|
Tsakonians
Tsakonia (, ''Tsakoniá''; Tsakonian: ) or the Tsakonian region () refers to the small area in the eastern Peloponnese where the Tsakonian language is spoken, in the area surrounding 13 towns, villages and hamlets located around Pera Melana in Arcadia. It is not a formally defined political entity of the modern Greek state. Extent In his ''Brief Grammar of the Tsakonian Dialect'' published in 1951, Prof. Thanasis Costakis defines Tsakonia as the area from the town of Agios Andreas in Kynouria south to Leonidio and Tyros and inland as far as Kastanitsa and Sitaina, but asserts that in former times the Tsakonian-speaking area extended as far as Cape Malea in eastern Laconia. The principal town in Tsakonia at this time was Prastos, which benefited from a special trading privilege granted by the authorities in Constantinople. Prastos was burned by Ibrahim Pasha in the Greek War of Independence and was abandoned, with many of its residents fleeing to the area around Leonidio an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniot Dialect
The Maniots () or Maniates () are an ethnic Greek subgroup that traditionally inhabit the Mani Peninsula; located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes, and the peninsula as ''Maina''. The Maniots claim to be the descendants of the ancient Spartans and they have often been described as such. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of the Ottoman Empire. Names The surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
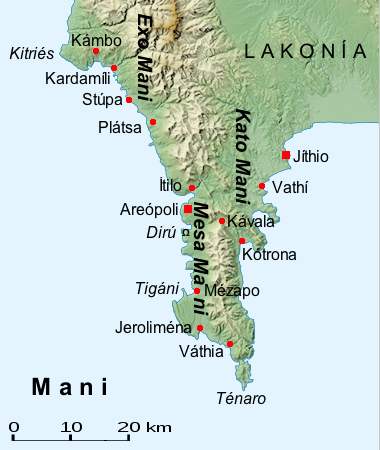
Maniots
The Maniots () or Maniates () are an ethnic Greeks, Greek subgroup that traditionally inhabit the Mani Peninsula; located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes, and the peninsula as ''Maina''. The Maniots claim to be the descendants of the ancient Sparta, Spartans and they have often been described as such. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce Feud#Blood feuds/vendetta, blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsakonian Language
Tsakonian or Tsaconian (also Tzakonian or Tsakonic, and Tsakonian: , ) is a highly divergent modern variety of Greek, spoken in the Tsakonian region of the Peloponnese, Greece Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th .... Unlike all other extant varieties of Greek, Tsakonian derives from Doric Greek rather than from the Attic Greek, Attic–Ionic Greek, Ionic branch. Although it is conventionally treated as a dialect of Greek, some compendia treat it as a separate language. Tsakonian is Critically endangered language, critically endangered, with only a few hundred or a few thousand, mostly elderly, fluent speakers left. Although Tsakonian and standard Modern Greek are related, they are not mutually intelligible. Etymology The term Tsakonas or Tzakonas first emerges in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvanites
Arvanites (; Arvanitika: , or , ; Greek: , ) are a population group in Greece of Albanian origin. They are bilingual, traditionally speaking Arvanitika, an Albanian language variety, along with Greek. Their ancestors were first recorded as settlers who came to what is today southern Greece in the late 13th and early 14th century. They were the dominant population element in parts of the Peloponnese, Attica and Boeotia until the 19th century.Trudgill (2000: 255). They call themselves Arvanites (in Greek) and Arbëror (in their language). Arvanites today self-identify as Greeks as a result of a process of cultural assimilation,GHM (1995). and do not consider themselves Albanian.Trudgill/Tzavaras (1977). Arvanitika is in a state of attrition due to language shift towards Greek and large-scale internal migration to the cities and subsequent intermingling of the population during the 20th century. Names The name Arvanites and its equivalents are today used both in Greek (, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kynouria
Cynuria ( – ''Kynouria'' or – ''Kynouriake'') is an ancient district on the eastern coast of the Peloponnese, between the Argolis and Laconia, so called from the Cynurians, one of the most ancient tribes in the peninsula. It was believed to have taken its name from the mythical Cynurus. Location and history Herodotus regarded the Cynurians as autochthones, but at the same time called them Ionians. There can be little doubt, however, that they were Pelasgians; but in consequence of their maritime position, they were regarded as a different race from the Arcadian Pelasgians, and came to be looked upon as Ionians, which was the case with the Pelasgians dwelling upon the coast of the Gulf of Corinth, in the district afterwards called Achaia. They were a semi-barbarous and predatory tribe, dwelling chiefly in the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon; but their exact boundaries cannot be defined, as they were only a tribe, and never formed a political body. At a later time they were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Greek Census
The 2011 Population and Housing Census (), branded as (), was a population census in Greece conducted by the Hellenic Statistical Authority on behalf of the Greek state between 10 and 24 May 2011. It was conducted as part of the 2011 European Union census. Its purpose was to enumerate the number of people in the country as well as survey the social characteristics of the population. The census was available in 8 languages other than Greek language, Greek: English language, English, Albanian language, Albanian, French language, French, Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, Russian language, Russian, Arabic, Urdu and Dari (Persian), Dari. The final results of the census were announced on 28 December 2012, with a minor correction in 2014. According to final results, the total resident population of Greece was 10,815,197 on census day. There was a margin of error of 2.84%. Scope and format The 2011 census was carried out to ascertain the number of people in Greece at the time of the census ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia (, , ) is a historical and Administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparti (municipality), Sparta. The word ''Laconic phrase, laconic''—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks. Geography Laconia is bordered by Messenia to the west and Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia to the north and is surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea to the east and by the Laconian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It encompasses Cape Malea and Cape Tainaron and a large part of the Mani Peninsula. The Mani Peninsula is in the west region of Laconia. The islands of Kythira and Antikythera lie to the south, but they administratively belong to the Attica (region), Attica regional unit of Islands (regional unit), islands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prastos
Prastos (, Tsakonian: Πραστέ) is a settlement in Arcadia, Greece. Formerly, Prastos was the premier town of the Tsakonian region, but declined in importance after its devastation by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt during the Greek War of Independence and a general economic migration to urban areas that occurred in the following decades. It is considered a traditional settlement. History During the Ottoman period, Prastos was the leading city of Tsakonia, and one of the richest in the Peloponnese. The inhabitants had special trading rights granted by the Sublime Porte, which contributed to the town's economic success. It was the seat of a bishopric, that of "Rheoi and Prastos." During the Greek War of Independence, the town was sacked by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt and its olive groves burned, making the settlement unsuitable for habitation for decades hence. Much of the surviving population fled to Leonidio and the Argolid and could not be persuaded to return to the relatively less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim Pasha Of Egypt
Ibrahim Pasha ( ''Ibrāhīm Bāshā''; 1789 – 10 November 1848) was an Egyptian general and politician; he was the commander of both the Egyptian and Ottoman armies and the eldest son of Muhammad Ali, the Ottoman Wāli and unrecognized Khedive of Egypt and Sudan. He was the second ruler of Egypt from the Muhammad Ali Dynasty and ruled from 20 July 1848 to 10 November 1848. Ibrahim served as a general in the Egyptian army that his father established during his reign, taking his first command of Egyptian forces when he was merely a teenager. In the final year of his life, he was appointed Regent for his still-living father and became the effective ruler of Egypt and Sudan, owing to the latter's ill health. His rule also extended over the other dominions that his father had brought under Egyptian rule, namely Syria, Hejaz, Morea, Thasos, and Crete. Ibrahim pre-deceased his father, dying 10 November 1848, only four months after rising to power. He was succeeded as Regent by his n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argolic Gulf
The Argolic Gulf (), also known as the Gulf of Argolis, is a gulf of the Aegean Sea off the east coast of the Peloponnese, Greece. It is about 50 km long and 30 km wide. Its main port is Nafplio, at its northwestern end. At the entrance to the gulf is the island Spetses. This gulf and its islands are sometimes combined with the Saronic Gulf and Saronic Islands, with the result called the Argo-Saronic Gulf and the Argo-Saronic Islands. It is surrounded by two regional units: Arcadia to the southwest and Argolis to the north and east. The river Inachos drains into the Argolic Gulf near Nea Kios. The main islands in the gulf are Psili, Plateia and Bourtzi, a small island with a Venetian fortress that protects the port of Nafplio. The surrounding mountains protect it from the strong summer Meltemi wind. The main towns that lie around the gulf are, from southwest to east: * Tyros * Paralio Astros * Myloi * Nea Kios *Nafplio * Tolo or Tolon, on Tolo Bay * Porto Chel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek War Of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted by the British Empire, Bourbon Restoration in France, Kingdom of France, and the Russian Empire, while the Ottomans were aided by their vassals, especially by the Eyalet of Egypt. The war led to the formation of modern Greece, which would be expanded to its modern size in later years. The revolution is celebrated by Greek diaspora, Greeks around the world as Greek Independence Day, independence day on 25 March. All Greek territory, except the Ionian Islands, the Mani Peninsula, and mountainous regions in Epirus, came under Ottoman rule in the 15th century. During the following centuries, there were Ottoman Greece#Uprisings before 1821, Greek uprisings against Ottoman rule. Most uprisings began in the independent Greek realm of the Mani Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |