Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 (ISTEA, ) is a
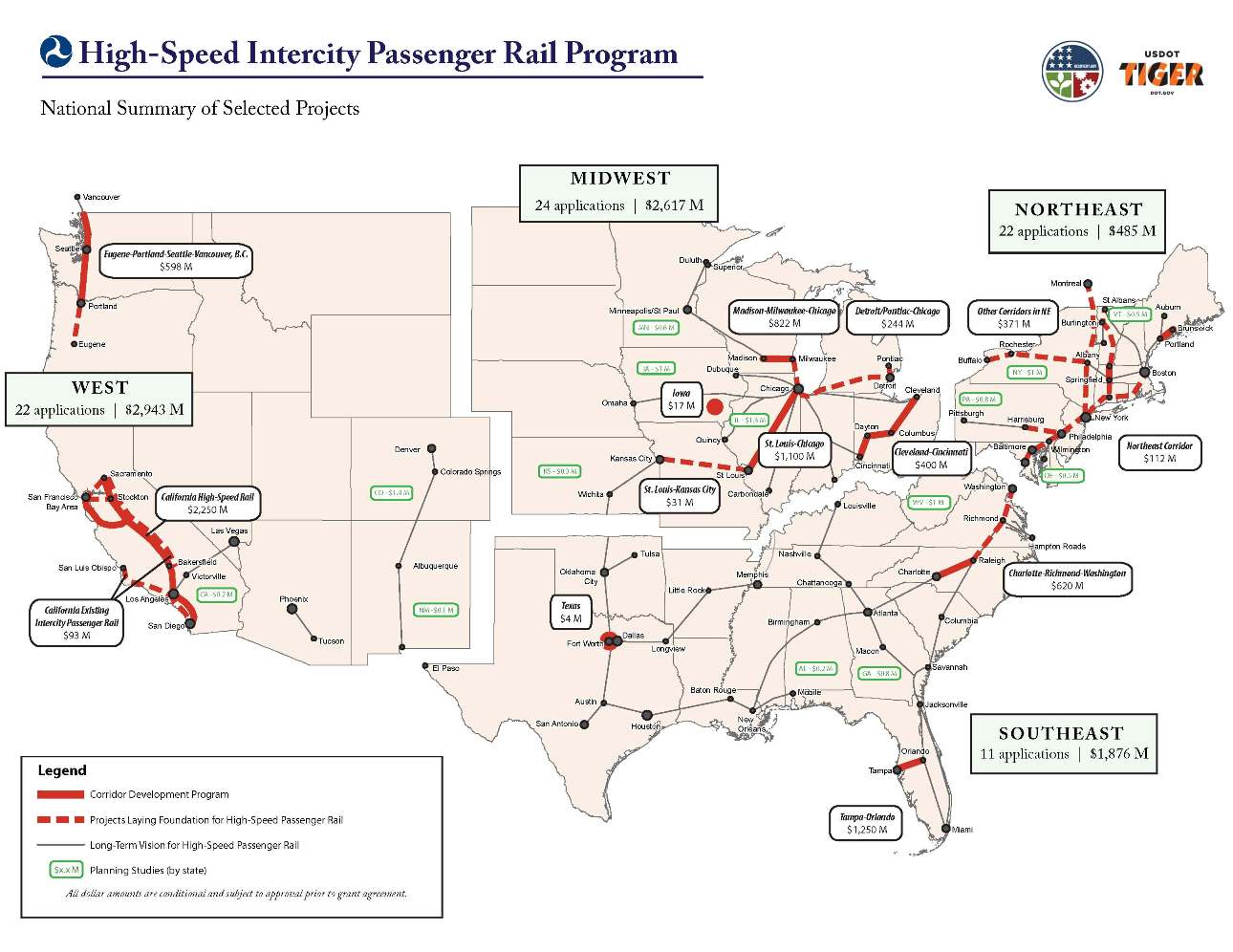 The legislation also called for the designation of up to five
The legislation also called for the designation of up to five
Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991
as amended
PDFdetails
in the GPObr>Statute Compilations collection
Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991
as enacted
details
in the US Statutes at Large * on Congress.gov * on Congress.gov
A Guide to Metropolitan Transportation Planning Under ISTEA - How the Pieces Fit Together (USDOT)
* * {{authority control United States federal transportation legislation United States railroad regulation 1991 in rail transport 1992 in rail transport 102nd United States Congress High-speed rail in the United States Airbags 1991 in American law
United States federal law
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the supreme law is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the ...
that posed a major change to transportation planning
Transportation planning is the process of defining future policies, goals, investments, and spatial planning designs to prepare for future needs to move people and goods to destinations. As practiced today, it is a collaborative process that i ...
and policy, as the first U.S. federal legislation on the subject in the post-Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Hi ...
era.
The act was signed into law on December 18, 1991, by President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
and codified as and . The bill was preceded by the Surface Transportation and Uniform Relocation Assistance Act in 1987 and followed by the Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21) in 1998, the Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA-LU) in 2005, the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21) in 2012, the Fixing America's Surface Transportation Act (FAST) in 2015, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act in 2021.
Objective
The act presented an overall intermodal approach to highway and transit funding with collaborative planning requirements, giving significant additional powers to metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs). ISTEA also provided funds for the conversion of dormant railroad corridors intorail trail
A rail trail or railway walk is a shared-use path on a Right of way#Rail right of way, railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed but may also share the rail corr ...
s; the first rail trail to be funded was the Cedar Lake Regional Rail Trail, in Minneapolis
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Locat ...
, Minnesota.
High priority corridors
Section 1105 of the act also defines a number of High Priority Corridors, to be part of the National Highway System. After various amendments in subsequent transportation bills and other legislation, this is a list of the corridors:High-speed rail corridors
 The legislation also called for the designation of up to five
The legislation also called for the designation of up to five high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated railway track, tracks. While there is ...
corridors. The options were studied for several months, and announced in October 1992. The first four were announced by United States Secretary of Transportation
The United States secretary of transportation is the head of the United States Department of Transportation. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to transportation. The secre ...
Andrew Card
Andrew Hill Card Jr. (born May 10, 1947) is an American politician and Academic administration, academic administrator who was White House Chief of Staff under President George W. Bush from 2001 to 2006, as well as head of Bush's White House Iraq ...
, while the last was announced by Federal Railroad Administration
The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) is an agency in the United States Department of Transportation (DOT). The agency was created by the Department of Transportation Act of 1966. The purpose of the FRA is to promulgate and enforce railroa ...
head Gil Carmichael.
*October 15, 1992: The Midwest high-speed rail corridor with three links from Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, Illinois to Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
, Michigan, St. Louis, Missouri, and Milwaukee
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States ...
, Wisconsin.
*October 16, 1992: The Florida high-speed rail corridor linking Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
with Orlando and Tampa
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
.
*October 19, 1992: The California high-speed rail corridor linking San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
and Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
with the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, commonly known as the Bay Area, is a List of regions of California, region of California surrounding and including San Francisco Bay, and anchored by the cities of Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose, California, S ...
and Sacramento
Sacramento ( or ; ; ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the seat of Sacramento County. Located at the confluence of the Sacramento and American Rivers in Northern California's Sacramento Valley, Sacramento's 2020 p ...
via the San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; Spanish language in California, Spanish: ''Valle de San Joaquín'') is the southern half of California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. Famed as a major breadbasket, the San Joaquin Valley is an importa ...
.
*October 20, 1992: The Southeast high-speed rail corridor connecting Charlotte, North Carolina
Charlotte ( ) is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina and the county seat of Mecklenburg County, North Carolina, Mecklenburg County. The population was 874,579 at the 2020 United ...
, Richmond, Virginia
Richmond ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Virginia. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city (United States), independent city since 1871. ...
, and Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
*October 20, 1992: The Pacific Northwest high-speed rail corridor linking Eugene and Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
with Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
, Washington and Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Canada.
There was not significant funding attached to these announcements: $30 million had been allocated to several states by 1997 to improve grade crossings, but that was a very tiny amount in comparison to the billions required for a true high-speed network. Aside from a few places in California and the Chicago–Detroit Line, most areas outside the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
continued to be limited to until $8 billion from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a Stimulus (economics), stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed ...
was distributed in January 2010.
Jeff Morales one of the principal drafters of this bill, served as CEO of the California High-Speed Rail Authority, which is currently constructing a high-speed rail line along the route originally proposed in this bill, from 2012 to 2017.
Airbags
The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 also mandated that passengerautomobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
s and light trucks built after September 1, 1998, to have airbag
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate in milliseconds during a collision and then deflate afterwards. It consists of an airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. ...
s installed as standard equipment for the driver and the right front passenger.
Notes
References
External links
Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991
as amended
in the GPObr>Statute Compilations collection
Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991
as enacted
details
in the US Statutes at Large * on Congress.gov * on Congress.gov
A Guide to Metropolitan Transportation Planning Under ISTEA - How the Pieces Fit Together (USDOT)
* * {{authority control United States federal transportation legislation United States railroad regulation 1991 in rail transport 1992 in rail transport 102nd United States Congress High-speed rail in the United States Airbags 1991 in American law