|
Typhoon Bualoi
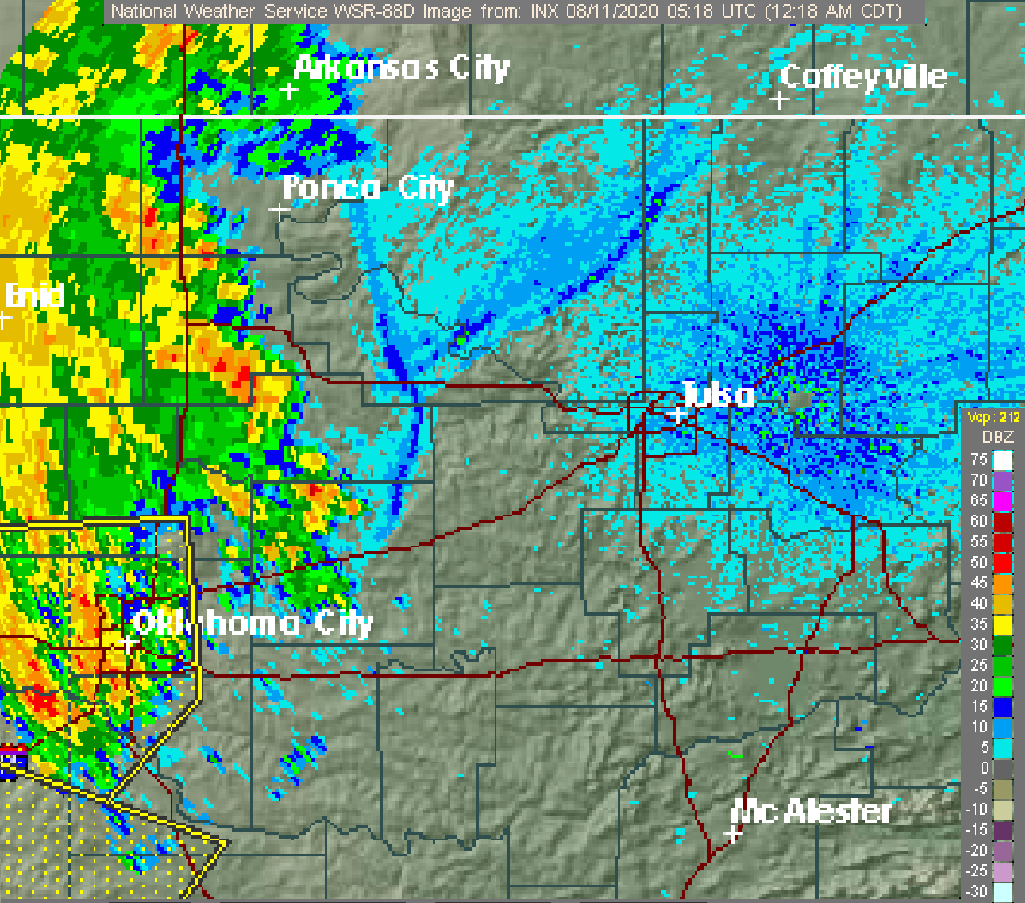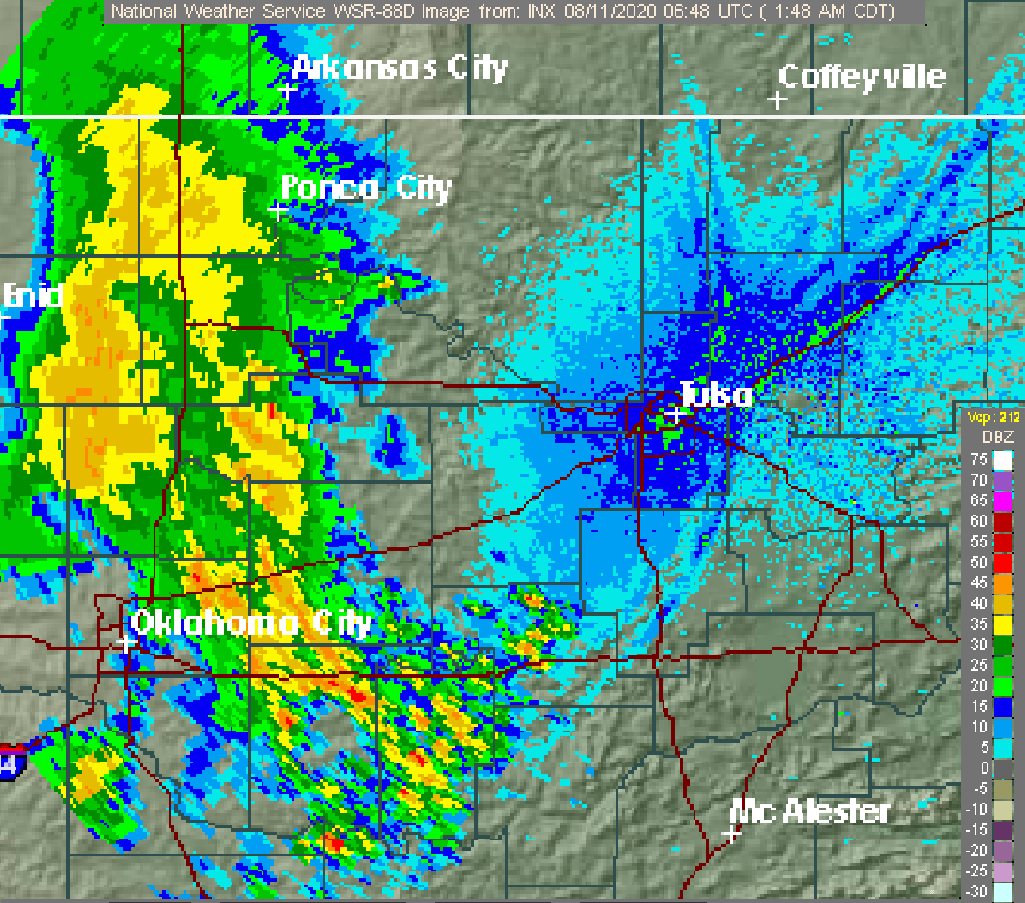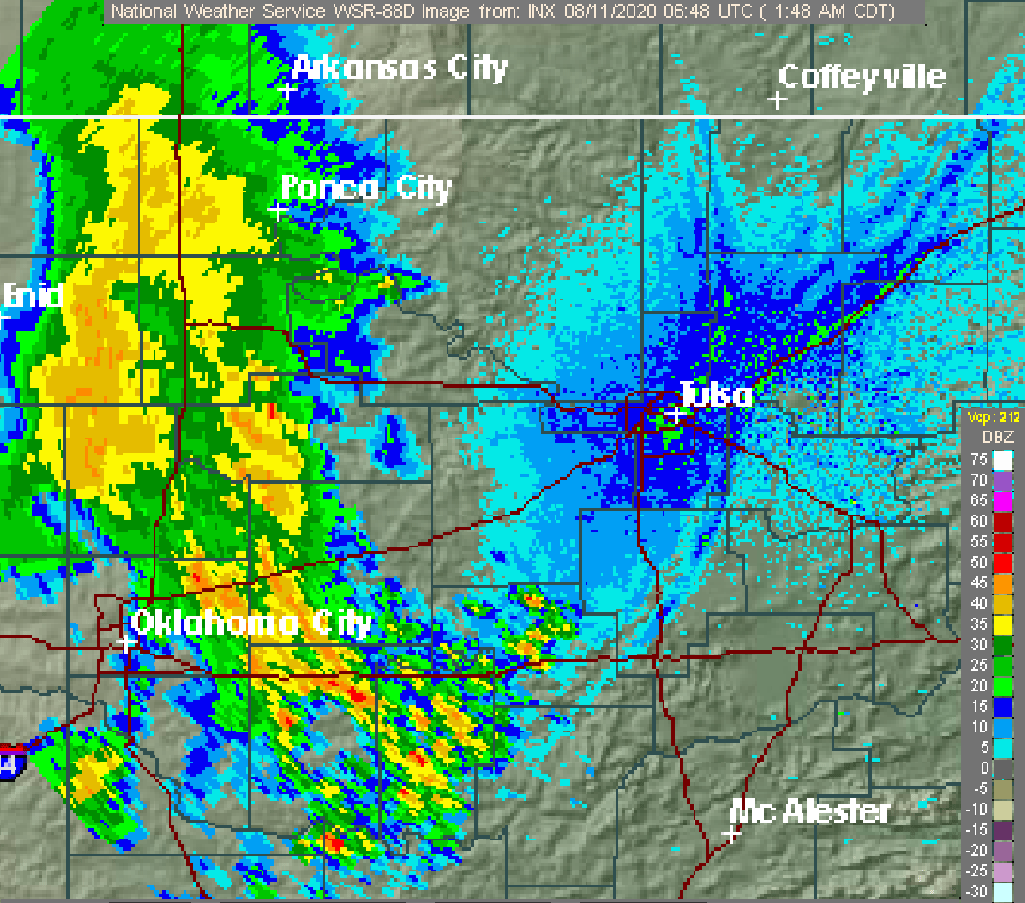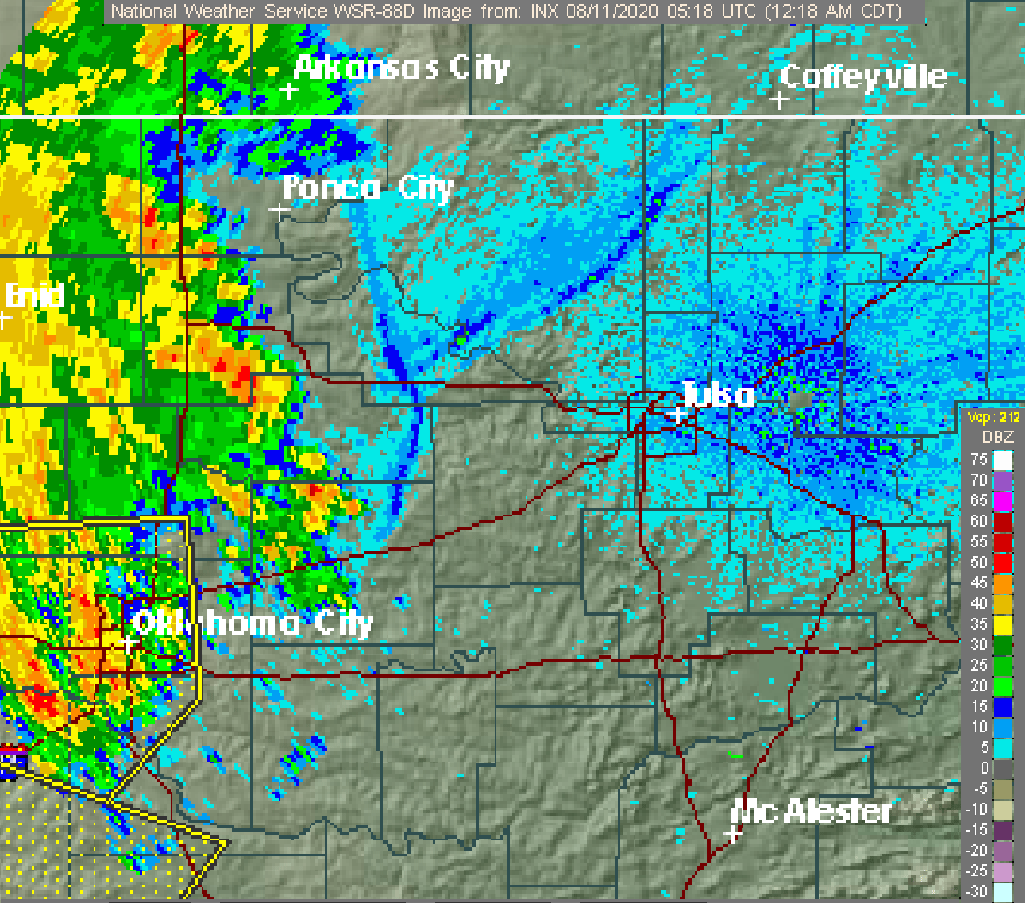
Typhoon Bualoi was a tropical cyclone in October 2019 that brought floods over Japan. The fortieth tropical depression, and the eleventh typhoon of the 2019 Pacific typhoon season, Bualoi originated from a disturbance east of the Marshall Islands on October 17, 2019, that quickly organized to a tropical depression on October 19, earning the designated name ''22W''. Favorable conditions strengthened the depression into a tropical storm. The Japan Meteorological Agency gave it the name ''Bualoi'' in response. Bualoi rapidly intensified and became a typhoon on October 20, before its rate of strengthening was stopped by a tropical upper tropospheric trough the following day. The rate was later recommenced through rapid intensification, making Bualoi reach its peak on October 22 as a Category 5-equivalent typhoon, with 10-minute sustained winds of and one-minute sustained winds of . Bualoi rapidly weakened on October 23 due to wind shear and continued before transitioning into an extra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately , from the westernmost island, Tobi (island), Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a Administrative divisions of the Federated States of Micronesia, state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of low, flat atoll, coral ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean for all branches of the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies. Their warnings are intended primarily for the protection of U.S. military ships and aircraft, as well as military installations jointly operated with other countries around the world. Its U.S. Navy components are aligned with the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command. History The origins of the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) can be traced back to June 1945, when the Fleet Weather Center/Typhoon Tracking Center was established on the island of Guam, after multiple typhoons, including Typhoon Cobra of December 1944 and Typhoon Connie in June 1945, had caused a significant loss of men and ships. At this time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saipan
Saipan () is the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands, an unincorporated Territories of the United States, territory of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Census Bureau, the population of Saipan was 43,385. Its people have been United States citizens since the 1980s. Saipan is one of the main homes of the Chamorro people, Chamorro, the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous people of the Mariana Islands. Saipan has been inhabited for over four thousand years. From the 17th century, the island experienced Spanish Empire#Pacific exploration and trade, Spanish occupation and rule until the Spanish–American War of 1898, when Saipan was briefly occupied by the United States, before being German–Spanish Treaty (1899), formally sold German New Guinea#Imperial German Pacific protectorates, to Germany. About 15 years of German rule were South Seas Mandate, followed by 30 years of Empire of Japan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Intensification
Rapid intensification (RI) is any process wherein a tropical cyclone strengthens very dramatically in a short period of time. Tropical cyclone forecasting agencies utilize differing thresholds for designating rapid intensification events, though the most widely used definition stipulates an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of at least in a 24-hour period. However, periods of rapid intensification often last longer than a day. About 20–30% of all tropical cyclones undergo rapid intensification, including a majority of tropical cyclones with peak wind speeds exceeding . Rapid intensification constitutes a major source of error for tropical cyclone forecasting, and its predictability is commonly cited as a key area for improvement. The specific physical mechanisms that underlie rapid intensification and the environmental conditions necessary to support rapid intensification are unclear due to the complex interactions between the environment surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclone, anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are close, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges or highs. It is a high-pressure area at the divergence of trade winds and the westerlies. Etymology A likely and documented explanation is that the term is derived from the "dead horse" ritual of seamen (see Beating a dead horse). In this practice, the seaman paraded a straw-stuffed effigy of a horse around the deck before throwing it overboard. Seamen were paid partly in advance before a long voyage, and they frequently spent their pay all at once, resulting in a period of time without income. This period was called the "dead horse" time, and it usually lasted a month or two. The seaman's ceremony was to celebrate having worked off the "dead horse" debt. As west-bound shipping from Europe usually reached the subtropics at about the time the "dead horse" was worke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Top
The cloud top (or the top of the cloud) is the highest altitude of the visible portion of a cloud. It is traditionally expressed either in metres above the Earth (or planetary) surface, or as the corresponding pressure level in hectopascal (hPa, equivalent to the traditional but now obsolete millibar). Measurement The cloud top is where the snow, rain and sleet come from. Cloud top height can be estimated from the ground by triangulation. However, this is often inconvenient as this is practically feasible only for isolated clouds in full view of (and some horizontal distance away from) the observers. Ground-based radars can be used to derive this cloud property. An alternative (but also more expensive) approach is to acquire airborne observations either visually or using specific instruments such as a lidar. This technique is very appropriate to characterize individual clouds (and specifically to control or evaluate the accuracy of other methods) but becomes unmanageable to repetit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of a tropical cyclone. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds of the cyclone occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is where the barometer reading is lowest. Structure A typical tropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainband
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands in tropical cyclones can be either stratiform or convective and are curved in shape. They consist of showers and thunderstorms, and along with the eyewall and the eye, they make up a tropical cyclone. The extent of rainbands around a tropical cyclone can help determine the cyclone's intensity. Rainbands spawned near and ahead of cold fronts can be squall lines which are able to produce tornadoes. Rainbands associated with cold fronts can be warped by mountain barriers perpendicular to the front's orientation due to the formation of a low-level barrier jet. Bands of thunderstorms can form with sea breeze and land breeze boundaries, if enough moisture is present. If sea breeze rainbands become active enough just ahead of a cold front, they can mask the location of the cold front itself. Banding within the comma head precipitation pattern of an extratrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Dense Overcast
The central dense overcast, or CDO, of a tropical cyclone or strong subtropical cyclone is the large central area of thunderstorms surrounding its circulation center, caused by the formation of its eyewall. It can be round, angular, oval, or irregular in shape. This feature shows up in tropical cyclones of tropical storm or hurricane strength. How far the center is embedded within the CDO, and the temperature difference between the cloud tops within the CDO and the cyclone's eye, can help determine a tropical cyclone's intensity with the Dvorak technique. Locating the center within the CDO can be a problem with strong tropical storms and minimal hurricanes as its location can be obscured by the CDO's high cloud canopy. This center location problem can be resolved through the use of microwave satellite imagery. After a cyclone strengthens to around hurricane intensity, an eye appears at the center of the CDO, defining its center of low pressure and its cyclonic wind field. Tropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. It occurs when warmer, less dense air rises, while cooler, denser air sinks. This process is driven by parcel-environment instability, meaning that a "parcel" of air is warmer and less dense than the surrounding environment at the same altitude. This difference in temperature and density (and sometimes humidity) causes the parcel to rise, a process known as buoyancy. This rising air, along with the compensating sinking air, leads to mixing, which in turn expands the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), the lowest part of the atmosphere directly influenced by the Earth's surface. This expansion contributes to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points (the temperature below which condensation occurs). Convection plays a crucial role in weather patterns, influencing cloud formation, wind, and the development of thunderstorms, which can be associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |