|
Transport In Hamburg
Transport in Hamburg comprises an extensive, Rail transport, rail system, rapid transit, subway system, airports and Waterway, maritime services for the more than 1.8 million inhabitants of the city of Hamburg and 5.3 million people in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Since the Middle Ages, as a Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City one part of Hamburg's transport was the economic trade with other cities or regions. In 2008, the port of Hamburg was the second-largest port in Europe. Hamburg is connected to four German Autobahnen, motorways and in Hamburg proper are two airports. The Hamburg traffic group ''Hamburger Verkehrsverbund'' was the first organisation of its kind in the world and in 2008, was in charge for the public transport management in three German states. In 2007, more than 618 million passengers used bus, rapid transit, ferries or light rail. History A charter in 1189 by Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor granted Hamburg the status of a free imperial city and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and rail freight transport, freight transport globally, thanks to its Energy efficiency in transport, energy efficiency and potentially high-speed rail, high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower friction, frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by Diesel locomotive, diesel or Electric locomotive, electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital intensity, capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeperbahn
The Reeperbahn () is a street and entertainment district in Hamburg's St. Pauli district, one of the two centres of Hamburg's nightlife (the other being Sternschanze) and also the city's major red-light district. In German, it is also nicknamed ''die sündige Meile'' (the sinful mile) and '' Kiez''. The Reeperbahn Festival is among the largest club festivals. Name and history The name ''Reeperbahn'' means ropewalk, which is a place where ropes are made ( = rope, the standard German word is ; = track). Until the 1620s Hamburg's ropewalks had been located in the Neustadt (New Town) quarter of the inner city close to the Elbe, which then became a densely built up area. Therefore, the ropewalks "had to be relocated outside the city walls on the country road leading toward Altona – which later took on the street name 'Reperbahn'." The street was a ropewalk in the 17th and 18th centuries. The street and its side streets The street is lined with restaurants, night clubs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuhlsbüttel
is an urban quarter in the north of Hamburg, Germany in the Hamburg-Nord district. It is known as the site of Hamburg's international airport, and as the location of a prison which served as a concentration camp in the Nazi system of repression. As a result of boundary changes, JVA Fuhlsbüttel prison is now in Ohlsdorf, Hamburg. History In 1871, at the declaration of the German Reich the village of Fuhlsbüttel was given to the State of Hamburg. Fuhlsbüttel airship base From 1912 ''Luftschiffhafen'' (Airship Port) Fuhlsbüttel was the first hangar and headquarters of the ''Marine-Luftschiff-Abteilung'' (Naval Airship Division) of the German ''Kaiserliche Marine'' (Imperial Navy). From there and several new bases recon missions over the North Sea and bombing mission against England were flown during World War I. Fuhlsbüttel concentration camp On 4 September 1933, seven months after Hitler’s appointment as Chancellor of Germany, parts of Fuhlsbüttel prison were conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155–157. and developed in detail in 1893.Dooley 2004, p. A.187. They were patented in German Empire, Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word ''zeppelin'' came to be commonly used to refer to all forms of rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins German strategic bombing during World War I, as bombers and aerial reconnaissance in World War I, as scouts. Numerous bombing raids on United Kingdom of Great Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanne-Eickel–Hamburg Railway
The Wanne-Eickel–Hamburg railway is the shortest railway link between the Metropole Ruhr and the Hamburg Metropolitan Region and hence one of the most important railway lines in northwest Germany. The Route runs over the cities Münster (Westfalen), Osnabrück and Bremen. It was built between 1870 and 1874 by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) based in Wanne-Eickel, and branched off their main (Cologne-)Deutz–Minden route as part of the Hamburg-Venlo railway. Today it is an electrified main line which has a minimum of two tracks throughout. Parts of the route are equipped with ''Linienzugbeeinflussung'' train control which enables speeds of up to 200 km/h to be attained. Due to its constant use by goods and passenger trains rolling along the line, day and night, it has been given the nickname ''Rollbahn'' ("Rolling Line"). History The railway was built by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) under contract to the Prussian state as the eastern element of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg Hauptbahnhof
Hamburg Hauptbahnhof (abbrev. ''Hamburg Hbf''), or Hamburg Central Railway Station in English, is the main railway station of the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1906 to replace four separate terminal stations, today Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is operated by DB Station&Service AG. With an average of 550,000 passengers a day, it is Germany's busiest railway station and the second-busiest in Europe after the Gare du Nord in Paris. It is classed by Deutsche Bahn as a category 1 railway station. The station is a through station with island platforms and is one of Germany's major transportation hubs, connecting long-distance Intercity Express routes to the city's U-Bahn and S-Bahn rapid transit networks. It is centrally located in Hamburg in the Hamburg-Mitte borough. The ''Wandelhalle'' shopping centre occupies the north side of the station building. History Before today's central station was opened, Hamburg had several smaller stations located around the city centre. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landungsbrücken
The St. Pauli Piers (, often only referred to as ''Landungsbrücken''; ), is the largest landing site in the Port of Hamburg, Germany, and also one of Hamburg's major tourist attractions. Other English language translations include St. Pauli Landing Stages or St. Pauli Landing Bridges. The piers are located in the St. Pauli area of Hamburg, between the lower harbour and the ''Fischmarkt'' (Fish Market), on the banks of the Elbe river. The ''Landungsbrücken'' today form a central transportation hub, with S-Bahn, U-Bahn and ferry stations, and are also a major tourist magnet with numerous restaurants and departure points for harbour pleasure boats. There is an entrance to the Old Elbe tunnel at the western end of the ''Landungsbrücken''. The eastern end of the building complex is marked by the ''Pegelturm'' (water level tower). Halfway up the tower, there is a water level indicator built into the wall, which indicates the current stage of the tides. Shipping piers The first pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or tram networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Because of their close similarities, trams are commonly included in the wider term ''light rail'', which also includes systems separated from other traffic. Tram vehicles are usually lighter and shorter than main line and rapid transit trains. Most trams use electrical power, usually fed by a pantograph sliding on an overhead line; older systems may use a trolley pole or a bow collector. In some cases, a contact shoe on a third rail is used. If necessary, they may have dual power systems—electricity in city streets and diesel in more rural environments. Occasionally, trams also carry freight. Some tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include segments on segregated Right-of-way (property access), right-of-way. The tramlines or tram networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Because of their close similarities, trams are commonly included in the wider term ''light rail'', which also includes systems separated from other traffic. Tram vehicles are usually lighter and shorter than Main line (railway), main line and rapid transit trains. Most trams use electrical power, usually fed by a Pantograph (transport), pantograph sliding on an overhead line; older systems may use a trolley pole or a bow collector. In some cases, a contact shoe on a third rail is used. If necessary, they may have dual power systems—electricity in city stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsecar
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is a tram or streetcar pulled by a horse. Summary The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public transport, public rail transport, which developed out of wagonway, industrial haulage routes that had long been in existence, and from the Omnibus (Horse-drawn vehicle), horse-drawn omnibus routes that first ran on public streets in the 1820s, using the newly improved iron or steel rail or 'Tramway (industrial), tramway'. They were local versions of the stagecoach lines and picked up and dropped off passengers on a regular route, without the need to be pre-hired. Horsecars on tramlines were an improvement over the omnibus, because the low rolling resistance of metal wheels on iron or steel track (rail transport), rails (usually Rail profile#Grooved rail, grooved Tram#History, from 1852 on) allowed the horses to haul a greater load for a given effort than the omnibus, and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
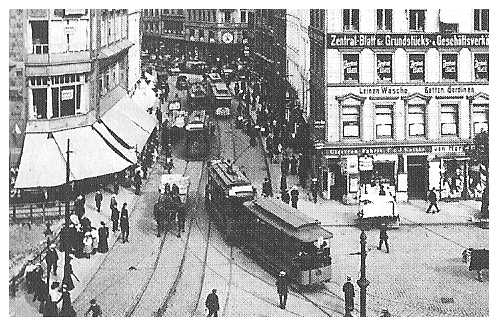
Trams In Hamburg
The Hamburg tramway network () once formed part of the public transport system in the city and federal state of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1866, the network lasted until 1978. Overview Hamburg's first tram service was with horsecars, beginning on 16 August 1866. Operation of steam-powered trams began on 13 May 1878 and continued until 1897, while horsecar service continued on some lines (with the last one surviving until 1922). Electric tram service was introduced on 5 March 1894 and continued until 1978, with the system closing on 1 October 1978. Proposed 21st century system A similar style of transport, light rail, was to have been provided by the Hamburg Stadtbahn project, but following the Hamburg state election, 2011, the newly elected First Mayor of Hamburg, Olaf Scholz, announced that that project would not be going ahead. See also * List of town tramway systems in Germany *Trams in Germany * Hamburg U-Bahn *Hamburg S-Bahn * Transport in Hamburg References Citati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |