|
Trolleybuses In Sofia
The Sofia trolleybus system () forms part of the Sofia Public Transport, public transport network of Sofia, the capital city of Bulgaria. Trolleybuses first began serving Sofia on 8 February 1941, on a route to the suburb of Gorna Banya, but that initial system closed on 9 September 1944. The current system opened only four years later, on 1 May 1948. The system presently comprises ten routes with network build, of which are currently in use. As of 2020, the average speed of the trolleybus system in Sofia is 15.7 km/h. History Trolleybus transport was the last form of surface public transport to develop in Sofia, after buses and trams. The first Sofia trolleybus line opened on 8 February 1941, in what was then the Kingdom of Bulgaria. It was more than long, and connected the city with the Gorna Banya quarter. The line was covered by 2 MAN Truck & Bus, MAN trolleybuses, which were stored on the last stops during the night, due to the lack of depot. It closed on 9 Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
҆koda 27Tr Solaris
҆koda 27Tr Solaris is a Low-floor bus, low-entry trolleybus model produced from 2010 by Czech Republic, Czech trolleybus manufacturer ''҆koda Electric'' (subsidiary of ҆koda Transportation), supplying electrical equipment, in cooperation with the Polish company Solaris Bus & Coach, Solaris, manufacturing the trolleybus body. Installation and assembly of the trolleybus is carried out at ҆koda's plant in PlzeŇą, Czech Republic. A similar type of trolleybus with the same chassis is the Solaris Trollino 18 model. History The prototype of the 27Tr trolleybus, which was manufactured in 2009, was delivered to Dopravn√≠ podnik Ostrava in 2010 together with two twelve-meter ҆koda 26Tr cars. Prototype 27Tr went on its first test runs in PlzeŇą around Christmas 2009, in Ostrava on February 4, 2010 and was first sent into test operation with passengers on February 11, 2010. As a type, the 27Tr car was approved by the Railway Authority in the first quarter of 2010. The trolleybus has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
҆koda Works
The ҆koda Works (, ) was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century. In 1859, Czech engineer Emil ҆koda bought a foundry and machine factory in Plzeҹ, Bohemia, Austria-Hungary that had been established ten years previously, founding ҆koda Works. By World War I, ҆koda Works had become the largest arms manufacturer in Austria-Hungary, supplying the Austro-Hungarian army with mountain guns, mortars and machine guns, including the ҆koda M1909, and the ships of the Austro-Hungarian navy with heavy guns. After the war and the creation of the First Czechoslovak Republic, the company, previously focusing on the manufacturing of armaments, diversified and became a major manufacturer of locomotives, aircraft, ships, machine tools, steam turbines, equipment for power utilities, among other industrial products. The deteriorating political situation in Europe by the latter half of the interwar period eventually led to a renewed focus on armament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia Tramway
The Sofia tram network is a vital part of the public transportation system of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. It began operation on January 1, 1901. As of 2006, the tram system included approximately of narrow and standard gauge one-way track. Most of the track is a narrow gauge (), with standard gauge () used on lines 20, 21, 22 and 23 and accounting for approximately of the system's track length. History The realization of the idea to build a network of tram lines in Sofia began on December 1, 1898, when the Sofia Municipality granted a concession for the construction of tram lines to companies from France and Belgium. The construction work lasted about a year and on 1 January 1901 the first tram in Sofia officially started. Initially, passengers were served by 25 cars and 10 trailers - two-axle, wooden-bodied, which ran on 6 routes with a total length of 23 km and a single track with a gauge of . Between 1903 and 1931, a large number of railcars and trailers were deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia Metro
The Sofia Metro (, also colloquially called ) is the rapid transit network servicing the Bulgarian capital city Sofia. It is the only metro in Bulgaria. It began operation on 28 January 1998. , the Sofia Metro consists of four interconnected lines, serving 47 stations, with a total route length of and also being among the top 15 of the most extensive European metro systems, ranking 14th as of 2023. The Metro links the densely populated districts of Lyulin ‚Äď Mladost (M1 line ‚Äď Red) and Nadezhda ‚Äď Lozenets (M2 line ‚Äď Blue), and serves the Sofia Airport. History Planned since the 1960s, construction of the metro started in the 80s with the demolition of a significant number of buildings. At the beginning of the 90s, construction stopped due to a lack of funds and the complexity of the construction work. Being one of the oldest cities in Europe, Sofia contains many historical layers underneath its central areas. Evidence of antiquity can be clearly seen at the Serdika ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linz
Linz (Pronunciation: , ; ) is the capital of Upper Austria and List of cities and towns in Austria, third-largest city in Austria. Located on the river Danube, the city is in the far north of Austria, south of the border with the Czech Republic. As of 1 January 2024, the city has a population of 212,538. It is the seventh-largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. History Linz originated as a Roman Empire, Roman fort named ''Lentia'', established in the first century. The name reflects its location at a bend in the Danube (Celtic languages, Celtic root ''lentos'' = "bendable"). This strategic position on the river made it the first Roman fort in the Noricum region, protecting a vital transportation route. The name "Linz" in its present form was first documented in 799. Linz was mentioned as a fortified city in 1236 and was granted city rights in 1324. Johannes Kepler spent several years of his life in the city teaching m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiepe
Kiepe Electric GmbH (formerly Vossloh Kiepe) is a German manufacturer of electrical traction equipment for trams, trolleybuses other road and rail transport vehicles, as well as air-conditioning and heating systems, and conveyor device components. Founded in 1906, it was known as Kiepe Elektrik GmbH until 2003, when it was renamed Vossloh Kiepe, following its acquisition by Vossloh AG. Vossloh sold the company to Knorr-Bremse in January 2017, and in May 2017 Knorr renamed it Kiepe Electric GmbH. History In 1906, Theodor Kiepe created an electric arc lamp repair workshop in D√ľsseldorf. Over the next 40 years the company's product range grew to include electrical switches, then electrical drum controllers and resistors for electric vehicles. By 1951, the product range included electro-pneumatic contactors, and traction motors; in 1952, the company supplied equipment for an order of 700 trolleybuses for Argentina. Between the 1950s and 1970s Kiepe Elektrik GmbH expanded, with for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kässbohrer Setra
Setra is a German bus brand of Daimler Buses, itself a wholly owned subsidiary of Daimler Truck AG. The name "Setra" comes from "selbsttragend" (self-supporting). This refers to the integral nature of the construction of the vehicles back in the 1950s when competitor vehicles still featured a separate chassis and body (often manufactured by separate companies). It is also possible that, with an eye to export markets, the company was mindful that for non-German speakers, the name " Kässbohrer" is difficult to pronounce. Until 1995 the firm operated under the name Karl Kässbohrer Fahrzeugwerke GmbH, but in that year economic difficulties enforced its sale to Daimler-Benz AG (between 1998 and 2008 known, especially in the United States, by the name of its holding company Daimler Chrysler). Since 1995, Setra has been a brand of the Daimler subsidiary, EvoBus GmbH. The North American distribution for Setra by Daimler was set to be partnered and taken over by Motor Coach Indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gräf & Stift GE 152 M18 Trolleybus In Sofia
(; feminine: ) is a historical title of the German nobility and later also of the Russian nobility, usually translated as "count". Considered to be intermediate among noble ranks, the title is often treated as equivalent to the British title of "earl" (whose female version is "countess"). The German nobility was gradually divided into high and low nobility. The high nobility included those counts who ruled immediate imperial territories of "princely size and importance" for which they had a seat and vote in the Imperial Diet. Etymology and origin The word derives from , which is usually derived from . is in turn thought to come from the Byzantine title , which ultimately derives from the Greek verb () 'to write'. Other explanations have been put forward, however; Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm, while still noting the potential of a Greek derivation, suggested a connection to , meaning 'decision, decree'. However, the Grimms preferred a solution that allows a connection to ' ree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
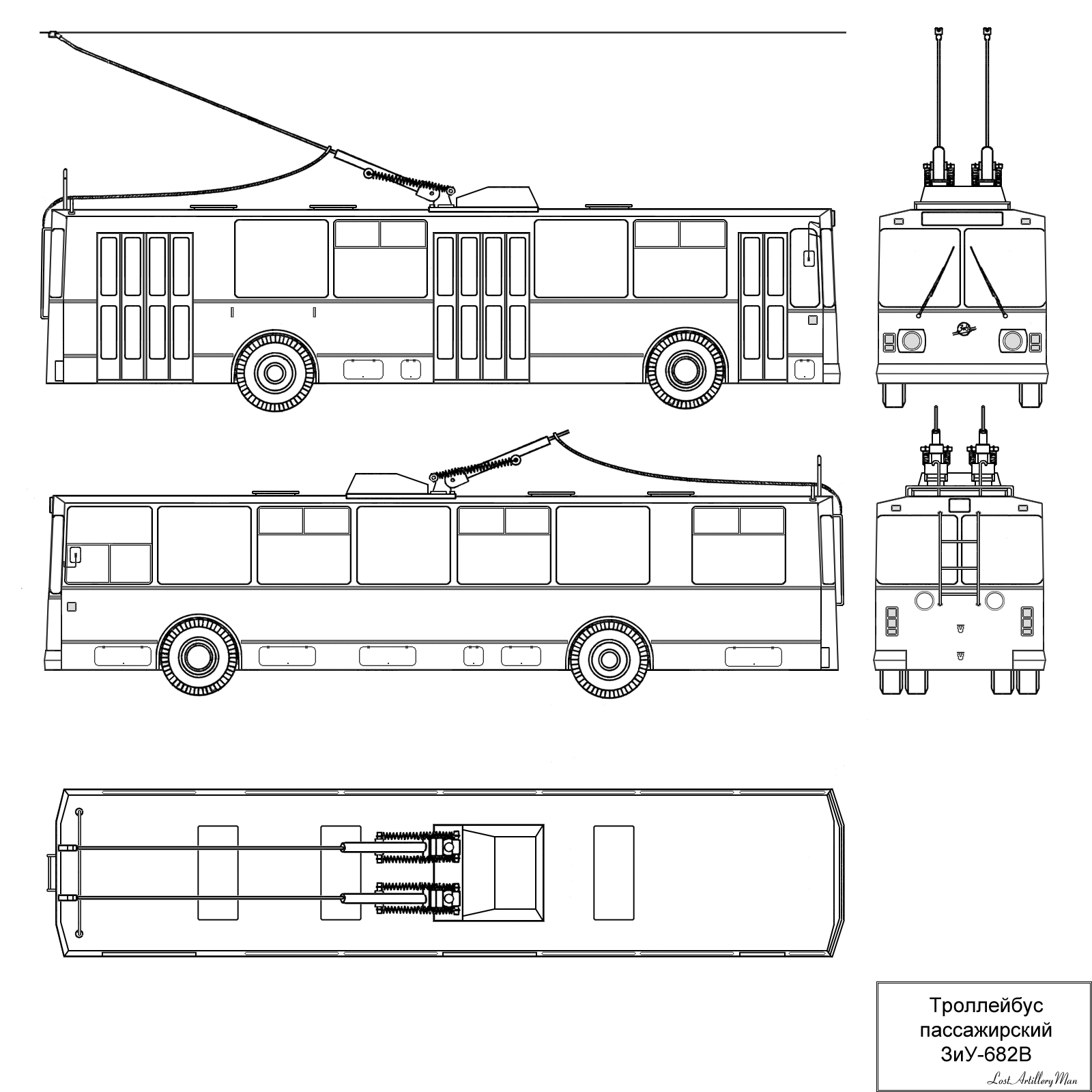
ZiU-9
ZiU-9, or ZIU-9 (Cyrillic: –ó–ł–£-9) is a Soviet Union, Soviet (and later Russian) trolleybus. Other names for the ZiU-9 are ZiU-682 and HTI-682 (Cyrillic: –ó–ł–£-682 and –•–Ę–ė-682). The ZiU acronym stands for "Zavod imeni Uritskogo", which means a factory named after Moisei Uritsky, the Russian revolutionary. Before 1996 this acronym was also a trademark of the vehicle manufacturer ''Trolza''. The ZiU-9 was first built in 1966, although it was only put into mass production in 1972 and it was still assembled along with other more advanced trolleybus vehicles in the Trolza (former ZiU) factory until 2015. The total number of produced ZiU-9s exceeds 42,000 vehicles making it the most produced trolleybus in the world. Many copies of the ZiU-9 were made in other factories of the former Soviet bloc. Following the Soviet era, many cities still utilize the ZiU-9 as their primary trolleybus; for example Cheboksary, Ryazan, Vinnitsa and others. History and development The explosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pernik
Pernik ( ) is List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, a town in western Bulgaria (about south-west of Sofia) with a population of 70,285 . Pernik is the most populated town in western Bulgaria after Sofia. It is the main town of Pernik Province and lies on both banks of the Struma River in the Pernik Valley between the Golo Bardo Mountain, Vitosha Mountain, Lyulin Mountain, Lyulin and Viskyar Mountain, Viskyar mountains. Pernik is the principal town of Pernik Province ‚Äď a province in western Bulgaria, which is next to the Serbian border. Originally the site of a Thrace, Thracian fortress founded in the 4th century BC, and later a Ancient Rome, Roman settlement, Pernik became part of the First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire in the early 9th century as an important fortress. The medieval town was a key Bulgarian stronghold during Bulgarian tsar Samuil of Bulgaria, Samuil's wars against the Byzantine Empire in the 11th century, when it was governed by the local noble Krakra of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chavdar (company)
Chavdar () was a Bulgarian Bus manufacturing, bus builder located in the town of Botevgrad, Sofia Province. Founded by Racho Dzhambov in 1924, the company that would later become "Chavdar" produced around 200 buses between 1927 and 1947 on chassis from Ford Motor Company, Mercedes-Benz and Dodge. In 1948 the company was nationalised and acquired the name "Chavdar" in honour of the revolutionary Chavdar Voyvoda. It produced buses on chassis of Skoda 706 RTO but later shifted to license production of Setra and Steyr-Daimler-Puch, Steyr buses. It also developed several models on its own, which had good commercial success. The company closed in 1999. History In 1924 Racho Valkov Dzhambov (1894-1983) opened an iron workshop in Botevgrad, Bulgaria. In 1927, Racho met with Ivan Valkov who had a transport business using rebuilt ambulances. He gave Racho one platform from Fiat to build his first vehicle on. After World War II, Bulgaria was ruled by a communist government and Dzhambov's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocar DAC
Rocar DAC was a series of buses and trolleybuses produced by the Autobuzul (later Rocar) company of Bucharest, Romania, between 1979 and 2000. They were available in both standard 12-meter models and articulated, 17-meter models. The first examples to enter service were DAC 117UDs that were made towards the end of 1978 and entered service with the ITB in Bucharest in April 1979. For much of the 1980s and early 1990s, these buses and trolleybuses were the backbone of the urban transportation network of Romania since, throughout the 1980s, public transportation companies were not allowed to import any type of vehicle. The buses were designed and built in a period of severe shortages, the main emphasis being put on economizing material usage and simplicity of the design. Most buses of this type did not have power or assisted steering, and only a small number of buses, built in the early part of the project (1979-1982) employed automatic gearboxes, which were abandoned as soluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |