|
UT-88
The UT-88 (russian: ЮТ-88) is a DIY educational computer designed in Soviet Union. Its description was published in ''YT dlya umelykh ruk'' (''Young technical designer for skilled hands'', russian: ЮТ для умелых рук) — a supplement to ''Yunij Technik'' (''Young technical designer'', russian: Юный техник) magazine in 1989. It was intended for building by school children of extracurricular hobby groups at Pioneers Palaces. Description At the time of publication, there were several DIY computers: Micro-80, Radio-86RK, Specialist. The main feature of UT-88 was the possibility to build a computer in stages while getting a workable construction at each step. This approach made it easier to build by less skilled hobbyists. The minimal configuration of the computer includes power supply, CPU, 1 KiB of ROM and 1 KiB of RAM, 6 seven-segment display A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneers Palace
Young Pioneer Palaces or Palaces of Young Pioneers and Schoolchildren were youth centers designated for the creative work, sport training and extracurricular activities of Young Pioneers and other schoolchildren. Young Pioneer Palaces originated in the Soviet Union. After the collapse of the Soviet Bloc and the Soviet Union itself, they were transformed into depoliticized youth extracurricular establishments. Description The predecessors of Young Pioneer Palaces were established during the 1920s and 1930s in Moscow and later in Leningrad, Sverdlovsk, Tbilisi, Kyiv, Irkutsk and other cities and towns of the Soviet Union. The first Young Pioneer Palace was established in Kharkov in the former House of the Assembly of Nobility on 6 September 1935. In 1971 there were more than 3,500 Young Pioneer Palaces in the country. The early ones were organized at re-equipped palaces and personal residences of aristocrats of the Russian Empire, and were nationalized shortly after Soviet power w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro-80
The Micro-80 (russian: Микро-80) was the first do-it-yourself home computer in the Soviet Union. Overview Schematics and information were published in the local DIY electronic magazine ''Radio'' in 1983. It was complex, using an KR580VM80A-based system (a clone of the Intel 8080) which contained about 200 ICs. This system gained low popularity, but set a precedent in getting the attention of hobbyists for DIY computers, and later other DIY computers were published by ''Radio'' and other DIY magazines.Сергей Попов (2011). История создания компьютеров "Микро-80", "Радио-86РК" и "Микрошаzxbyte.ru/ref> History of creation The creation of the Micro-80 prototype began in 1978, when a package from the Kiev NPO Kristall arrived at the Moscow Institute of Electronic Machine Building Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics, MIEM (russian: Московский институт электроники и математ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio-86RK
The Radio-86RK (russian: Радио-86РК) is a build-it-yourself home computer designed in the Soviet Union. It was featured in the popular ''Radio'' (russian: Радио) magazine for radio hams and electronics hobbyists in 1986. The letters RK in the title stands for the words ''Radio ham's Computer'' (russian: Радиолюбительский компьютер). Design of the computer was published in a series of articles describing its logical structure, electrical circuitry, drawings of printed circuit boards and firmware. The computer could be built entirely out of standard off-the-shelf parts. Later it was also available in a kit form as well as fully assembled form. Predecessors The Radio-86RK is the successor of earlier build-it-yourself computer of the same designers, the Micro-80, and has limited compatibility with it. Its description was also published in a series of articles in the ''Radio'' magazine in the early 1980s. But its complex design, consisting of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialist (computer)
The Specialist (russian: Специалист) is a DIY computer designed in Soviet Union. Its description was published in ''Modelist-Konstructor'' (russian: Моделист-Конструктор), a magazine for scale model builders in 1987. It was the first such publication in a magazine not oriented on electronics. Overview The original construction was developed by a professional technical school teacher two years earlier. It was much more advanced than previous DIY computers, because it had a higher graphical image resolution (384x256) and a "transparent" video system, which did not slow down the CPU when both the CPU and the video system tried to access the RAM simultaneously. It gained limited popularity with hobbyists, though some factories produced DIY kits (Lik for example). Technical specifications * CPU: KR580VM80A ( Intel 8080A clone) clocked at 2 MHz. * RAM: 32 or 48 KiB. * ROM: 2 KiB, expandable to 12 KiB. ROM contains monitor firmware. * Video: m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
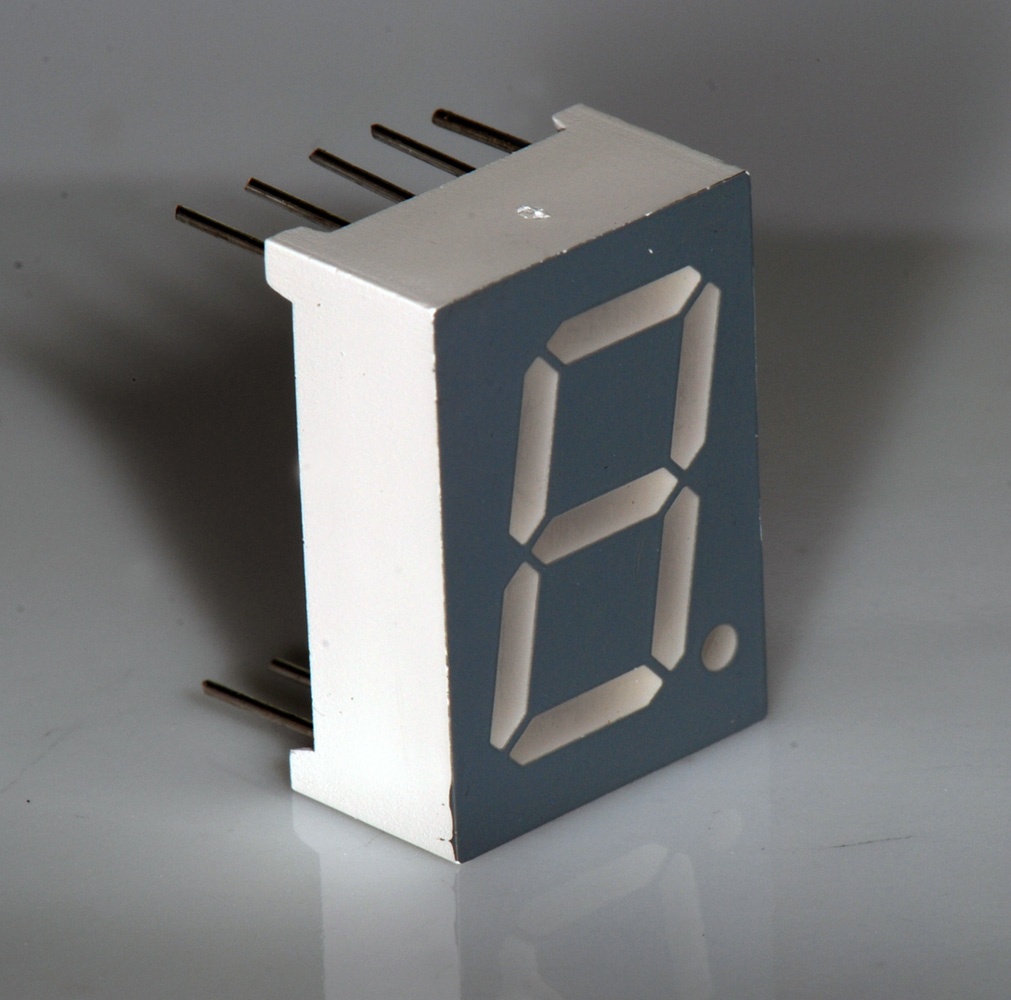
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of LEDs in the 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |