|
Transistor Model
Transistors are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design. Models for device design The modern transistor has an internal structure that exploits complex physical mechanisms. Device design requires a detailed understanding of how device manufacturing processes such as ion implantation, impurity diffusion, oxide growth, annealing, and etching affect device behavior. Process models simulate the manufacturing steps and provide a microscopic description of device "geometry" to the device simulator. "Geometry" does not mean readily identified geometrical features such as a planar or wrap-around gate structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminal (electronics), terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or Electric current, current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits. Because transistors are the key active components in practically all modern electronics, many people consider them one of the 20th century's greatest inventions. Physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Circuit Simulation
Electronic circuit simulation uses mathematical models to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit. Simulation software allows for the modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool. Due to its highly accurate modeling capability, many colleges and universities use this type of software for the teaching of electronics technician and electronics engineering programs. Electronics simulation software engages its users by integrating them into the learning experience. These kinds of interactions actively engage learners to analyze, synthesize, organize, and evaluate content and result in learners constructing their own knowledge. Simulating a circuit’s behavior before actually building it can greatly improve design efficiency by making faulty designs known as such, and providing insight into the behavior of electronic circuit designs. In particular, for integrated circuits, the tooling ( photomasks) is expensive, breadboards are impr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-point
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an electronic component that processes time-varying signals. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit that supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects. In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to thermodynamics. Any conductor with electrical resistance will generate thermal noise inherently. The final elimination of thermal noise in electronics can only be achieved cryogenically, and even then quantum noise would remain inherent. Electronic noise is a common component of noise in signal processing. In communication systems, noise is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal in a communication channel. The noise is a summation of unwanted or disturbing energy from natural and sometimes man-made sources. Noise is, however, typically distinguished from interference, for example in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and signal-to-noise plus interference ratio (SNIR) measures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gain (electronics)
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units ("dB gain"). A gain greater than one (greater than zero dB), that is, amplification, is the defining property of an active device or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one. The term ''gain'' alone is ambiguous, and can refer to the ratio of output to input voltage (''voltage gain''), current (''current gain'') or electric power (''power gain''). In the field of audio and general purpose amplifiers, especially operational amplifiers, the term usually refers to voltage gain, but in radio frequency amplifiers it usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIBO Stability
In signal processing, specifically control theory, bounded-input, bounded-output (BIBO) stability is a form of stability for signals and systems that take inputs. If a system is BIBO stable, then the output will be bounded for every input to the system that is bounded. A signal is bounded if there is a finite value B > 0 such that the signal magnitude never exceeds B, that is :For discrete-time signals: \exists B \forall n(\ , y \leq B) \quad n \in \mathbb :For continuous-time signals: \exists B \forall t(\ , y(t), \leq B) \quad t \in \mathbb Time-domain condition for linear time-invariant systems Continuous-time necessary and sufficient condition For a continuous time linear time-invariant (LTI) system, the condition for BIBO stability is that the impulse response, h(t) , be absolutely integrable, i.e., its L1 norm exists. : \int_^\infty \left, h(t)\\,\mathordt = \, h \, _1 \in \mathbb Discrete-time sufficient condition For a discrete time LTI system, the condition f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
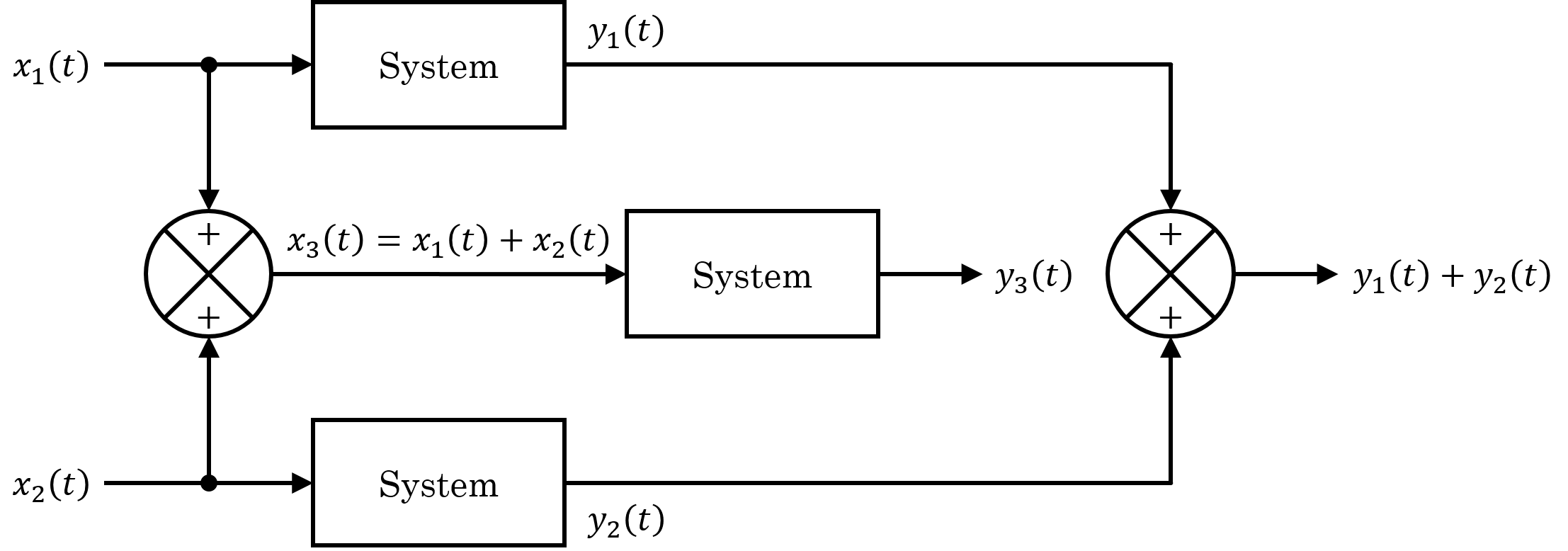
Linear System
In systems theory, a linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator. Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications. For example, the propagation medium for wireless communication systems can often be modeled by linear systems. Definition A general deterministic system can be described by an operator, , that maps an input, , as a function of to an output, , a type of black box description. A system is linear if and only if it satisfies the superposition principle, or equivalently both the additivity and homogeneity properties, without restrictions (that is, for all inputs, all scaling constants and all time.) The superposition principle means that a linear combination of inputs to the system produces a linear com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-signal Model
Small-signal modeling is a common analysis technique in electronics engineering used to approximate the behavior of electronic circuits containing nonlinear devices, such as diodes, transistors, vacuum tubes, and integrated circuits, with linear equations. It is applicable to electronic circuits in which the AC signals (i.e., the time-varying currents and voltages in the circuit) are small relative to the DC bias currents and voltages. A small-signal model is an AC equivalent circuit in which the nonlinear circuit elements are replaced by linear elements whose values are given by the first-order (linear) approximation of their characteristic curve near the bias point. Overview Many of the electrical components used in simple electric circuits, such as resistors, inductors, and capacitors are linear. Circuits made with these components, called linear circuits, are governed by linear differential equations, and can be solved easily with powerful mathematical frequency domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
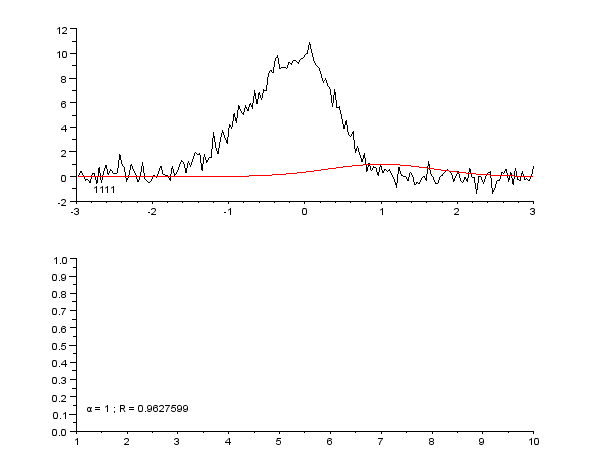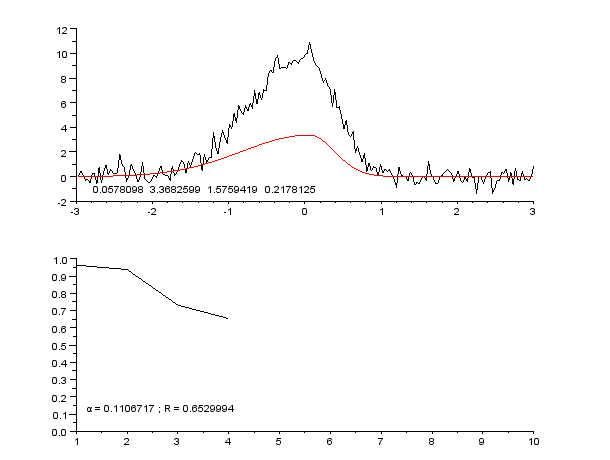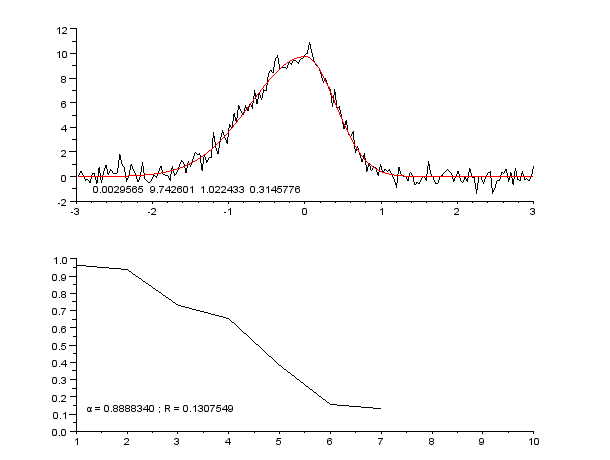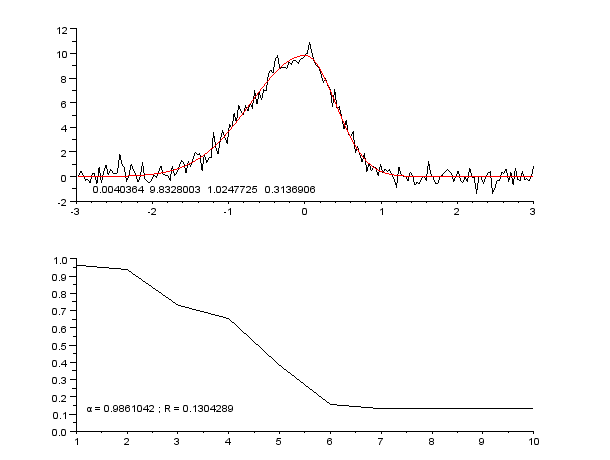
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fitted to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinearity
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current–voltage Characteristic
A current–voltage characteristic or I–V curve (current–voltage curve) is a relationship, typically represented as a chart or graph, between the electric current through a circuit, device, or material, and the corresponding voltage, or potential difference, across it. In electronics In electronics, the relationship between the direct current (DC) through an electronic device and the DC voltage across its terminals is called a current–voltage characteristic of the device. Electronic engineering, Electronic engineers use these charts to determine basic parameters of a device and to model its behavior in an electrical circuit. These characteristics are also known as I–V curves, referring to the standard symbols for current and voltage. In electronic components with more than two terminals, such as vacuum tubes and transistors, the current–voltage relationship at one pair of terminals may depend on the current or voltage on a third terminal. This is usually display ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |