Rurikids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the
Varangian
The Varangians ( ; ; ; , or )Varangian
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
Rurik
Rurik (also spelled Rorik, Riurik or Ryurik; ; ; died 879) was a Varangians, Varangian chieftain of the Rus' people, Rus' who, according to tradition, was invited to reign in Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod in the year 862. The ''Primary Chronicle' ...
, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
H ...
of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
and its principalities following its disintegration.
The ''Romanovichi'' ruled the southwestern territories, which were unified by Roman the Great
Roman Mstislavich ( – 19 June 1205), also known as Roman the Great, was Prince of Novgorod (1168–1170), Volhynia (1170–1189; 1189–1205), and Galicia (1189; 1198/99–1205). He founded the ''Romanovichi'' branch of Rurikids, which wou ...
and his son Daniel, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV (; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universities of Parma and Bolo ...
as the king of Ruthenia
King of Ruthenia, King of Rus', King of Galicia and Lodomeria, Lord and Heir of Ruthenian Lands (Latin: ''Rex Rusiae'', ''Rex Ruthenorum'', ''Rex Galiciae et Lodomeriae'', ''Terrae Russiae Dominus et Heres''; ) was a title of Kingdom of Galicia� ...
. Galicia–Volhynia was eventually annexed by Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
. The northern and northeastern territories were unified by the ''Daniilovichi'' of Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
; by the 15th century, Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
and assumed the title of sovereign of all Russia. Ivan IV was crowned as the tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
of all Russia, where the Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were eventually succeeded by the House of Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transliterated as Romanoff; , ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after Anastasia Romanovna married Ivan the Terrible, the first crowned tsar of all Russi ...
.
As a ruling house, the Rurikids held their own for a total of 21 generations in male-line succession, from Rurik () to Feodor I of Russia
Feodor I Ioannovich () or Fyodor I Ivanovich (; 31 May 1557 – 17 January 1598), nicknamed the Blessed (), was Tsar of all Russia from 1584 until his death in 1598.
Feodor's mother died when he was three, and he grew up in the shadow of his ...
(), a period of more than 700 years. Numerous princely families have claimed to trace their lineage to Rurik. They are one of Europe's oldest royal houses, with numerous existing cadet branch
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets (realm, titles, fiefs, property and incom ...
es.
Origins
Genealogical issues
The origins of the Rurikids are unclear, as its namesakeRurik
Rurik (also spelled Rorik, Riurik or Ryurik; ; ; died 879) was a Varangians, Varangian chieftain of the Rus' people, Rus' who, according to tradition, was invited to reign in Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod in the year 862. The ''Primary Chronicle' ...
, a Varangian
The Varangians ( ; ; ; , or )Varangian
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
The Viking World
'', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rus'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
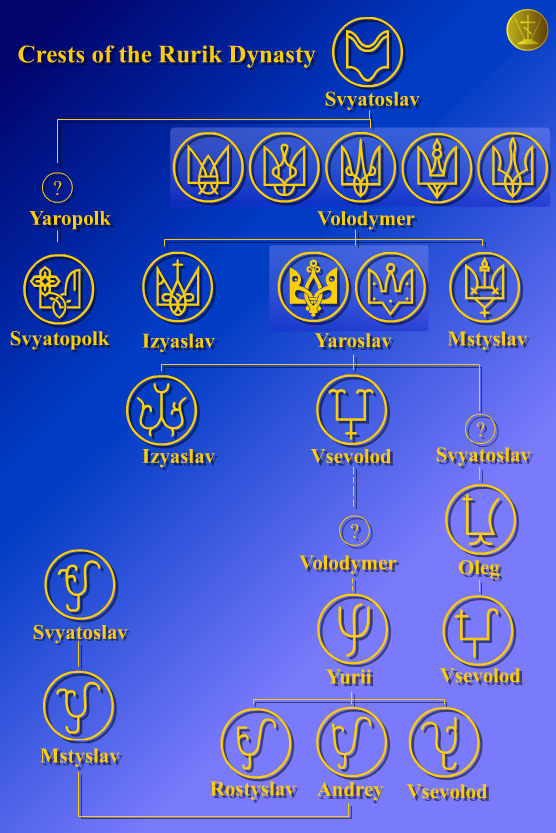 Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent
Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent
File:COA Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov chivalric.svg, Arms of the House of
," Online Etymology Dictionary were
Calling of the Varangians
The calling of the Varangians, calling of the (Varangian) princes or invitation to the Varangians (; ) is a legend about the origins of the Rus' people, the Rurik dynasty and the Kievan Rus' state, recorded in many divergent versions in various ma ...
", is considered to be a legendary, mythical and perhaps even entirely fictional character by modern scholars. Nicholas V. Riasanovsky (1947) stated: '...no Kievan sources anterior to the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Primary Chronicle'', shortened from the common ''Russian Primary Chronicle'' (, commonly transcribed ''Povest' vremennykh let'' (PVL), ), is a Rus' chronicle, chronicle of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110. It is believed to have been or ...
'' (early twelfth century), knew of Riurik. In tracing the ancestry of Kievan princes they usually stopped with Igor.' As an example, Hilarion of Kiev
Hilarion or Ilarion was the first non-Greek Metropolitan of Kiev and all Rus'. He held the metropolitan post before or during the ongoing 11th century East–West Schism. While there is not much verifiable information regarding Hilarion's biograp ...
's '' Sermon on Law and Grace'' (1050s), praising Volodimer I of Kiev, only goes back to his father Sviatoslav I
Sviatoslav or Svyatoslav I Igorevich (; Old Norse: ''Sveinald''; – 972) was Prince of Kiev from 945 until his death in 972. He is known for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers ...
and grandfather Igor of Kiev. Even if Rurik did exist, scholars have long doubted or rejected his paternity
Paternity may refer to:
*Father, the male parent of a (human) child
*Paternity (law), fatherhood as a matter of law
* ''Paternity'' (film), a 1981 comedy film starring Burt Reynolds
* "Paternity" (''House''), a 2004 episode of the television seri ...
of Igor. The connections between Rurik, Oleg and Igor, as attested in the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Primary Chronicle'', shortened from the common ''Russian Primary Chronicle'' (, commonly transcribed ''Povest' vremennykh let'' (PVL), ), is a Rus' chronicle, chronicle of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110. It is believed to have been or ...
'' and ''Novgorod First Chronicle
The Novgorod First Chronicle ( rus, Новгоро́дская пе́рвая ле́топись, Novgoródskaya pérvaya létopisʹ, nəvɡɐˈrot͡skəjə ˈpʲervəjə ˈlʲetəpʲɪsʲ, commonly abbreviated as NPL), also known by its 1914 Eng ...
'', are tenuous at best; in all other cases, these two chronicles base any particular ruler's legitimacy on the fact that their father or grandfather previously "sat on the throne in Kiev", and never refer back to Rurik. Legitimacy in the ''Kievan Chronicle
The ''Kievan Chronicle'' or ''Kyivan Chronicle'' is a chronicle of Kievan Rus'. It was written around 1200 in Vydubychi Monastery as a continuation of the ''Primary Chronicle''. It is known from two manuscripts: a copy in the '' Hypatian Codex'' ...
'' is also heavily based on a ruler being descended from his father and grandfather, with the exception of two 5-generation lists. Before the mid-15th century, no historical source claims that Rurik founded a dynasty; the Hypatian Codex of 1425 began its list of ''knyaz
A , also , ''knjaz'' or (), is a historical Slavs, Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English language, English as 'prince', 'king' or 'duke', depending on specific historical c ...
i'' of Kiev with "Dir and Askold", then "Oleg", then "Igor", up to 1240, and does not mention Rurik anywhere. It was not until the 16th century that Rus' churchmen developed an explicit tradition, described in the 1560 '' Book of Royal Degrees'' by Macarius, Metropolitan of Moscow, according to which the reigning Danilovichi house of the Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Principality of Moscow, or Muscovy, known as the Principality of Moscow until 1389, was a late medieval Russian monarchy. Its capital was the city of Moscow. Originally established as a minor principality in the 13th century, the gra ...
(Muscovy) was part of a "Rurikid dynasty", which not only traced back all the way to the legendary Rurik, but was purportedly descended from a certain Prus, a supposed kinsman of Augustus Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
. According Ostrowski (2018), the Rus' churchmen developed this concept of a R(i)urikid dynasty for the purpose of "bolstering the Muscovite dynastic state". Although many later historians would accept the 16th-century Rus' churchmen's dynastic claim that the Danilovichi were descended from Rurik, they did not accept Prus as the ancestor of the Muscovite princes. Because of these issues, various scholars have instead named the dynasty the ''Volodimerovichi'', descendants of grand prince Volodimer I of Kiev.
Ethnographic issues
The scholarly consensus is that theRus' people
The Rus, also known as Russes, were a people in early medieval Eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally Norsemen, mainly originating from present-day Sweden, who settled and ruled along the river-routes between t ...
originated in what is currently coastal eastern Sweden around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago.
Historically, it was the name for all the coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, including the eastern par ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
(with the older name being '' Roden'').
According to the prevalent theory, the name ''Rus'', like the Proto-Finnic name for Sweden (''*Ruotsi''), is derived from an Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
term for "the men who row" (''rods-'') as rowing was the main method of navigating the rivers of Eastern Europe, and that it could be linked to the Swedish coastal area of Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago.
Historically, it was the name for all the coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, including the eastern par ...
(''Rus-law'') or ''Roden'', as it was known in earlier times.Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in The Viking World
'', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rus'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
Estonian
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also ...
names for Sweden: ''Ruotsi'' and ''Rootsi''."Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
The ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Primary Chronicle'', shortened from the common ''Russian Primary Chronicle'' (, commonly transcribed ''Povest' vremennykh let'' (PVL), ), is a Rus' chronicle, chronicle of Kievan Rus' from about 850 to 1110. It is believed to have been or ...
'' gives the following account the "Calling of the Varangians
The calling of the Varangians, calling of the (Varangian) princes or invitation to the Varangians (; ) is a legend about the origins of the Rus' people, the Rurik dynasty and the Kievan Rus' state, recorded in many divergent versions in various ma ...
", dating it to the Byzantine years of the world 6368–6370 (AD 860–862):
There is some ambiguity even in the ''Primary Chronicle'' about the specifics of the story, "hence their paradoxical statement 'the people of Novgorod are of Varangian stock, for formerly they were Slovenes. However, archaeological evidence such as " Frankish swords, a sword chape and a tortoiseshell brooch" in the area suggest that there was, in fact, a Scandinavian population during the tenth century at the latest.
Genetic studies
A genetic study on the origins of Rurikids (Zhur et al. 2023) analysed "for the first time", remains belonging to Prince Dmitry Alexandrovich. The study found that Dmitry Alexandrovich and most of the "medieval and modern Rurikids", starting with PrinceYaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav I Vladimirovich ( 978 – 20 February 1054), better known as Yaroslav the Wise, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death in 1054. He was also earlier Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1034 and Prince of Rostov from 987 to 1010, ...
, belong to paternal haplogroup N-M231 (N1a). The genetic results suggest that the formation of the Rurikid lineage included a population from eastern Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
(Öland
Öland (, ; ; sometimes written ''Oland'' internationally) is the second-largest Swedish island and the smallest of the traditional provinces of Sweden. Öland has an area of and is located in the Baltic Sea just off the coast of Småland. ...
), a population from Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
or the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
Eurasian Steppe, and an East Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
component via Siberian geneflow to Northeastern Europe.
History
 Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent
Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often ...
, each ruled by a different branch of the Rurikid house. The dynasty followed agnatic seniority
Agnatic seniority is a patrilineality, patrilineal principle of inheritance where the order of succession to the throne prefers the monarch's younger brother over the monarch's own sons. A monarch's children (the next generation) succeed only ...
and the '' izgoi'' principle. The house underwent a major schism after the death of Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav I Vladimirovich ( 978 – 20 February 1054), better known as Yaroslav the Wise, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death in 1054. He was also earlier Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1034 and Prince of Rostov from 987 to 1010, ...
in 1054, dividing into three branches on the basis of descent from three successive ruling Grand Princes: Iziaslav (1024–1078), Sviatoslav
Sviatoslav (, ; , ) is a Russian and Ukrainian given name of Slavic origin. Cognates include Svetoslav, Svatoslav, , Svetislav. It has a Pre-Christian pagan character and means "one who worships the light" (likely in reference to the sun). In C ...
(1027–1076), and Vsevolod (1030–1093). In addition, a line of Polotsk princes assimilated themselves with the princes of Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
. In the 10th century the Council of Liubech The Council of Liubech (sometimes referred to as the Liubech Conference) (, ) was one of the best documented princely meetings in Kievan Rus' that took place in Liubech (today in Chernihiv Oblast, Ukraine) on October 19, 1097. The council ended the ...
made some amendments to a succession rule and divided Ruthenia
''Ruthenia'' is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Rus'. Originally, the term ''Rus' land'' referred to a triangular area, which mainly corresponds to the tribe of Polans in Dnieper Ukraine. ''Ruthenia' ...
into several autonomous principalities that had equal rights to obtain the Kievan throne.
Vsevolod's line eventually became better known as the Monomakhovichi and was the predominant one. The line of Sviatoslav later became known as Olegovychi and often laid claim to the lands of Chernihiv
Chernihiv (, ; , ) is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within the oblast. Chernihiv's population is
The city was designated as a Hero City of Ukraine ...
and Severia
Severia (, ; ) or Siveria ( / , ''Siveria'' / ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, and eastern Belarus. The largest part lies in modern Russia, while the central part of the region is the c ...
. The Izyaslavychi who ruled Turov and Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in ...
were eventually replaced by a Monomakhovychi branch.
According to Jaroslaw Pelenski,
This caused the Rurikid house to effectively dissolve into several sub-dynasties ruling smaller states in the 10th and 11th centuries. These were the ''Olgoviches'' of Severia
Severia (, ; ) or Siveria ( / , ''Siveria'' / ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, and eastern Belarus. The largest part lies in modern Russia, while the central part of the region is the c ...
who ruled in Chernigov
Chernihiv (, ; , ) is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within the oblast. Chernihiv's population is
The city was designated as a Hero City of Ukrain ...
, ''Yuryeviches'' who controlled Vladimir-Suzdal
The Principality of Suzdal, from 1157 the Grand Principality of Vladimir, commonly known as Vladimir-Suzdal, or simply Suzdalia, was a medieval principality that was established during the disintegration of Kievan Rus'. In historiography, the ...
, and ''Romanoviches'' in Galicia-Volhynia.
Descendants of Sviatoslav II of Kiev
The Olgovichi descended fromOleg I of Chernigov
Oleg Svyatoslavich (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian: Олег Святославич; 1052 – 1 August 1115), nicknamed Gorislavich (Гориславич, literally "of famous woe") was a prince from Kievan Ru ...
, a son of Sviatoslav II of Kiev and grandson of Yaroslav the Wise. They continued to rule until the early 14th century when they were torn apart by the emerging Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
and Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Principality of Moscow, or Muscovy, known as the Principality of Moscow until 1389, was a late medieval Russian monarchy. Its capital was the city of Moscow. Originally established as a minor principality in the 13th century, the gra ...
. The line continued through Oleg's son Vsevolod II of Kiev
Vsevolod II Olgovich (died August 1, 1146) was Prince of Chernigov (1127–1139) and Grand Prince of Kiev (1139–1146). He was a son of Oleg I of Chernigov, Oleg Svyatoslavich, Prince of Chernigov.
Family
Vsevolod married Maria Mstislavna of Ki ...
, grandson Sviatoslav III of Kiev, great-grandson Vsevolod IV of Kiev and great-great-grandson Michael of Chernigov, from whose sons the extant lines of the Olegoviches are descended, including the Massalsky, Gorchakov, Baryatinsky, Volkonsky and Obolensky, including Repnin.
Descendants of Vsevolod I of Kiev
Vsevolod I of Kiev was the father ofVladimir II Monomakh
Vladimir II Monomakh (; Christian name: ''Vasily''; 26 May 1053 – 19 May 1125) was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1113 to 1125. He is considered a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church and is celebrated on May 6 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), May 6 ...
, giving rise to the name Monomakh for his progeny. Two of Vladimir II's sons were Mstislav I of Kiev
Mstislav I Vladimirovich Monomakh (; Christian name: ''Fedor''; February 1076 – 14 April 1132), also known as Mstislav the Great, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1125 until his death in 1132. After his death, the state began to quickly disin ...
and Yuri Dolgorukiy
Yuri I Vladimirovich (; ; c. 1099 – 15 May 1157), commonly known as Yuri Dolgorukiy (, ) or the Long Arm, was a Monomakhovichi prince of Rostov and Suzdal, acquiring the name ''Suzdalia'' during his reign. Noted for successfully curbing t ...
.
The Romanovichi (Izyaslavichi of Volhynia) were the line of Roman the Great
Roman Mstislavich ( – 19 June 1205), also known as Roman the Great, was Prince of Novgorod (1168–1170), Volhynia (1170–1189; 1189–1205), and Galicia (1189; 1198/99–1205). He founded the ''Romanovichi'' branch of Rurikids, which wou ...
, descended from Mstislav I of Kiev through his son Iziaslav II of Kiev and his grandson Mstislav II of Kiev, father of Roman the Great. The older Monomakhovychi line that ruled the Principality of Volhynia
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often ...
were eventually crowned kings of Galicia and Volhynia and ruled until 1323. The Romanovychi displaced the older line of Izyaslavychi from Turov and Volhynia as well as Rostyslavychi from Galicia. The last were two brothers of Romanovychi, Andrew
Andrew is the English form of the given name, common in many countries. The word is derived from the , ''Andreas'', itself related to ''aner/andros'', "man" (as opposed to "woman"), thus meaning "manly" and, as consequence, "brave", "strong", "c ...
and Lev II, who ruled jointly and were slain trying to repel Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
incursions. The Polish king, Władysław I the Elbow-high Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
People Mononym
* Włodzis ...
, in his letter to the Pope wrote with regret: "The two last Ruthenian kings, that had been firm shields for Poland from the Tatars, left this world and after their death Poland is directly under Tatar threat." Losing their leadership role, the Rurikids, however, continued to play a vital role in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
and the later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
. Most notably, the Ostrogski family held the title of Grand Hetman of Lithuania and strove to preserve the Ruthenian language
Ruthenian (see also #Nomenclature, other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely related group of East Slavic languages, East Slavic linguistic Variety (linguistics), varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in ...
and Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
in this part of Europe. It is thought that the Drutsk and related princely families may also descend from Roman the Great.
The Rostislavichi were the line of Rostislav I of Kiev
Rostislav Mstislavich ( – 1167) was Prince of Smolensk (1125–1160), Novgorod (1154) and Grand Prince of Kiev (1154–1155; 1159–1161; 1161–1167). He is the founder of the Rostislavichi branch of Rurikid princes in Smolensk
Smolensk ...
, another son of Mstislav I of Kiev, who was Prince of Smolensk and a progenitor of the lines descending from the princes of Smolensk and Yaroslavl.
The Shakhovskoys were founded by Konstantin "Shakh" Glebovich, Prince of Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl (; , ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl rivers. ...
, and traces its lineage to Rostislav I of Kiev
Rostislav Mstislavich ( – 1167) was Prince of Smolensk (1125–1160), Novgorod (1154) and Grand Prince of Kiev (1154–1155; 1159–1161; 1161–1167). He is the founder of the Rostislavichi branch of Rurikid princes in Smolensk
Smolensk ...
through his son Davyd Rostislavich. This branch also descends cognatically of Ivan I of Moscow, through the latter's daughter Evdokia Ivanovna Moskovskaya (1314–1342), who married , Prince of Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl (; , ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl rivers. ...
(died 1345). They were the great-grandparents of Andrey and Yuriy, the first Shakhovskoy princes. This is possibly the most senior extant branch of the Rurikids, with many Shakhovskoys living outside of Russia after having fled during the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
.
The Yurievichi were founded by Yuriy Dolgorukiy, the founder of Moscow and spread vastly in the north-east. Yuri's son Vsevolod the Big Nest was Prince of Vladimir-Suzdal
The Principality of Suzdal, from 1157 the Grand Principality of Vladimir, commonly known as Vladimir-Suzdal, or simply Suzdalia, was a medieval principality that was established during the disintegration of Kievan Rus'. In historiography, the ...
, a precursor state to the Grand Principality of Moscow and thus of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. Vsevolod's son Konstantin of Rostov
Konstantin Vsevolodovich () (18 May 1186 in Rostov – 2 February 1218) was the eldest son of Vsevolod the Big Nest and Maria Shvarnovna.
In 1206 and 1207, he was the prince of Novgorod. In 1207, his father sent him to rule the towns of R ...
was Prince of Rostov and the progenitor of various Rostov princely lines. Another son, Ivan Vsevolodich, was Prince of Starodub
Starodub (, , ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, on the Babinets (river), Babinets River in the Dnieper basin, southwest of Bryansk. Population: 16,000 (1975).
History
Starodub has been known ...
and progenitor of a number of extant lines, most notably the Gagarin line.
Vsevolod's son Yaroslav II of Vladimir
Yaroslav II Vsevolodovich (; Christian name: ''Theodor'' (); 8 February 1191 – 30 September 1246), also transliterated as Iaroslav, was Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1238 to 1246. He collaborated with Batu Khan following the Mongol invasion, be ...
was the father of Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (; ; monastic name: ''Aleksiy''; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) was Prince of Novgorod (1236–1240; 1241–1256; 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249–1263), and Grand Prince of Vladimir (1252–1263).
...
, whose son Daniel of Moscow sired the ruling house of Moscow until the end of the 16th century; the princes of Moscow are often referred to as the ''Daniilovichi''.
Beginning with the reign of Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all R ...
, the Muscovite branch used the title "Tsar of All Russia" and ruled over the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
. The death in 1598 of Tsar Feodor I ended the rule of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty was briefly revived in the person of Vasili IV of Russia
Vasili IV Ivanovich Shuisky (, 12 September 1612) was Tsar of all Russia from 1606 to 1610, after the murder of False Dmitri I. His rule coincided with the Time of Troubles. He was the only member of Shuysky, House of Shuisky to become t ...
, a descendant of Shuyskiy line of the Rurik dynasty, but he died without issue. The unstable period known as the Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (), also known as Smuta (), was a period of political crisis in Tsardom of Russia, Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Feodor I of Russia, Feodor I, the last of the Rurikids, House of Rurik, and ended in 1613 wit ...
followed Feodor's death and lasted until 1613.
In that year, Mikhail I ascended the throne, founding the Romanov dynasty that would rule until 1762 and as Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transliterated as Romanoff; , ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after Anastasia Romanovna married Ivan the Terrible, the first crowned tsar of all Russi ...
until the revolutions of 1917. Tsar Mikhail's father Patriarch Filaret of Moscow was descended from the Rurik dynasty through the female line. His mother, Evdokiya Gorbataya-Shuyskaya, was a Rurikid princess from the Shuysky
The House of Shuysky (Shuisky; ) was a Russian family of boyars and tsars, a cadet branch of the Rurikids.
The surname is derived from the town of Shuya, of which the Shuiskys gained ownership in 1403. From 1606 to 1610, Vasili Shuisky ...
branch, daughter of Alexander Gorbatyi-Shuisky. Tsar Mikhail's first wife Maria Dolgorukova was of Rurikid stock but their marriage produced no children.
Branches
Volodimerovichi, grand princes of Kiev * Izyaslavichi of Polotsk, princes of Polotsk ** Putyatin, princes Putyatin (extant) * Izyaslavichi of Turov, princes of Turiv and Volhynia * Monomakhovichi, princes of Pereyaslav ** Izyaslavichi of Volhynia, princes of Volhynia, kings of Rus (senior branch) ** Rostislavichi of Smolensk, princes of Smolensk (middle branch) ***Kropotkin
Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (9 December 1842 – 8 February 1921) was a Russian anarchist and geographer known as a proponent of anarchist communism.
Born into an aristocratic land-owning family, Kropotkin attended the Page Corps and later ...
, princes Kropotkin (extant)
*** Lvov princely family, emerged in the 17th century as descendants of the Rostislavichi princes of Yaroslavl (before 1260 Yaroslavl was in Yurievichi hands)
*** Rzhesvsky, non-titled (extant)
*** Prozorovsky (extinct since 1914)
** Yurievichi, princes of Vladimir-Suzdal; until 1260 princes of Yaroslavl
*** Daniilovichi, princes of Moscow. This branch would reign in Muscovy Muscovy or Moscovia () is an alternative name for the Principality of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721).
It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
*Muscovy duck (''Cairina mosch ...
and the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
until it went extinct with the 1598 death of Feodor I, which caused the Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (), also known as Smuta (), was a period of political crisis in Tsardom of Russia, Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Feodor I of Russia, Feodor I, the last of the Rurikids, House of Rurik, and ended in 1613 wit ...
.
***Konstantinovichi, princes of Galich, Russia
Galich () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Kostroma Oblast, Russia, located on the southern bank of Lake Galichskoye. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, its population was 12,856.
History
It was first chro ...
(1247–1362). Progenitor: , son of Yaroslav II of Vladimir
Yaroslav II Vsevolodovich (; Christian name: ''Theodor'' (); 8 February 1191 – 30 September 1246), also transliterated as Iaroslav, was Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1238 to 1246. He collaborated with Batu Khan following the Mongol invasion, be ...
**** Lyapunov family, emerged in the 16th century as descendants from the Konstantinovichi princes of Galich, Russia
Galich () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Kostroma Oblast, Russia, located on the southern bank of Lake Galichskoye. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, its population was 12,856.
History
It was first chro ...
** Shakhovskoy, princes of Yaroslavl (senior extant branch)
** Lobanov-Rostovsky, princes of Rostov (middle extant branch)
** Gagarin, princes of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma (junior extant branch)
* Sviatoslavichi, princes of Ryazan and Murom
** Olgovichi, princes of Chernihiv
*** Skarzynski, Belarusian nobles
*** Gorchakov, princes Gorchakov (extant)
*** Massalski family, princes of Mosalsky (Massalsky)
***Obolensky
The House of Obolensky () is an ancient Russian princely family, claiming descent from the Olgovichi branch of the Rurik dynasty.
History
Their name is said to derive from the town of Obolensk in the Upper Oka Principalities near Moscow. ...
, princes Obolensky (extant)
**** Dolgorukov, princes Dolgorukov (extant; cadet branch of the Obolensky family)
* Rostislavichi of Tmutarakan, princes of Tmutarakan
* Rostislavichi of Halych, princes of Halych
*Vadbosky, a branch of the princes Belozersky (extant)
*Volkonsky, a branch of the princes of Tarusa (extant)
Disputed
*Possibly theOgiński family
The House of Ogiński, feminine form: Ogińska, plural: Ogińscy (, ) was a noble family of Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Poland (later, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth), member of the Princely houses of Poland and Lithuania.
They were most ...
; various "Rurikid" branches have been proposed, as well as Lithuanian ones.
*Possibly the Ostrogski family, a branch of the Romanovichi, but could also be descended from the Lithuanian Gediminids
The House of Gediminas (), or simply the Gediminids, were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reigned from the 14th to the 16th century. A cadet branch of this family, known as the Jagiellonian dynasty, reigned also in th ...
.
*Possibly the Wiśniowiecki
The House of Wiśniowiecki () was a Princely houses of Poland and Lithuania, Polish-Lithuanian princely family of Ruthenian origin, notable in the history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. They were powerful magnates with estates predo ...
family, a branch of the House of Zbaraski (extinct), but could also be descended from the Lithuanian Gediminids
The House of Gediminas (), or simply the Gediminids, were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reigned from the 14th to the 16th century. A cadet branch of this family, known as the Jagiellonian dynasty, reigned also in th ...
.
Legacy
Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
and Ukrainian historians have debated for many years about the legacy of the Rurikid dynasty. The Russian view sees the Principality of Moscow
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often ...
ruled by the Rurikid dynasty as the sole heir to the Kievan Rus' civilisation, this view is "resting largely on religious-ecclesiastical and historical claims" because Eastern Russian lands managed to establish themself as independent state that was ruled by the Rurikid dynasty until 16th century. This view started in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
as ruled by the original Rurikid dynasty between the 1330s and the late 1560s. At the same time Ukrainian view of sole succession is based on continuity from the Kievan Rus and its subsequent Kingdom of Ruthenia, Lithuania-Ruthenia, Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate (; Cossack Hetmanate#Name, see other names), officially the Zaporozhian Host (; ), was a Ukrainian Cossacks, Cossack state. Its territory was located mostly in central Ukraine, as well as in parts of Belarus and southwest ...
. For that it had utilised mainly territorial, ethnodemographic, social, and institutional arguments.
The predominant Ukrainian view had gradually changed over time. After decline of Kievan Rus rulers of Galicia-Volhynia claimed sole succession and the title of ruler of all former Rus lands as was noted in Kievan and then Galician–Volhynian Chronicles. Following downfall of Galicia-Volhynia, monarchs of Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ruthenia and then Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
claimed sole succession as well, which in turn was supported by Ruthenian population and historians at the time. But that view had shifted by mid 17th century, especially after Pereiaslav Agreement
The Pereiaslav Agreement or Pereyaslav AgreementPereyaslav Agreement
Bri ...
and publication of Kievan Synopsis in 1674 that viewed people of Bri ...
Great Russia
Great Russia, sometimes Great Rus' ( , ; , ; , ), is a name formerly applied to the territories of "Russia proper", the land that formed the core of the Grand Duchy of Moscow and later the Tsardom of Russia. This was the land to which the e ...
, Little Russia and White Russia as single All-Russian nation under leadership of Tsar. Though latter was challenged, but eventually became predominantly accepted until History of Ruthenians was written at the break of the 18th and 19th centuries underlying foundation for separate Ukrainian historiography with later monolineal and exclusivist Ukrainian national theory being advanced by national historiography between the 1840s and the end of the 1930s. It was summarised most clearly by Mykhailo Hrushevsky in his History of Ukraine-Rusʹ laying foundation for current sole succession view.
During Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
times by 1930s prior All-Russian nation ideology was a modified to "allot equal rights to the Kievan inheritance to the Three Slavic peoples, that is the Russians, the Ukrainians, and the Belorussians", but later elevated the Russian nation as the elder brother to give the others "needed guidance in revolutionary struggles and socialist construction."
There are currently various extant branches of the Rurikids, for instance: the Houses of Shakhovskoy, Gagarin, and Lobanov-Rostovsky. Their representatives include Prince Dmitriy Mikhailovich Shakhovskoy (born 1934); Prince Dmitri Andreevich Gagarin (born 1934); and Prince Nikita Lobanov-Rostovsky (born 1935), a descendant of Prince Konstantin Vasilyevich of Rostov. The three of them are of the Monomakhovichi branch. While the Shakhovskoys claim descent from Mstislav I of Kiev
Mstislav I Vladimirovich Monomakh (; Christian name: ''Fedor''; February 1076 – 14 April 1132), also known as Mstislav the Great, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1125 until his death in 1132. After his death, the state began to quickly disin ...
, the Gagarins and the Lobanov-Rostovskys are descendants of Vsevolod III of Vladimir, which makes the Shakhovskoys the most senior.
Gallery
Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transliterated as Romanoff; , ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after Anastasia Romanovna married Ivan the Terrible, the first crowned tsar of all Russi ...
File:RU COA Dolgorukov.svg, Coat of arms of the Dolgoruky family
File:RU COA Beloselsky-Belozersky.svg, Coat of arms of the Belosselsky-Belozersky family
File:RU COA Kropotkin.svg, Coat of arms of the Kropotkin family
The House of Kropotkin ({{langx, ru, Князья Кропоткины, translit=Knyaz'ya Kropotkiny) is an ancient Russian nobility, Russian noble family of Rurik dynasty, Rurik stock descending from Prince Dmitry Vasilyevich nicknamed ''Kropotk ...
File:Coat of Arms of Aladin.jpg, Coat of arms of the families of Monastyrev stock is composed of Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow.
First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of ...
and Belozersk emblems.
File:Coats of arms of the house of Gagarin.svg, Gagarin family / Khilkoff Coat of arms
File:Golitsyn dukes v1 p2.png, Coat of arms of the Golitsyn family
File:Gorchakov arms.jpg, Coat of arms of the Gorchakov family
File:RU COA Mosalsky XV, 2.jpg, Coat of arms of the Mosalsky family
File:Herb Ostrogski.jpg, Coat of arms of the Ostrogski
The House of Ostrogski (; ; ) was one of the more prominent families in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The family spanned from the 14th century Rut ...
family
File:Repnin coat.jpg, The Obolensky
The House of Obolensky () is an ancient Russian princely family, claiming descent from the Olgovichi branch of the Rurik dynasty.
History
Their name is said to derive from the town of Obolensk in the Upper Oka Principalities near Moscow. ...
– Repnin coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
is composed of the emblems of Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
and Chernigov
Chernihiv (, ; , ) is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within the oblast. Chernihiv's population is
The city was designated as a Hero City of Ukrain ...
.
File:RU COA Romodanovsky.svg, Coat of arms of the Romodanowski family
File:RU COA Shujski.png, Coat of arms of the Shuyski family
File:RU_COA_Tatischev_II,_17.png, Coat of arms of the Tatischev family
image:POL COA Korybut.svg, Korybut coat of arms
See also
*Grand Prince of Kiev
The Grand Prince of Kiev (sometimes also Grand Duke) was the title of the monarch of Kievan Rus', residing in Kiev (modern Kyiv) from the 10th to 13th centuries. In the 13th century, Kiev became an appanage principality first of the grand prin ...
* Shum-gora
* Prince of Tver
*Knyaz
A , also , ''knjaz'' or (), is a historical Slavs, Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English language, English as 'prince', 'king' or 'duke', depending on specific historical c ...
* Symbols of the Rurikids
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
{{Authority control Russian noble families Nobility from Kievan Rus'