro#English, taro'' was :wikt:taro#Maori, borrowed from the Māori language when James Cook, Captain Cook first observed ''Colocasia'' plantations in New Zealand in 1769. The form ''taro'' or ''talo'' is widespread among Polynesian languages:*''talo'': taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – entry in the ''Polynesian Lexicon Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweet Potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of the world. Cultivars of the sweet potato have been bred to bear tubers with flesh and skin of various colors. Moreover, the young shoots and leaves are occasionally eaten as greens. The sweet potato and the potato are in the order Solanales, making them distant relatives. Although darker sweet potatoes are often known as "yams" in parts of North America, they are even more distant from actual yams, which are monocots in the order Dioscoreales. The sweet potato is native to the tropical regions of South America in what is present-day Ecuador. Of the approximately 50 genera and more than 1,000 species of Convolvulaceae, ''I. batatas'' is the only crop plant of major importance—some others are used locally (e.g., ''I. aquatica'' "ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saba Banana
Saba banana (pron. or ) is a triploid hybrid (ABB) banana cultivar originating from the Philippines. It is primarily a cooking banana, though it can also be eaten raw. It is one of the most important banana varieties in Philippine cuisine. It is also sometimes known as the "cardaba banana", though the latter name is more correctly applied to the cardava, a very similar cultivar also classified within the saba subgroup. Description Saba bananas have very large, robust pseudostems that can reach heights of . The trunk can reach diameters of . The trunk and leaves are dark blue-green in color. Like all bananas, each pseudostem flowers and bears fruits only once before dying. Each mat bears about eight suckers. The fruits become ready for harvesting 150 to 180 days after flowering, longer than other banana varieties. Each plant has a potential yield of per bunch. Typically, a bunch has 16 hands, with each hand having 12 to 20 fingers. Saba bananas grow best in well-drained, fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |