|
Tryzub
The coat of arms of Ukraine is a blue shield with a golden trident. It is colloquially known as the ''tryzub'' (, , ). The small coat of arms was officially adopted on 19 February 1992, while constitutional provisions exist for establishing the great coat of arms, which is not yet officially adopted as of March 2024. The small coat of arms was designed by Andriy Grechylo, Oleksii Kokhan, and Ivan Turetskyi. It appears on the presidential standard. Blue-coloured tridents are considered to be an irregular representation by the Ukrainian Heraldry Society. The greater coat of arms which has not been adopted consists of the small coat of arms and the coat of arms of the Zaporizhian Host (Constitution of Ukraine, Article 20). The trident was not thought of as a national symbol until 1917, when one of the most prominent Ukrainian historians, Mykhailo Hrushevskyi, proposed to adopt it as a national symbol (alongside other variants, including an arbalest, a bow or a cossack carryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Symbols Of Ukraine
The national symbols of Ukraine include a variety of official and unofficial National symbol, symbols and other items that are used in Ukraine to represent what is unique about the nation, reflecting different aspects of its cultural life and history. Symbols References {{Europe topic, National symbols of National symbols of Ukraine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamga
A tamga or tamgha (from ) was an abstract seal or brand used by Eurasian nomads initially as a livestock branding, and by cultures influenced by them. The tamga was used as a livestock branding for a particular tribe, clan or family. They were common among the Eurasian nomads throughout Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages. As clan and family identifiers, the collection and systematic comparison of tamgas is regarded to provide insights into relations between families, individuals and ethnic groups in the steppe territory. Similar tamga-like symbols were sometimes adopted by sedentary peoples adjacent to the Pontic–Caspian steppe both in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Branding of livestock was a common practice across most sedentary populations, as far back as the ancient Egyptians. It has been speculated that Turkic tamgas represent one of the sources of the Old Turkic script of the 6th–10th centuries, but since the mid-20th century, this hypothesis is widely reject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rurikids
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' and its principalities following its disintegration. The ''Romanovichi'' ruled the southwestern territories, which were unified by Roman the Great and his son Daniel, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV as the king of Ruthenia. Galicia–Volhynia was eventually annexed by Poland and Lithuania. The northern and northeastern territories were unified by the ''Daniilovichi'' of Moscow; by the 15th century, Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde and assumed the title of sovereign of all Russia. Ivan IV was crowned as the tsar of all Russia, where the Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were eventually succeeded by the House of Romanov. As a rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
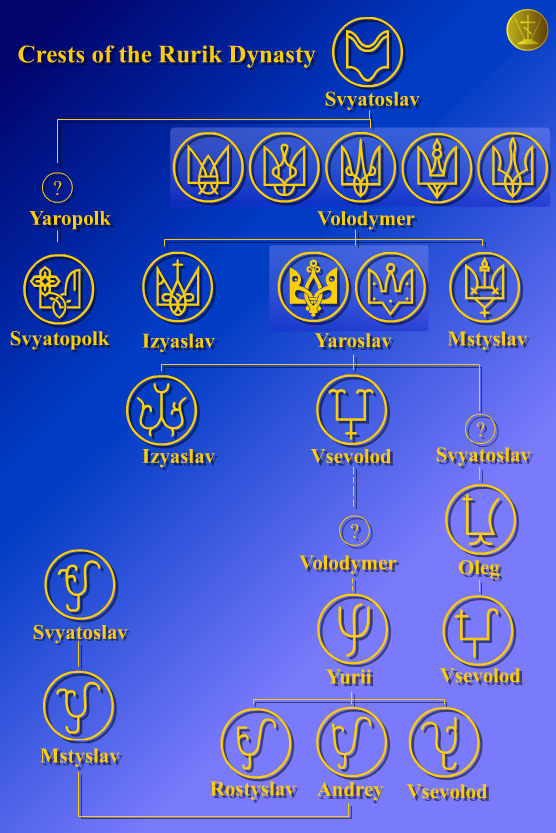
Symbols Of The Rurikids
Throughout the early Middle Ages, the Rurikid knyazes of the Kievan Rus' used unique symbols to denote property rights over various items. They are depicted on Punch (tool), punches, Seal (emblem), seals, and coins of the Rurikids. In contrast to Western European heraldry, where coat of arms, coats of arms belonged to entire families, or were inherited without changes by firstborn sons, Rurikid symbols were personal, with every knyaz devising an emblem of their own for themselves. Images of knyazes’ symbols As a rule, on the coins of Kievan knyazes, one encounters figures in the form of bidents and tridents. The same symbols could look different depending on the item on which they were depicted. Thus, the emblems of the knyazes on seals are depicted schematically, in a maximally simplified form, whilst on coins the same symbols have a large number of additional ornamental elements. The heraldic symbols of Rus’ knyazes are known to us not only in the form of depictions on co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The President Of Ukraine
The flag (standard) of the president of Ukraine () is the official flag of the president of Ukraine. The presidential flag of Ukraine was confirmed by the decree of the president of Ukraine as of November 29, 1999 and used during their inaugural ceremony, during which the chairman of the Constitutional Court of Ukraine presents it to the president. On delivering his inaugural address, the president takes a special seat at the session hall of the Verkhovna Rada next to which the president's colour is placed. Design The president's colour represents a blue square cloth bearing a golden trident A trident (), () is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm. As compared to an ordinary spear, the three tines increase the chance that a fish will be struck and decrease the chance that a fish will b ... ('' tryzub''), the coat of arms of Ukraine, in the center: the Sign of Prince Volodymyr the Great's State, edged with gold vegetative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the north; Poland and Slovakia to the west; Hungary, Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and List of cities in Ukraine, largest city, followed by Kharkiv, Odesa, and Dnipro. Ukraine's official language is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. Humans have inhabited Ukraine since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, it was the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion and later became a key centre of East Slavs, East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful realm in Europe in the 10th and 11th centuries, but gradually disintegrated into rival regional powers before being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
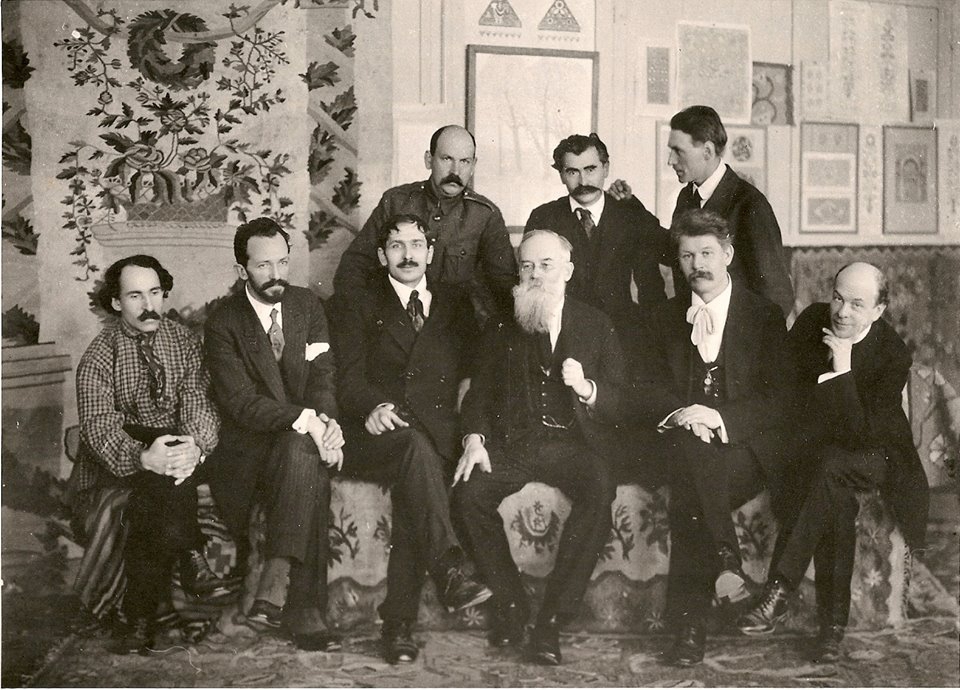
Central Rada
The Central Rada of Ukraine, also called the Central Council (), was the All-Ukrainian council that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputies as well as few members of political, public, cultural and professional organizations of the Ukrainian People's Republic.Arkadii Zhukovsky. Central Rada'. Encyclopedia of Ukraine. After the All-Ukrainian National Congress (19–21 April 1917), the Council became the revolutionary parliament in the interbellum lasting until the Ukrainian-Soviet War. Unlike with many other councils in the Russian Republic, Bolshevization of the Rada failed completely, prompting the Ukrainian Bolsheviks to form a rival government in Kharkov. Overview From its beginning the council directed the Ukrainian national movement and with its four Universals led the country from autonomy to full sovereignty. During its brief existence from 1917 to 1918, the Central Rada, which was headed by the Ukrainian historian and ethnologist Mykhailo Hrushevs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
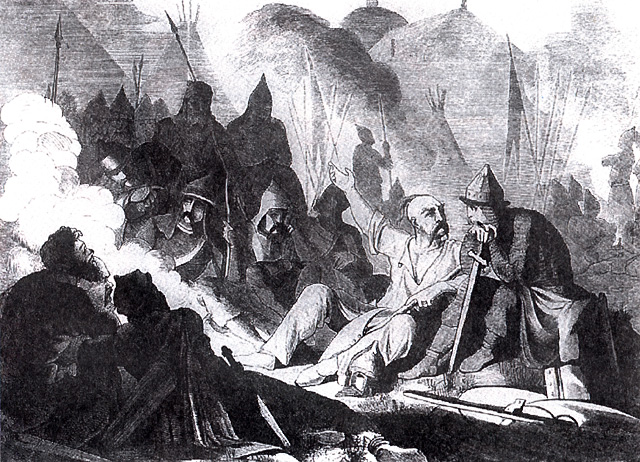
Sviatoslav I
Sviatoslav or Svyatoslav I Igorevich (; Old Norse: ''Sveinald''; – 972) was Prince of Kiev from 945 until his death in 972. He is known for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers in Eastern Europe, Khazars, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian Empire. He conquered numerous East Slavs, East Slavic tribes, defeated the Alans and attacked the Volga Bulgaria, Volga Bulgars, and at times was allied with the Pechenegs and Hungarian people, Magyars (Hungarians). Following the death of his father Igor of Kiev, Igor in 945, Sviatoslav's mother Olga of Kiev, Olga reigned as regent in Kiev until 962. His decade-long reign over the Kievan Rus' was marked by rapid expansion into the Volga, Volga River valley, the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe, and the Balkans, leading him to carve out for himself the largest state in Europe. In 969, he moved his seat to Pereyaslavets on the Danube. In 970, he appointed his sons Yaropolk I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omeljan Pritsak
Omeljan Yosypovych Pritsak (; 7 April 1919 – 29 May 2006) was the first Mykhailo Hrushevsky Professor of History of Ukraine, Ukrainian History at Harvard University and the founder and first director (1973–1989) of the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. Career From 1921 to 1936 he lived in Ternopil, where he graduated the state Polish gymnasium. Pritsak began his academic career at the University of Lviv in History of Poland (1918–1939), interwar Poland where he studied Middle Eastern languages under local orientalists and became associated with the Shevchenko Scientific Society and attended its seminar on Ukrainian history led by Ivan Krypiakevych. After the Soviet Union, Soviet annexation of Galicia, he moved to Kyiv where he briefly studied with the premier Ukraine, Ukrainian orientalist, Ahatanhel Krymsky. During World War II, Pritsak was taken to the west as a Ostarbeiter. Following the war, he studied at the universities in Berlin and University of Göttingen, Gö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,. * was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavs, East Slavic, Norsemen, Norse, and Finnic peoples, Finnic, it was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, founded by the Varangians, Varangian prince Rurik.Kievan Rus , Encyclopædia Britannica Online. The name was coined by Russian historians in the 19th century to describe the period when Kiev was preeminent. At its greatest extent in the mid-11th century, Kievan Rus' stretched from the White Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south and from the River source, headwaters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasyl Krychevsky
Vasyl Hryhorovych Krychevsky (; January 12, 1873 – November 15, 1952) was a Ukrainian painter, architect, art scholar, graphic artist, film art consultant, pedagogue and master of applied art and decorative art. He is the designer of the 1918 Ukrainian coat of arms, state seals, banknotes. He was the brother of Ukrainian painter Fedir Krychevsky. Biography Vasyl Krychevsky was born in the village of Vorozhba, near Lebedyn, to a family of eight children where he was the eldest. His father Hryhoriy Yakymovych Krychevsky was a county state doctor of Jewish descent who converted to Orthodox Christianity and married a Ukrainian woman, Praskovia Hryhorivna. Krychevsky had little formal education, but a deep interest in Ukrainian folklore and art history. During the First World War, he was one of the founders and rectors of the Ukrainian State Academy of Arts. In the 1920s he taught at the Kyiv Institute of Plastic Arts, the Kyiv Architectural Institute. Among the students ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falco RusticolusAWP366AAA
Falco may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Falco (musician) (1957–1998), an Austrian singer and musician * ''Falco'' (book series), historical novels by Lindsey Davies ** Marcus Didius Falco, protagonist of the book series * ''Falcó'' (novel), a 2016 novel by Arturo Pérez-Reverte * "Falco" (song), by Hitomi Shimatani * ''Falco'' (TV series) * Falco (Groove-On Fight character), a videogame character * Falco Lombardi, a videogame character from the ''Star Fox'' series * Falco Grice, a character from the anime series ''Attack on Titan'' Aviation * Fiat CR.42 Falco, Italian World War II biplane fighter aircraft * Reggiane Re.2000 Falco I, Italian World War II fighter aircraft * Selex ES Falco, an Italian tactical unmanned aerial vehicle * Sequoia Falco, an aerobatic aircraft People * Falco (surname), a list of people with the surname Falco or Falcó * Quintus Pompeius Falco (c. 70 – after 140), ancient Roman senator, general and governor of Britannia * Falco of Maastric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |