|
USS L-5 (SS-44)
USS ''L-5'' (SS-44) was an L-class submarine built for the United States Navy during the 1910s. Description The L-class boats designed by Lake Torpedo Boat (''L-5'' through ''L-8'') were built to slightly different specifications from the other L boats, which were designed by Electric Boat, and are sometimes considered a separate ''L-5'' class. The Lake boats had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The L-class submarines had a crew of 28 officers and enlisted men. They had a diving depth of .Friedman, p. 307 For surface running, the boats were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, the Lake boats had a range of at and at submerged.Gardiner & Gray, p. 129 The boats were armed with four 18-inch (450 mm) torpedo tubes in the bow. They carried four reloads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Torpedo Boat
The Lake Torpedo Boat Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut, was an early builder of submarines for the United States Navy in the early 20th century. History Founded by Simon Lake in 1912, the company was located at the east end of Seaview Avenue in Bridgeport, Connecticut. Most of the submarines completed by Lake Torpedo Boat were completed from 1918 to 1922. The firm competed with the Electric Boat Company until financial difficulties led to the company's demise in 1924. The Navy ceased awarding contracts to Lake shortly before that time, partly because , the company's entry in the S-class submarine design competition, was not selected for further production. Only nine S-boats were built by Lake. Also, the yard was not physically able to build the large submarine cruisers then envisioned, such as . The Washington Naval Treaty's limits on submarines were also a major factor. At the time, the Navy wished to concentrate submarine construction at Navy Yards, particularly Portsmou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often the initial step in constructing a ship. In the British and American shipbuilding traditions, this event marks the beginning date of a ship's construction. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English language, Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careening, careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
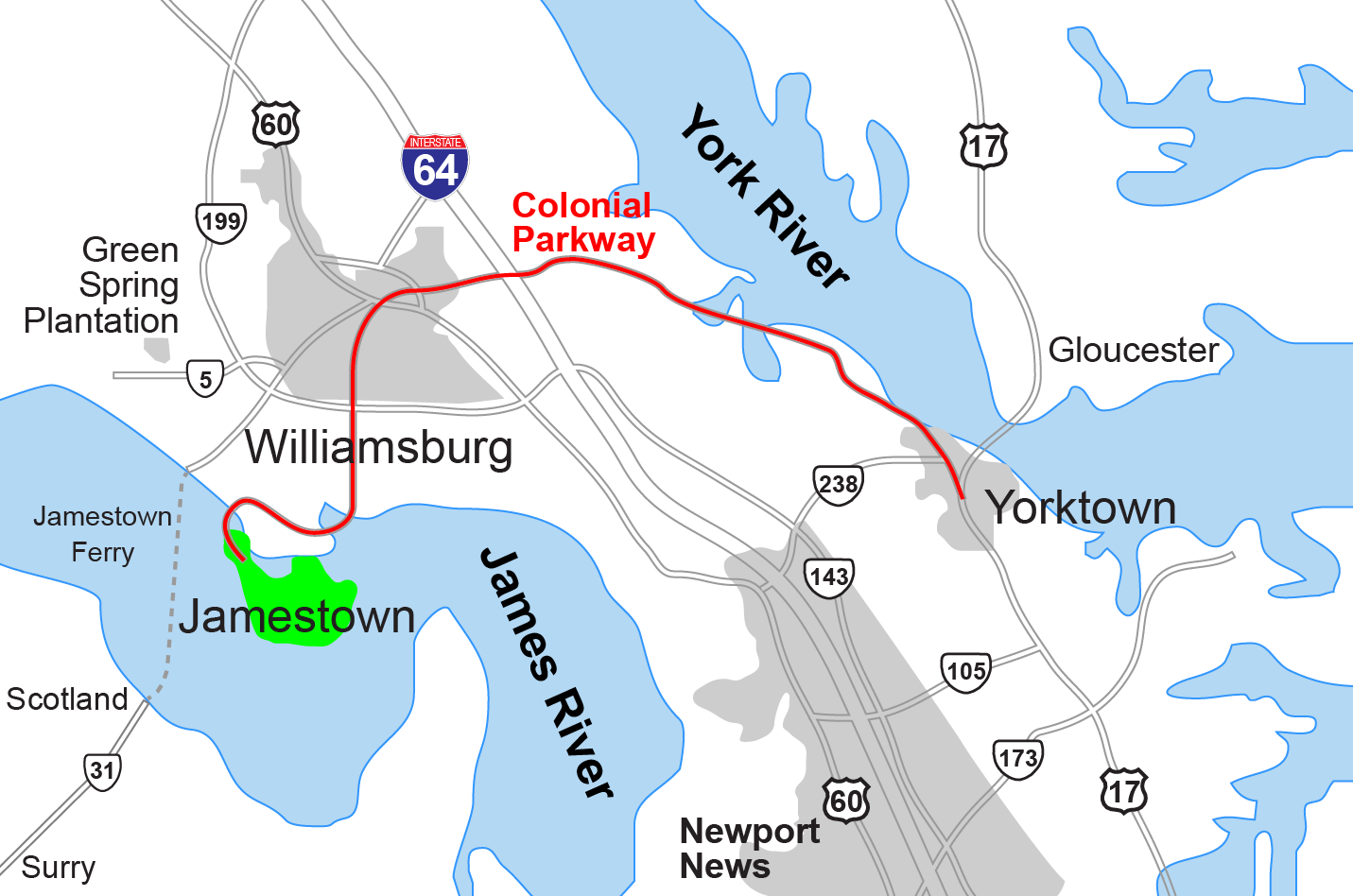
Hampton Roads
Hampton Roads is a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James River, James, Nansemond River, Nansemond, and Elizabeth River (Virginia), Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point near where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic Ocean. It also gave its name to the surrounding metropolitan region located in the southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina portions of the Tidewater (region), Tidewater Region. Comprising the Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC, metropolitan area and an extended combined statistical area that includes the Elizabeth City, North Carolina micropolitan area, Elizabeth City, North Carolina, micropolitan statistical area and Dare County, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, micropolitan statistical area, Hampton Roads is known for its large military presence, ice-free harbor, shipyards, coal piers, and miles of waterfront property and beaches, all of which cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone (), also known as just the Canal Zone, was a International zone#Concessions, concession of the United States located in the Isthmus of Panama that existed from 1903 to 1979. It consisted of the Panama Canal and an area generally extending on each side of the centerline, but excluding Panama City and Colón, Panama, Colón. Its capital was Balboa, Panama, Balboa. The Panama Canal Zone was created on November 18, 1903, from the Separation of Panama from Colombia, territory of Panama; it was established with the signing of the Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty, which allowed for the construction of the Panama Canal within the territory by the United States. The zone existed until October 1, 1979, when it was incorporated back into Panama. In 1904, the Isthmian Canal Commission, Isthmian Canal Convention was proclaimed. In it, the Republic of Panama granted to the United States in perpetuity the use, occupation, and control of a zone of land and land underwater for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America after Guatemala and Honduras. Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean and shares maritime borders with El Salvador to the west and Colombia to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is Managua, the List of largest cities in Central America#Largest cities proper, fourth-largest city in Central America, with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is Spanish language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the List of countries by area, thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the List of countries by population, tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the Hispanophone#Countries, largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city, which ranks among the List of cities by population, most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Pedro, California
San Pedro ( ; ) is a neighborhood located within the South Bay (Los Angeles County), South Bay and Los Angeles Harbor Region, Harbor region of the city of Los Angeles, California, United States. Formerly a separate city, it consolidated with Los Angeles in 1909. The Port of Los Angeles, a major international seaport, is partially located within San Pedro. The district has grown from being dominated by the fishing industry, to a working class in the United States, working-class community within the city of Los Angeles, to an increasingly dense and diverse community. History Indigenous The peninsula, including all of San Pedro, was the homeland of the Tongva for thousands of years, home to the village of Chowigna, California, Chowigna along and the nearby Suangna, California, Suangna. In other areas of the Los Angeles Basin archeological sites date back to at least about 10,000 years old. The Tongva used seafaring plank canoes or ''Te'aat, te'aats'', found all throughout the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuela, Venezuelan coastline to the Colombia, Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The Geopolitics, geopolitical region around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas on Earth and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, the Gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of List of islands of Bermuda, 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of . Bermuda has a tropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. Its climate also exhibits Oceanic climate, oceanic features similar to other coastal areas in the Northern Hemisphere with warm, moist air from the ocean ensuring relatively high humidity and stabilising temperatures. Bermuda is prone to severe weather from Westerlies#Interaction with tropical cyclones, recurving tropical cyclones; however, it receives some protection from a coral reef and its position north of the Main Development Region, which limits the direction and severity of approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistice With Germany (Compiègne)
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed in a railroad car, in the Compiègne Forest near the town of Compiègne, that ended fighting on land, at sea, and in the air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices had been agreed with Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. It was concluded after the German government sent a message to American president Woodrow Wilson to negotiate terms on the basis of a recent speech of his and the earlier declared "Fourteen Points", which later became the basis of the German surrender at the Paris Peace Conference, which took place the following year. Also known as the Armistice of Compiègne (, ) from the town near the place where it was officially agreed to at 5:00 a.m. by the Allied Supreme Commander, French Marshal Ferdinand Foch, it came into force at 11:00 a.m. Central European Time (CET) on 11 November 1918 and marked a vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about west of Lisbon, about northwest of Morocco, about southeast of Newfoundland, Canada, and the same distance southwest of Cork, Ireland. Its main industries are agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing, and tourism, which has become a major service activity in the region. In the 20th century and to some extent into the 21st, they have served as a waypoint for refueling aircraft flying between Europe and North America. The government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The largest city of the Azores is Ponta Delgada. The culture, dialect, cuisine, and traditions of the Azorean islands vary considerably, because these remote island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |