|
Typothoracine
Typothoracinae is a clade of aetosaurs within the subfamily Aetosaurinae. It was originally defined as a stem-based taxon including all aetosaurs closer to ''Typothorax'' than to ''Stagonolepis'' or ''Desmatosuchus''. This definition was later expanded to specifically exclude ''Aetosaurus''; as of 2016, Typothoracinae is defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Typothorax'' and ''Paratypothorax'', but not ''Aetosaurus,'' ''Stagonolepis'', or ''Desmatosuchus''. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Typothoracisinae, after its namesake ''Typothorax''. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Typothoracinae in 2016. Typothoracines can be distinguished by their wide bodies. The transverse processes of the dorsal (trunk) vertebrae are reinforced and elongated, more than twice the width of the centrum. Their neural spines, on the other hand, are short. The overlying carapace A carapace is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgetosuchus
''Gorgetosuchus'' is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic of the North Carolina, represented by the type species ''Gorgetosuchus pekinensis''. It is mainly known from osteoderms, including the front half of an articulated carapace. ''Gorgotesuchus'' is typically considered a basal desmatosuchin, though alternative interpretations exist. Discovery ''G. pekinensis'' was named and described by Heckert ''et al.'' (2015) on the basis of ten rows of bony plates called osteoderms, representing the front part of an armored carapace that would have covered the back of the animal. These plates were found embedded in sandstone and conglomerate boulders near a brick quarry in Chatham County, North Carolina, which likely originated from the Late Triassic Pekin Formation. (The Pekin Formation consists of interbedded red mudstones, siltstones, sandstones and conglomerates; it was the fine-grained mudstones and siltstones that the mining operation was targeting for brick-makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothorax Coccinarum
''Typothorax'' is an extinct genus of typothoracine aetosaur that lived in the Late Triassic. Its remains have been found in North America. Two species are known: ''T. coccinarum'', the type species, and ''T. antiquum''. Description ''Typothorax'' was an aetosaur, a pseudosuchian distantly related to modern crocodilians. Unlike modern crocodilians, aetosaurs were herbivorous. ''Typothorax'' and other aetosaurs possess small, leaf-shaped teeth that were unsuited for a diet consisting of meat.Martz, J.W. 2002. The morphology and ontogeny of Typothorax coccinarum (Archosauria, Stagonolepididae) from the Upper Triassic of the American southwest. M.S. thesis, Geosciences, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, 279 pp. Unlike some aetosaurs such as ''Desmatosuchus'', ''Typothorax'' does not have large shoulder spikes. It does, however, have a pair of enlarged spikes on the neck projecting from the third row of scutes. It has lateral scutes that bear horns that are posteriorly hooked along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaurs
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum. The carapace is calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single plate which carries the eyes, ocularium, ozopores (a pair of openings of the scent gland of Opilione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Spines
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaurus
''Aetosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian reptile belonging to the order Aetosauria. It is generally considered to be the most primitive aetosaur. Three species are currently recognized: ''A. ferratus'', the type species from Germany and Italy; ''A. crassicauda'' from Germany; and ''A. arcuatus'' from eastern North America. Additional specimens referred to ''Aetosaurus'' have been found in the Chinle Group of the southwestern United States, and the Fleming Fjord Formation of Greenland. Specimens of ''Aetosaurus'' occur in Norian-age strata. Description ''Aetosaurus'' was a small, primitive aetosaur. Unlike more derived aetosaurs such as ''Desmatosuchus'' or ''Typothorax'', the carapace was long and narrow and lacked spikes. The paramedian scutes that covered the back (with one row on each side of the vertebrae) are considerably wider than they are long. The lateral scutes, which are beneath the paramedians and formed a row on either side of the animal, do not bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
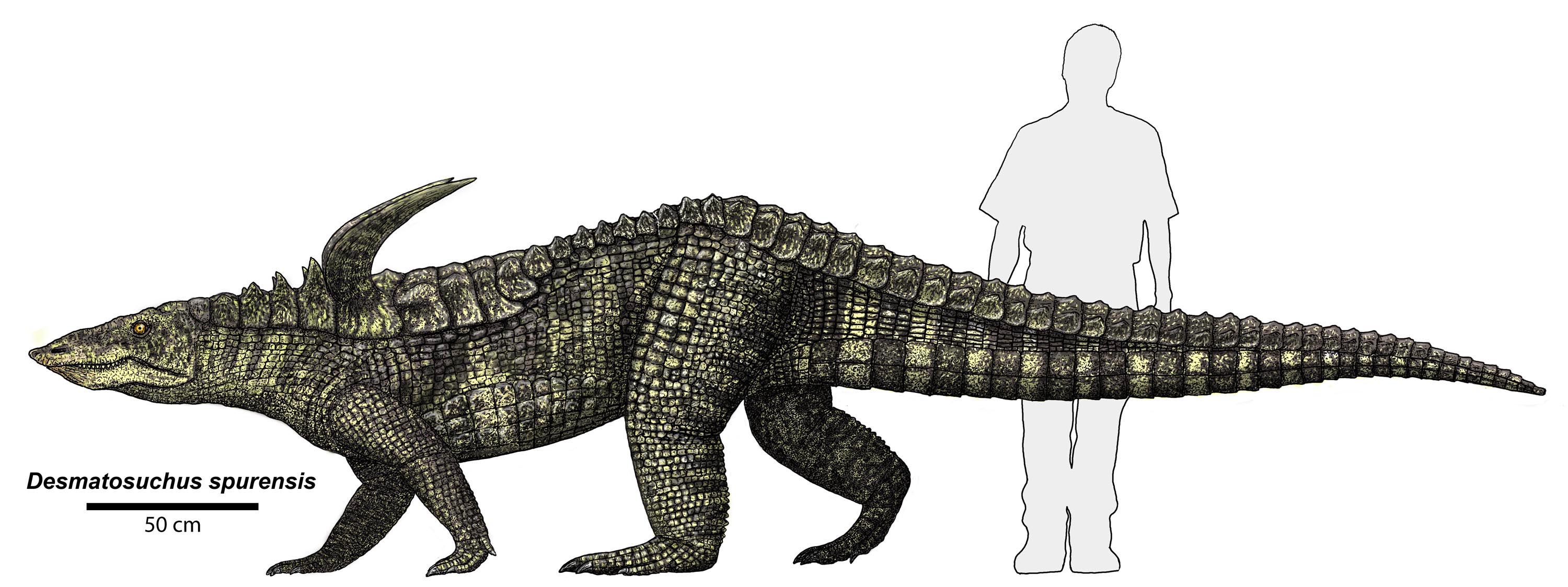
Desmatosuchus
''Desmatosuchus'' (, from Greek δεσμός ''desmos'' 'link' + σοῦχος ''soûkhos'' 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosaur belonging to the Order Aetosauria. It lived during the Late Triassic. Description ''Desmatosuchus'' was a large quadrupedal reptile upwards of to in lengthvon Baczko, M. B., Desojo, J. B., Gower, D. J., Ridgely, R., Bona, P., & Witmer, L. M. (2021)New digital braincase endocasts of two species of Desmatosuchus and neurocranial diversity within Aetosauria (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia) The Anatomical Record, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24798 and in weight. Its vertebral column had amphicoelus centra and 3 sacral vertebrae. This archosaur's most distinguishing anatomical characteristics were its scapulae which possessed large acromion processes commonly referred to as "shoulder spikes". The forelimbs were much shorter than the hindlimbs, with humeri less than two-thirds the length of the femurs. The pelvic girdle consisted of a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagonolepis
''Stagonolepis'' is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic (Carnian stage) Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, and the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. Supposed fossils from North and South America have been placed into their own genera, ''Calyptosuchus'' and ''Aetosauroides'', respectively. Description ''Stagonolepis robertsoni'' was about long. It was a quadrupedal animal covered in thick armoured scales that ran down the length of its body. A slow-moving browser, it would have used this heavy body armour to repel attacks from contemporary thecodont carnivores. ''Stagonolepis'' had a very small head for its size; it was only , accounting for less than 10% of the total body length. It had no teeth in the front of its jaws, but instead had a beak-like tip that arched upwards. This would have allowed it to uproot plants in a similar manner to a modern pig. The peg-like teeth at the back of its mouth would have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-based Taxon
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with the traditional approach, in which taxon names are defined by a ''type'', which can be a specimen or a taxon of lower rank, and a description in words. Phylogenetic nomenclature is currently regulated by the ''International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'' (''PhyloCode''). Definitions Phylogenetic nomenclature ties names to clades, groups consisting of an ancestor and all its descendants. These groups can equivalently be called monophyletic. There are slightly different ways of specifying the ancestor, which are discussed below. Once the ancestor is specified, the meaning of the name is fixed: the ancestor and all organisms which are its descendants are included in the named taxon. Listing all these organisms (i.e. providing a full circumscription) requires the full phylogenetic tree to be known. In practice, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |