|
U V Swaminatha Iyer
U.V. Swaminatha Iyer (19 February 1855 – 28 April 1942) was a Tamil scholar and researcher who was instrumental in bringing many long-forgotten works of classical Tamil literature to light. His singular efforts over five decades brought to light major literary works in Tamil and contributed vastly to the enrichment of its literary heritage. Iyer published over 90 books in his lifetime, on a variety of matters connected to classical Tamil literature, and collected over 3,000 paper manuscripts, palm-leaf manuscripts and notes of various kinds. He is affectionately called ''Tamil Thatha'' (literally, "Tamil grandfather"). Early life Swaminatha Iyer was born in Tamil-speaking Brahmin family on 19th February 1855 in the village of Suriyamoolai and grew up in Uthamadhanapuram, near Kumbakonam in Tamil Nadu. In his early years, he studied Tiruvilaiyadal Puranam, Kamba Ramayanam, Tamil Grammar - Nanool. He got married in 1868. Between 1870 and 1875, he trained under the great Tamil s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanjavur Maratha Kingdom
The Thanjavur Maratha kingdom ruled by the Bhonsle dynasty, Bhonsle dynasty was a principality of Tamil Nadu between the 17th and 19th centuries. Their native language was Thanjavur Marathi dialect, Thanjavur Marathi. Vyankoji Bhosale was the founder of the dynasty. Maratha conquest of Thanjavur Following the demise of Chola rule in the 13th century (specifically around 1279), the Thanjavur area came under the rule of the Pandyas and then, following Malik Kafur's invasion of the Pandya kingdom, the invasion of Malik Kafur, it fell into disorder. Pandya nadu very quickly reasserted their independence and added Thanjavur to their domain. Soon afterwards, however, they were conquered by the Vijayanagara Empire. The Emperor appointed his trusted Kin, who belonged to the Telugu people, Telugu-speaking Balija caste as Governors (Nayakas) of Madurai and Tanjavur. An internal family squabble between Chokkanatha Nayak of Madurai Nayak, Madurai Nayak dynasty and his uncle Thanjavur Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiruvaduthurai Adheenam
Thiruvavaduthurai Adheenam is a Saivite mutt (शैव मठ), based in the town of Thiruvavaduthurai in Kuthalam taluk of Mayiladuthurai District, Tamil Nadu, India. The adheenam maintains the Mayuranathaswami temple at Mayiladuthurai. As of 1987, there were a total of 15 Shiva temples under the control of the adheenam. Key activities The Adheenam is involved in publishing Saivite literature, specifically '' Thevaram'' and '' Tiruvasakam'' and its translations. It is also involved in literary scholarship. Some of the prominent Tamil literary personalities like Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai had their tutorship in the Adheenam. His disciple U V Swaminatha Iyer, who published many Tamil classical texts also was associated with the organization. The Adheenam along with Thiruppanandal Adheenam and Dharmapuram Adheenam were founded during the 16th century to spread the ideology of Saiva Sidhantam. Notable events In connection with India's Independence in August 14, 1947, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
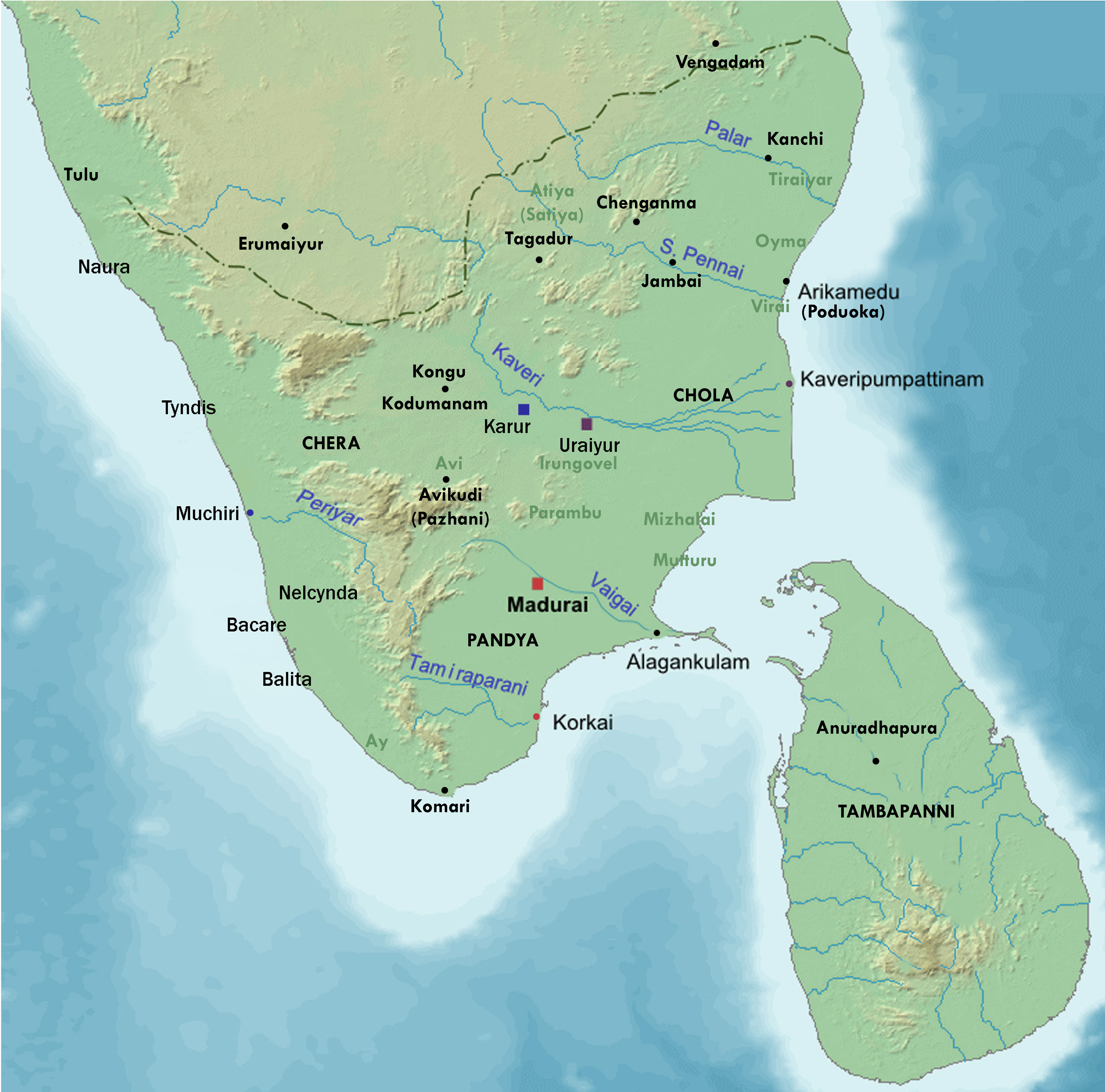
Ainkurunuru
Ainkurunuru ( meaning ''five hundred short poems'') is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the third of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. It is divided into five groups of 100 short stanzas of 3 to 6 lines, each hundred subdivided into 10s, or ''pattu''. The five groups are based on ''tinai'' (landscapes): riverine, sea coast, mountain, arid and pastoral. According to Martha Selby, the love poems in ''Ainkurunuru'' are generally dated from about the late-2nd-to-3rd-century-CE (Sangam period).Selby, Martha Ann. Tamil Love Poetry: The Five Hundred Short Poems of the Aiṅkuṟunūṟu, an Early Third-Century Anthology. Columbia University Press, 2011. . pp. 1-6 According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, these poems were likely composed between 300 and 350 CE based on the linguistic evidence, while Kamil Zvelebil – another Tamil literature scholar – suggests the Ainkurunuru poems were composed by 210 CE, with som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' (, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably somewhere between the 2nd century to the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic '' Cilappatikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karikala
Karikala (), often referred to as Karikala the Great, was a Tamils, Tamil Emperor of the Early Cholas of the Chola dynasty who ruled ancient Tamilakam (Modern day Tamil Nadu in Southern India) from Uraiyur. He is credited with the construction of the flood banks of the Kaveri, river Kaveri and conquest of Tamilakam, Andhra and Sri Lanka. He is recognised as the greatest of the Early Cholas. In Thiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola I, Medieval Cholas, Medieval Tamil Cholas listed Karikala Chola as one of their ancestors. Several Telugu dynasties also claimed descendant from Karikala. Sources The story of Karikala is mixed with legend and anecdotal information gleaned from Sangam literature. The period covered by the extant literature of the Sangam is not easy to determine with any measure of certainty. ''Paṭṭiṉappālai'', ''Poruṇarāṟṟuppaṭai'' and a number of individual poems in the ''Akanaṉūṟu'' and ''Purananuru'' have been the main source for the inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athiyamān
Athiyaman, also known as Athiyan, Adhiyaman, Adigaman, or as Sathiyaputhra in Indo-Aryan, were a line of rulers based in Thagadur, present day Dharmapuri, in northern Tamil country, dating back to at least the 3rd century BCE. They were one of the four major powers of the Tamilakam (the Tamil country) during the second half of the first millennium BCE, bordered by the Cheras to the southwest and the Pandyas and Cholas to the south. The Athiyamans are mentioned in early historic Tamil literature (the Sangam Literature), as well as in inscriptions such as the edicts of the Maurya emperor Asoka (3rd century BCE) and a Tamil-Brahmi cave record from Jambai. The Tamil-Brahmi inscription at Jambai, Tirukkoyilur, provide details of their sovereignty in the 1st century CE. The most well-known ruler of this dynasty was Athiyaman Neduman Anchi, who is listed as one of the kadai ezhu vallal (the last seven great patrons) in early historic Tamil literature. Their rule is mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purananuru
The ''Purananuru'' (, literally "four hundred [poems] in the genre puram"), sometimes called ''Puram'' or ''Purappattu'', is a classical Tamil literature, Tamil poetic work and traditionally the last of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. It is a collection of 400 heroic poems about kings, wars and public life, of which two are lost and a few have survived into the modern age in fragments. The collected poems were composed by 157 poets, of which 14 were anonymous and at least 10 were women. This anthology has been variously dated between 1st century BCE and 5th century CE, with Kamil Zvelebil, a Tamil literature scholar, dating predominantly all of the poems of ''Purananuru'' sometime between 2nd and 5th century CE. Nevertheless, few poems are dated to the period of 1st century BCE. The ''Purananuru'' anthology is diverse. Of its 400 poems, 138 praise 43 kings – 18 from the Chera dynasty, 13 Chola dynasty kings, and 12 Early Pandya dynasty kings. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theological v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten Idylls
The Ten Idylls, known as Pattuppāṭṭu () or Ten Lays, is an anthology of ten longer poems in the Sangam literature – the earliest known Tamil literature. They range between about 100 and 800 lines, and the collection includes the celebrated Nakkīrar's ''Tirumurukāṟṟuppaṭai'' (lit. "Guide to Lord Murukan"). The collection was termed as "Ten Idylls" during the colonial era, though this title is considered "very incorrect" by Kamil Zvelebil – a scholar of Tamil literature and history. He suggests "Ten Lays" as the more apt title. Five of these ten ancient poems are lyrical, narrative bardic guides (''arruppatai'') by which poets directed other bards to the patrons of arts such as kings and chieftains. The others are guides to religious devotion (Murugan) and to major towns, sometimes mixed with akam- or puram-genre poetry. The ''Pattuppāṭṭu'' collection is a later dated collection, with its earliest layer composed sometime between 2nd and 3rd century CE, the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culamani
Culamani or Sulamani is one of the five minor epic poems of post Sangam era Tamil literature. It was written by Tamil Jain scholar Tolamoli Thevar. The work does not have a single major plot, and consists of 2131 quatrains across 12 cantos. Description The text is written in ''viruttam'' metre similar to Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi. It consists of 2131 quatrains organised into 12 cantos. Many of the words used in the text are not used in contemporary Tamil language. The text incorporates elements from mythology, and supernatural elements. Though its style is similar to Cintamani, it has an easier and sweeter flow of words. It is mentioned in the Jain inscriptions in Sravanabelagola, and is inline with other classical Jain texts describing pathways to attain moksha. Author The text was written by Tamil Jain scholar Tolamoli Thevar. He probably lived after Tiruttakkatēvar, the author of Cintamani and was a follower of Digambara tradition. The introduction of the book states that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |