|
Tubeworm
A tubeworm is any worm-like sessile invertebrate that anchors its tail to an underwater surface and secretes around its body a mineral tube, into which it can withdraw its entire body. Tubeworms are found among the following taxa: * Annelida, the phylum containing segmented worms ** Polychaetea, the class containing bristle worms *** Canalipalpata, the order containing bristle-footed annelids or fan-head worms **** Siboglinidae, the family of beard worms ***** ''Riftia pachyptila'', a species known as giant tube worms ***** Lamellibrachia, a genus **** Serpulidae, a family **** Sabellidae, the family containing feather duster worms * Phoronid Phoronids (scientific name Phoronida, sometimes called horseshoe worms) are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore (a "crown" of tentacles), and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies. ...a, the phylum containing horseshoe worms * Microconchida, an order of extinct tubeworms * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Tube Worm
''Riftia pachyptila'', commonly known as the giant tube worm and less commonly known as the Giant beardworm, is a marine invertebrate in the phylum Annelida (formerly grouped in phylum Pogonophora and Vestimentifera) related to tube worms commonly found in the intertidal and pelagic zones. ''R. pachyptila'' lives on the floor of the Pacific Ocean near hydrothermal vents, the vents provide a natural ambient temperature in their environment ranging from 2 to 30 °C, at the same time it can tolerate extremely high hydrogen sulfide levels. These worms can reach a length of , and their tubular bodies have a diameter of . Its common name "giant tube worm" is, however, also applied to the largest living species of shipworm, '' Kuphus polythalamius'', which despite the name "worm", is a bivalve mollusc rather than an annelid. Discovery ''R. pachyptila'' was discovered in 1977 on an expedition of the American bathyscaphe DSV ''Alvin'' to the Galápagos Rift led by geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
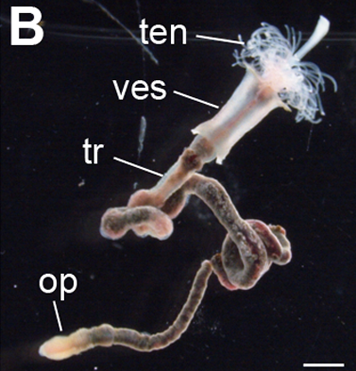
Siboglinidae
Siboglinidae is a family of polychaete annelid worms whose members made up the former phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of about 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buried in sediments (Pogonophora) or in tubes attached to hard substratum (Vestimentifera) at ocean depths ranging from . They can also be found in association with hydrothermal vents, methane seeps, sunken plant material, and whale carcasses. The first specimen was dredged from the waters of what is now Indonesia in 1900. These specimens were given to French zoologist Maurice Caullery, who studied them for nearly 50 years. Anatomy Most siboglinids are less than in diameter, but in length. They inhabit tubular structures composed of chitin and fixed to rocks or substrate. The tubes are often clustered together in large colonies. Their bodies are divided into four regions. The anterior end is called the cephalic lobe, which bears from one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microconchida
The order Microconchida is a group of small, spirally-coiled, encrusting fossil "worm" tubes from the class Tentaculita found from the Upper Ordovician to the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) around the world. They have lamellar calcitic shells, usually with pseudopunctae or punctae and a bulb-like origin. Many were long misidentified as the polychaete annelid '' Spirorbis'' until studies of shell microstructure and formation showed significant differences. All pre-Cretaceous "''Spirorbis''" fossils are now known to be microconchids. Their classification at the phylum level is still debated. Most likely they are some form of lophophorate, a group which includes phoronids, bryozoans and brachiopods. Microconchids may be closely related to the other encrusting tentaculitoid tubeworms, such as ''Anticalyptraea'', trypanoporids and cornulitids. References * Wilson, M.A., Yancey, T.E. and Vinn, O. 2011. "A new microconchid tubeworm from the Lower Permian (Artinskian) of central Tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the sandworm or clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepest known spot in the Earth's oceans. Only 168 species (less than 2% of all polychaetes) are known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canalipalpata
Canalipalpata, also known as bristle-footed annelids or fan-head worms, is an order of polychaete worms, with 31 families in it including the suborder Sabellida (families Serpulidae (tubeworms) and Sabellidae (fanworms and feather duster worms) and the Alvinellidae, a family of deep-sea worms associated with hydrothermal vents. The Canalipalpata have no teeth or jaws. Most are filter feeders. They have grooved palpi, which are covered in cilia. These cilia are used to transport food particles to the mouth. However, the cilia and grooves have been lost in the Siboglinidae family. Fossil record The earliest known member of the Canalipalpata is '' Terebellites franklini'', which was found in the Clouds Rapids Formation of Newfoundland, and dates from the mid Cambrian (St David's series). Use in aquaria Many species of Canalipalpata are visually attractive. Fanworms and Christmas tree worms (a type of serpulid) are recommended as species for beginners to keep in a marine aqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, '' Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for their nutrition. The symbionts, gammaproteobacteria, require sulfide and inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide). The tube worms extract dissolved oxygen and hydrogen sulfide from the sea water with the crown of plumes. Species living near seeps can also obtain sulfide through their "roots", posterior extensions of their body and tube. Several sorts of hemoglobin are present in the blood and coelomic fluid to bind to the different components and transport them to the symbionts. ''L. luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpulidae
The Serpulidae are a family of sessile, tube-building annelid worms in the class Polychaeta. The members of this family differ from other sabellid tube worms in that they have a specialized operculum that blocks the entrance of their tubes when they withdraw into the tubes. In addition, serpulids secrete tubes of calcium carbonate. Serpulids are the most important biomineralizers among annelids. About 300 species in the family Serpulidae are known, all but one of which live in saline waters. The earliest serpulids are known from the Permian (Wordian to late Permian). The blood of most species of serpulid and sabellid worms contains the oxygen-binding pigment chlorocruorin. This is used to transport oxygen to the tissues. It has an affinity for carbon monoxide which is 570 times as strong as that of the haemoglobin found in human blood. Empty serpulid shells can sometimes be confused with the shells of a family of marine gastropod mollusks, the Vermetidae or worm snails. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabellidae
Sabellidae, or feather duster worms, are a family of marine polychaete tube worms characterized by protruding feathery branchiae. Sabellids build tubes out of a tough, parchment-like exudate, strengthened with sand and bits of shell. Unlike the other sabellids, the genus ''Glomerula'' secretes a tube of calcium carbonate instead. Sabellidae can be found in subtidal habitats around the world. Their oldest fossils are known from the Early Jurassic. Characteristics Feather-duster worms have a crown of feeding appendages or radioles in two fan-shaped clusters projecting from their tubes when under water. Each radiole has paired side branches making a two-edged comb for filter feeding. Most species have a narrow collar below the head. The body segments are smooth and lack parapodia. The usually eight thoracic segments bear capillaries dorsally and hooked chaetae (bristles) ventrally. The abdominal segments are similar, but with the position of the capillaries and chaetae reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabellida
Sabellida is an order of annelid worms in the class Polychaeta Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are .... They are filter feeders with no buccal organ. The prostomium is fused with the peristomium and bears a ring of feathery feeding tentacles. They live in parchment-like tubes made of particles from their environment such as sand and shell fragments cemented together with mucus. Members of the suborder include the feather duster worms (Sabellidae) and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuphus Polythalamia
''Kuphus polythalamius'' is a species of shipworm, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Teredinidae. Description The tube of ''Kuphus polythalamius'' is known as a crypt and is a calcareous secretion designed to enable the animal to live in its preferred habitat, the mud of mangrove swamps. A typical specimen measures in length and is shaped like a truncated elephant's tusk. The wider, anterior end is closed, has a rounded tip, and is about in diameter. From there the tube tapers to an open, posterior end about in diameter, with a central septum. Siphons project through this end for feeding and respiration. They can be withdrawn inside the tube and the end can be sealed with a set of specialised plates or "pallets". The two small valves of the mollusc are inside the tube along with the mantle, gut and other soft organs. In the intact but otherwise empty tube found on the strandline, they can be seen by X-ray photography. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(22754473376).jpg)
.jpg)
