|
Turkish Independence War
, strength1 = May 1919: 35,000November 1920: 86,000Turkish General Staff, ''Türk İstiklal Harbinde Batı Cephesi'', Edition II, Part 2, Ankara 1999, p. 225August 1922: 271,000Celâl Erikan, Rıdvan Akın: ''Kurtuluş Savaşı tarihi'', Türkiye İş̧ Bankası Kültür Yayınları, 2008, p. 339. , strength2 = 60,000 30,000 20,000 7,000 , casualties1 = 13,000 killedKate Fleet, Suraiya Faroqhi, Reşat Kasaba: The Cambridge History of Turkey Volume 4'', Cambridge University Press, 2008, , p. 159.22,690 died of diseaseSabahattin Selek: ''Millî Mücadele – Cilt I (engl.: National Struggle – Edition I)'', Burçak yayınevi, 1963, p. 109. 5,362 died of wounds or other non-combat causes35,000 wounded7,000 prisonersAhmet Özdemir''Savaş esirlerinin Milli mücadeledeki yeri'', Ankara University, Türk İnkılap Tarihi Enstitüsü Atatürk Yolu Dergisi, Edition 2, Number 6, 1990, pp. 328–332Total: 83,052 casualties , casualties2 = 24,240 kill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1917–1923
The revolutions of 1917–1923 were a revolutionary wave that included political unrest and armed revolts around the world inspired by the success of the Russian Revolution and the disorder created by the aftermath of World War I. The uprisings were mainly Socialism, socialist or anti-Colonialism, colonial in nature. Most socialist revolts failed to create lasting socialist states. The revolutions had lasting effects in shaping the future European political landscape, with, for example, the German Revolution of 1918–1919, collapse of the German Empire and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary. World War I mobilized millions of troops, reshaped political powers and drove social turmoil. From the turmoil outright revolutions broke out, massive strikes occurred, and many soldiers mutinied. In Russian Empire, Russia, the Emperor of all the Russias, Tsar Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II abdicated during the February Revolution. The short-lived liberal Russian Provisional Government w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian–Azerbaijani War (1918–1920)
The Armenian–Azerbaijani war (1918–1920) was a conflict that took place in the South Caucasus in regions with a mixed Armenian- Azerbaijani population, broadly encompassing what are now modern-day Azerbaijan and Armenia. It began during the final months of World War I and ended with the establishment of Soviet rule. The conflict took place against the backdrop of the Russian Civil War and the partition of the Ottoman Empire. Mutual territorial claims, made by the newly formed Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and Republic of Armenia, led to their respective support for Azerbaijani and Armenian militias in the disputed territories. Armenia fought against Azerbaijani militias in the Erivan Governorate of the former Russian Empire, while Azerbaijan fought Armenian claims to the Karabakh region. The war was characterized by outbreaks of massacres and ethnic cleansing (such as the March Days, the September Days, the Shusha massacre, and more broadly, the Massacres of Azerbai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when Sultan Abd al-Hafid signed the Treaty of Fez, though the French military occupation of Morocco had begun with the invasion of Oujda and the bombardment of Casablanca in 1907. The French protectorate lasted until the dissolution of the Treaty of Fez on 2 March 1956, with the Franco-Moroccan Joint Declaration. Morocco's independence movement, described in Moroccan historiography as the Revolution of the King and the People, restored the exiled Mohammed V but it did not end the French presence in Morocco. France preserved its influence in the country, including a right to station French troops and to have a say in Morocco's foreign policy. French settlers also maintained their rights and property. While the agreements with France had provided for interdependent foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Algeria
French Algeria ( until 1839, then afterwards; unofficially ; ), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of History of Algeria, Algerian history when the country was a colony and later an integral part of France. French rule lasted until the end of the Algerian War which resulted in Algeria's Independence Day (Algeria), gaining independence on 5 July 1962. The French conquest of Algeria began in 1830 with the Invasion of Algiers (1830), invasion of Algiers which toppled the Regency of Algiers, though Algeria was not fully conquered and Pacification of Algeria, pacified until 1903. It is estimated that by 1875, approximately 825,000 indigenous Algerians were killed. Various scholars describe the French conquest as genocide. Algeria was ruled as a French colony, colony from 1830 to 1848, and then as multiple Departments of France#Departments of Algeria (Départements d'Algérie), departments, an integral part of France, with the implementing of the French Constitution of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Armenian Legion
The Armenian Legion () was a volunteer unit that was raised by the Allied Powers to serve in the Middle East Theatre during World War I. Trained and led by French army commanders, the ''Légion d'Orient'' (Eastern Legion), as the unit was originally known, was created in 1916, its ranks chiefly drawn from Levantine and Armenian exiles and refugees from the Ottoman Empire. In 1919, it was renamed the ''Légion Arménienne'' (Armenian Legion). Background The establishment of an Armenian fighting force was first proposed by Boghos Nubar, the head of the Armenian National Delegation in Paris, during the landing of Allied forces to Alexandretta (İskenderun) in 1914, to British military planners. The British government rejected the plan, on the basis that such a plan would lead to the massacres of local Armenians. However, appeals by the Armenian National Defense Committee continued into 1915. French authorities also rejected the plan at the end of 1915. In 1916, British and Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French West Africa
French West Africa (, ) was a federation of eight French colonial empires#Second French colonial empire, French colonial territories in West Africa: Colonial Mauritania, Mauritania, French Senegal, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), French Ivory Coast, Ivory Coast, French Upper Volta, Upper Volta (now Burkina Faso), French Dahomey, Dahomey (now Benin) and Colony of Niger, Niger. The federation existed from 1895 until 1958. Its capital was Saint-Louis, Senegal, Saint-Louis in Senegal until 1902, and then Dakar until the federation's collapse in 1960. With an area of 4,689,000 km2, French West Africa was eight times the size of Metropolitan France. French Equatorial Africa had an additional area of 2,500,000 km2. History Until after World War II, almost none of the Africans living in the colonies of France were citizens of France. Rather, they were "French subjects," lacking rights before the law, property ownership rights, rights to travel, dissen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Ankara (1921)
The Ankara Agreement (1921) (or the Accord of Ankara; Franklin-Bouillon Agreement; Franco-Turkish Agreement of Ankara, Turkish: ''Ankara Antlaşması'', French: Traité d'Ankara) was signed on 20 October 1921"Ankara, Treaty of" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 423. at Ankara (also known as Angora) between France and the Grand National Assembly of Turkey, ending the Franco-Turkish War. The signatories were French diplomat Henry Franklin-Bouillon and Turkish foreign minister Yusuf Kemal Bey. Based on the terms of the agreement, the French acknowledged the end of the Franco-Turkish War and ceded large areas to Turkey. However other French units in Turkey were not affected, in return for economic concessions from Turkey. In return, the Turkish government acknowledged French imperial sovereignty over the French Mandate of Syria. The treaty was registered in ''League of Nations Treaty Series'' on 30 Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
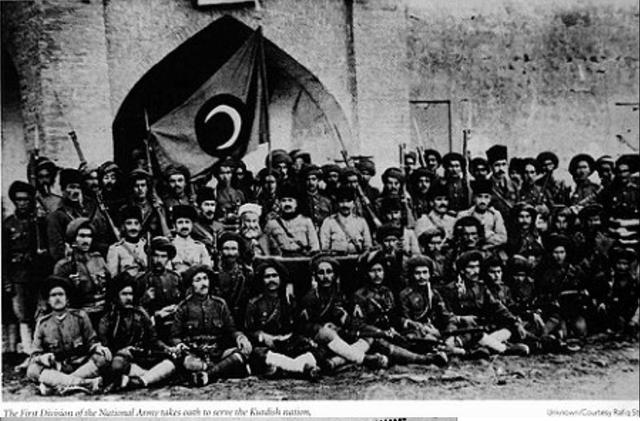
Kurdish State (1918–1919)
The Kurdish state was an autonomous government in Southern Kurdistan that existed from October 1918 to June 1919. Though it was initially subordinate to Britain, it was eventually dissolved following an anti-British rebellion. Name "Kurdish state" is an exonym that was used by British officials in London and the Middle East to describe this polity during its existence. Saad Eskander argues that this term is incorrect, as it was not fully independent. History Establishment With the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in October 1918, Mahmud Barzanji sought to break away from the Ottomans and create an autonomous southern Kurdistan under British supervision. He was elected as the head of government by a council of Kurdish notables in the Sulaimaniya region, and as soon as the British captured Kirkuk (25 October 1918) he captured Ottoman troops present in his district and declared the end of Ottoman rule, pledging allegiance to Britain. Other Kurdish regions followed suit, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Kurdistan
The Kingdom of Kurdistan was a short-lived and self-proclaimed Kurdish state declared in the city of Sulaymaniyah following the collapse of the Ottoman Empire. It lasted from September 1921 until July 1925. Officially, the territory involved was under the jurisdiction of the British Mandate of Mesopotamia. Sheikh Mahmud revolts During the collapse of the Ottoman Empire, the Kurds attempted to establish an independent state. Mahmud Barzanji, the Shaykh of the Qadiriyyah order of Sufis, the most influential personality in Southern Kurdistan, was appointed governor of the former ''sanjak'' of Duhok, but rallied against the British and declared an independent Kurdistan in May 1919. He was defeated in June. On 10 October 1921, a statement was issued in Suleymanyah, the capital of Kurdistan, to establish a Kurdish government. Sheikh Mahmud Barzanji declared himself as the King of the Kingdom of Kurdistan. After the Treaty of Sèvres, which settled some territories, Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuva-yi Seyyare
Kuvâ-yi Seyyâre (), also known as the Green Army Society ( Turkish: Yeşil Ordu Cemiyeti) or the People's Branch ( Turkish: ''Halk Zümresi'') was a force of Circassian and Abkhazian volunteers led by Çerkes Ethem against the Allied invasion forces during the Turkish War of Independence. The group saw themselves as a force to fight against "those who caused disturbance to the greater good of Anatolia". The forces put down several rebellions and played a big role in significantly slowing down the Greek army during the Greco-Turkish War (1919-1922). In time, as Ethem's Islamic socialist views clashed with the Turkish nationalism of Mustafa Kemal's Turkish National movement, he eventually cut ties with them, and was declared a traitor due to clashes with İsmet İnönü. History Kuvâ-yi Seyyâre, founded by Ethem Dipsheu, was the only semi-organized military force in Anatolia during 1919–1920 period between the Armistice of Mudros and the Treaty of Sèvres. After the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |