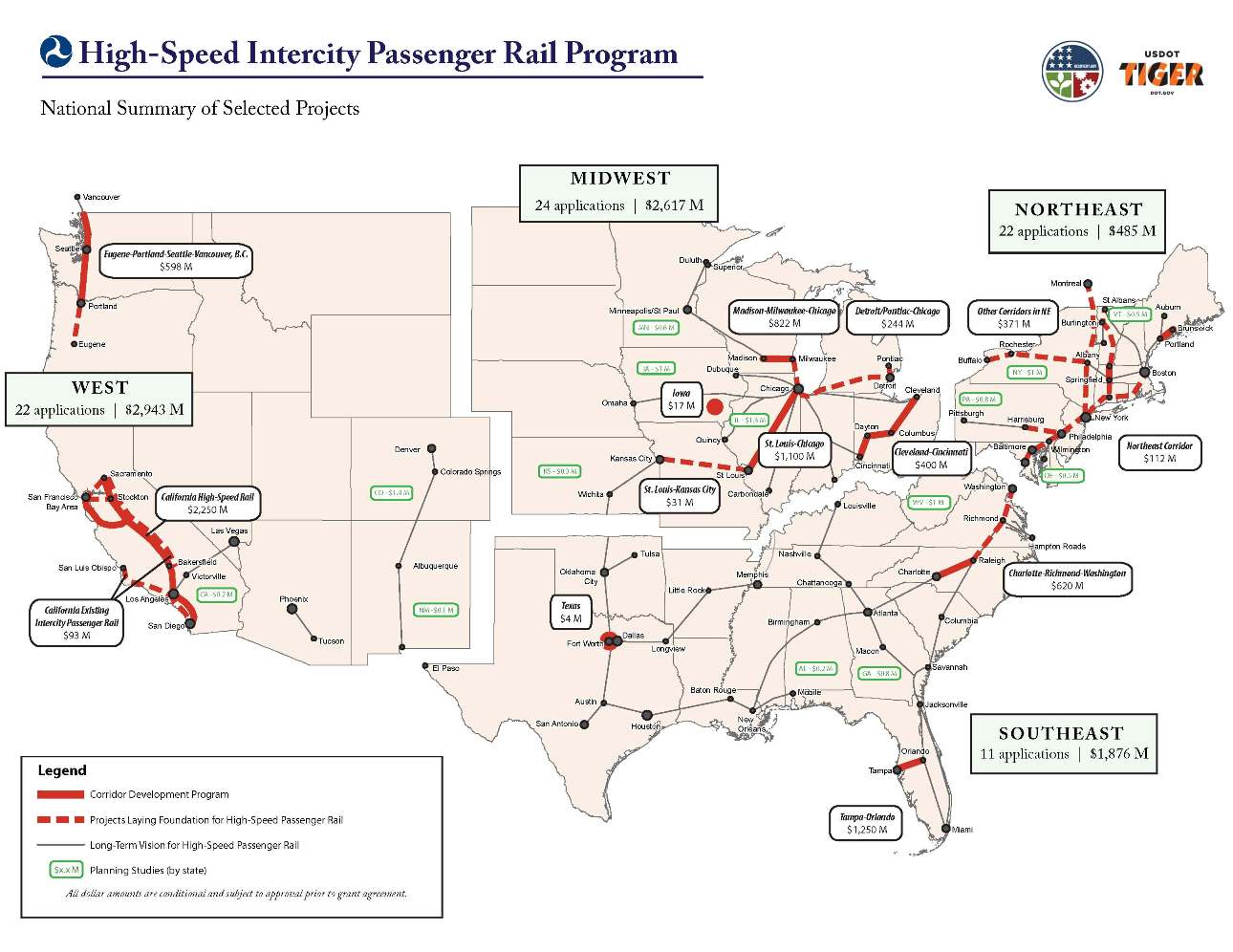
|
Transportation Bill
In the United States, the federal transportation bill refers to any of a number of multi-year funding bills for surface transportation programs. These have included: * Surface Transportation and Uniform Relocation Assistance Act, 1987 * Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act (ISTEA), 1991 * The National Highway System Designation Act (NHS), 1995 * Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21), 1998 * Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA-LU), 2005 * Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21), 2012 * Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act (FAST), 2015 * Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, 2021 Previous multi-year highway spending bills were known as Federal-Aid Highway Act The following bills and Acts of Congress in the United States have been known as the Federal-Aid Highway Act or similar names: * Federal Aid Road Act of 1916: July 11, 1916, ch. 241, (first) * Federal Aid Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Transportation And Uniform Relocation Assistance Act
The Surface Transportation and Uniform Relocation Assistance Act of 1987 (Pub. L. 100–17, 101 Stat. 132) is a United States Act of Congress, containing in Title I, the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1987. History The bill was introduced in House by Glenn Anderson ( D- CA) on January 6, 1987. The bill nominally gave power to apportion money to the Secretary of Transportation. It also allowed states to raise the speed limit to on rural Interstate highways ( of the act, amending ). It was followed by the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act (ISTEA). The local agencies (counties and cities) in California were assured that an equal or not less amount of monies will still be annually apportioned to the counties and cities as they received in 1990–91 under the Federal Highway Act of 1987 under the old Federal Aid Urban (FAU) and Federal Aid Secondary Program. References External links Surface Transportation and Uniform Relocation Assistance Act of 1987 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act
The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 (ISTEA, pronounced ''Ice-Tea'') is a United States federal law that posed a major change to transportation planning and policy, as the first U.S. federal legislation on the subject in the post- Interstate Highway System era. Objective The act presented an overall intermodal approach to highway and transit funding with collaborative planning requirements, giving significant additional powers to metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs). The act was signed into law on December 18, 1991, by President George H. W. Bush and codified as and . The bill was preceded by the Surface Transportation and Uniform Relocation Assistance Act in 1987 and followed by the Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21) in 1998, the Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA-LU) in 2005, the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21) in 2012, the FIxing Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transportation Equity Act For The 21st Century
The United States federal Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21) is a federal transportation bill enacted June 9, 1998, as and . TEA-21 authorized federal surface transportation programs for highways, highway safety, and transit for a 6-year period from 1998 to 2003. Because Congress could not agree on funding levels, the Act, which had continued past 2003 by means of temporary extensions, was allowed to lapse. History The bill was introduced in the House by Bud Shuster ( R– PA) on September 4, 1997. The transportation equity act requires that seven planning factors be included in regional transportation plans. The plans must: # support the economic vitality of the metropolitan planning area, especially by enabling global competitiveness, productivity and efficiency; # increase the safety and security of the transportation system for motorized and non-motorized users ; # increase the accessibility and mobility options available to people and for freight; # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Legacy For Users
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Ahead For Progress In The 21st Century Act
The Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21) is a funding and authorization bill to govern United States federal surface transportation spending. It was passed by Congress on June 29, 2012, and President Barack Obama signed it on July 6. The vote was 373–52 in the House of Representatives and 74–19 in the Senate. The $105 billion two-year bill does not significantly alter total funding from the previous authorization, but does include many significant reforms. The Congressional Budget Office estimates that enacting MAP-21 will reduce the federal budget deficit over the 2012–22 period by $16.3 billion. Key provisions * The number of funding programs is consolidated by two-thirds. * The environmental review process is reformed in an effort to speed up project development. More projects will be categorically excluded from review, and there will be a four-year review deadline enforced with financial penalties. (In 2011 the average review took 8.1 years.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act
The Fixing America's Surface Transportation Act or the FAST Act is a funding and authorization bill to govern United States federal surface transportation spending. It was passed by Congress on December 3, 2015, and President Barack Obama signed it on the following day. The vote was 359–65 in the House of Representatives and 83–16 in the United States Senate. History The bill was introduced to the House by Rodney Davis () as the "Hire More Heroes Act of 2015" on January 6, 2015. The $305 billion, five-year bill is funded without increasing transportation user fees. (The federal gas tax was last raised in 1993.) Instead, funds were generated through changes to passport rules, Federal Reserve Bank dividends, and privatized tax collection. In Section 6021, Congress asked the Transportation Research Board (TRB) to conduct a study of the actions needed to upgrade and restore the Interstate Highway System to fulfill its role as a crucial national asset, serving the needs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrastructure Investment And Jobs Act
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), also known as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Bill and originally in the House as the INVEST in America ActH.R. 3684, is a United States federal statute enacted by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on November 15, 2021. The act was initially a infrastructure package that included provisions related to federal-aid highway, transit, highway safety, motor carrier, research, hazardous materials and rail programs of the Department of Transportation. After congressional negotiations, it was amended and renamed to the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act to include funding for broadband access, clean water and electric grid renewal in addition to the transportation and road proposals of the original House bill. This amended version included approximately $1.2 trillion in spending, with $550 billion being newly authorized spending on top of what Congress was planning to author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal-Aid Highway Act
The following bills and Acts of Congress in the United States have been known as the Federal-Aid Highway Act or similar names: * Federal Aid Road Act of 1916: July 11, 1916, ch. 241, (first) * Federal Aid Highway Act of 1921 (Phipps Act): November 9, 1921, *Amendment and Authorization of 1925: merely continued existing funding, February 12, 1925, *Amendment and Authorization of 1926: June 22, 1926, *Federal Aid for Toll Bridges: March 3, 1927, *Amendment of 1928: May 21, 1928, *Authorization for Forest Roads and Amendment of 1930: May 5, 1930, *Provision for National-Park Approaches: January 31, 1931, * Hayden-Cartwright Act of 1934: June 18, 1934, *Authorization and Amendment of 1936: June 16, 1936, *Federal Aid Highway Act of 1938: June 8, 1938, ch. 328, *Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1944: December 20, 1944, * Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1948: June 29, 1948, *Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1950: September 7, 1950, *Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1952: June 25, 1952, *Federal-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |