|
Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers Order of the British Empire, MBE (22 December 1905 – 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's first programmable electronic computer, to help decipher encrypted German messages. Early life Flowers was born at 160 Abbott Road, Bromley-by-Bow, then the Metropolitan Borough of Poplar, on 22 December 1905, the son of a bricklayer. He came from an impoverished working class background and his grandmother had been a charwoman. He later recalled that as children "we were taught to be frugal in everything". Whilst undertaking an apprenticeship in mechanical engineering at the Royal Arsenal, Woolwich, he took evening classes at the University of London to earn a degree in electrical engineering. In 1926, he joined the telecommunications branch of the General Post Office (GPO), moving to the Post Office Research Station at Dollis Hill in Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the Second World War. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powers most importantly the German Enigma machine, Enigma and Lorenz cipher, Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included John Tiltman, Dilwyn Knox, Alan Turing, Harry Golombek, Gordon Welchman, Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander, Hugh Alexander, Donald Michie, W. T. Tutte, Bill Tutte and Stuart Milner-Barry. The team at Bletchley Park devised automatic machinery to help with decryption, culminating in the development of Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's first programmable digital electronic computer. Codebreaking operations at Bletchley Park ended in 1946 and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office Research Station
The Post Office Research Station was first established as a separate section of the General Post Office in 1909. In 1921, the Research Station moved to Dollis Hill, north west London, initially in ex-army huts. The main permanent buildings at Dollis Hill were opened in 1933 by Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald. In 1968 it was announced that the station would be relocated to a new centre to be built at Martlesham Heath in Suffolk. This was formally opened on 21 November 1975 by Queen Elizabeth and is today known as Adastral Park. The old Dollis Hill site was released for housing, with the main building converted into a block of luxury flats and an access road named Flowers Close, in honour of Tommy Flowers. Much of the rest of the site contains affordable housing administered by Network Housing. World War II In 1943 the world's first programmable electronic computer, Colossus Mark 1, was built by Tommy Flowers and his team, followed in 1944 and 1945 by nine Colossus Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
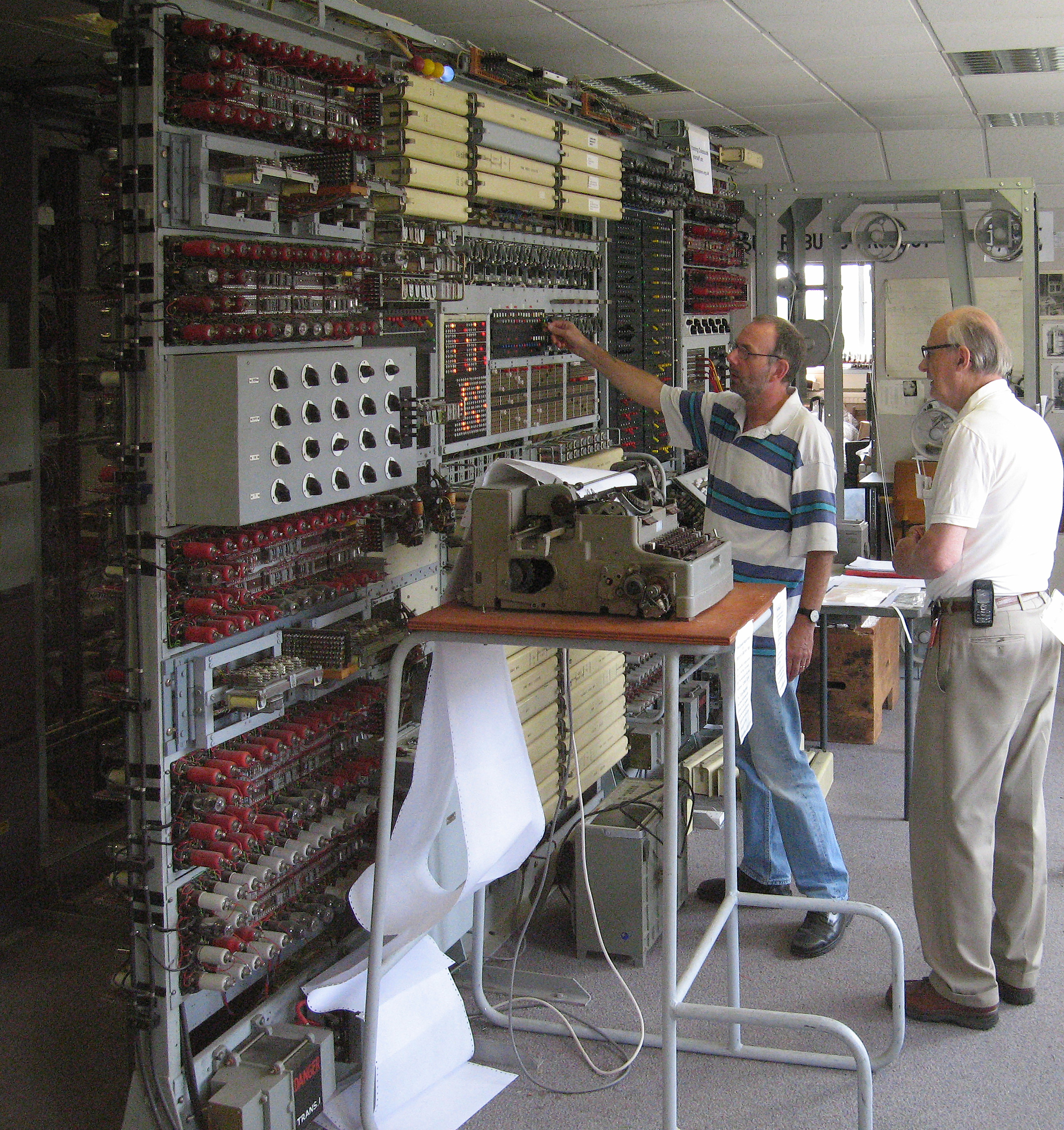
Heath Robinson (codebreaking Machine)
Heath Robinson was a machine used by British codebreakers at the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park during World War II in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. This achieved the decryption of messages in the German teleprinter cipher produced by the Lorenz SZ40/42 in-line cipher machine. Both the cipher and the machines were called "Tunny" by the codebreakers, who named different German teleprinter ciphers after fish. It was mainly an electro-mechanical machine, containing no more than a couple of dozen valves (vacuum tubes), and was the predecessor to the electronic Colossus computer. It was dubbed "Heath Robinson" by the Wrens who operated it, after cartoonist William Heath Robinson, who drew immensely complicated mechanical devices for simple tasks, similar to (and somewhat predating) Rube Goldberg in the U.S. The functional specification of the machine was produced by Max Newman. The main engineering design was the work of Frank Morrell at the Post Off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenz Cipher
The Lorenz SZ40, SZ42a and SZ42b were German Rotor machine, rotor stream cipher machines used by the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army during World War II. They were developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The model name ''SZ'' is derived from ''Schlüssel-Zusatz'', meaning ''cipher attachment''. The instruments implemented a Gilbert Vernam#The Vernam cipher, Vernam stream cipher. British cryptanalysts, who referred to encrypted German Electrical telegraph, teleprinter traffic as Fish (cryptography), ''Fish'', dubbed the machine and its traffic ''Tunny'' (meaning tunafish) and deduced its logical structure three years before they saw such a machine. The SZ machines were in-line attachments to standard teleprinters. An experimental link using SZ40 machines was started in June 1941. The enhanced SZ42 machines were brought into substantial use from mid-1942 onwards for high-level communications between the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht, German High Command in Wünsdorf close to Berlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis Of The Lorenz Cipher
Cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher was the process that enabled the British to read high-level German army messages during World War II. The British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park decrypted many communications between the ''Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW, German High Command) in Berlin and their army commands throughout occupied Europe, some of which were signed "Adolf Hitler, Führer". These were intercepted non-Morse code, Morse radio transmissions that had been enciphered by the Lorenz cipher, Lorenz SZ teleprinter Rotor machine, rotor stream cipher attachments. Decrypts of this traffic became an important source of "Ultra (cryptography), Ultra" intelligence, which contributed significantly to Allied victory. For its high-level secret messages, the German armed services enciphered each Character (computing), character using various online ''Geheimschreiber'' (secret writer) stream cipher machines at both ends of a Electrical telegraph, telegraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Newman
Maxwell Herman Alexander Newman, FRS (7 February 1897 – 22 February 1984), generally known as Max Newman, was a British mathematician and codebreaker. His work in World War II led to the construction of Colossus, the world's first operational, programmable electronic computer, and he established the Royal Society Computing Machine Laboratory at the University of Manchester, which produced the world's first working, stored-program electronic computer in 1948, the Manchester Baby. Early life and education Newman was born Maxwell Herman Alexander Neumann in Chelsea, London, England, to a Jewish family, on 7 February 1897. His father was Herman Alexander Neumann, originally from the German city of Bromberg (now in Poland), who had emigrated with his family to London at the age of 15.William Newman, "Max Newman – Mathematician, Codebreaker and Computer Pioneer", pp. 176–188 in Herman worked as a secretary in a company, and married Sarah Ann Pike, an Irish schoolteacher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enigma Machine
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early- to mid-20th century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication. It was employed extensively by Nazi Germany during World War II, in all branches of the Wehrmacht, German military. The Enigma machine was considered so secure that it was used to encipher the most top-secret messages. The Enigma has an electromechanical Rotor machine, rotor mechanism that scrambles the 26 letters of the alphabet. In typical use, one person enters text on the Enigma's keyboard and another person writes down which of the 26 lights above the keyboard illuminated at each key press. If plaintext is entered, the illuminated letters are the ciphertext. Entering ciphertext transforms it back into readable plaintext. The rotor mechanism changes the electrical connections between the keys and the lights with each keypress. The security of the system depends on machine settings that were generally changed daily, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decrypt
In cryptography, encryption (more specifically, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Despite its goal, encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often used in military m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombe
The bombe () was an Electromechanics, electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma machine, Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The United States Navy, US Navy and United States Army, US Army later produced their own machines to the same functional specification, albeit engineered differently both from each other and from Polish and British bombes. The British bombe was developed from a device known as the "Bomba (cryptography), bomba" (), which had been designed in Poland at the Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau) by cryptologist Marian Rejewski, who had been breaking German Enigma machine, Enigma messages for the previous seven years, using it and earlier machines. The initial design of the British bombe was produced in 1939 at the UK Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park by Alan Turing, with an important refinement devised in 1940 by Gordon Welchman. The engineering design and construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (, abbreviated ''Bucks'') is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-east, Hertfordshire to the east, Greater London to the south-east, Berkshire to the south, and Oxfordshire to the west. The largest settlement is the city of Milton Keynes, and the county town is Aylesbury. The county has an area of and had a population of 840,138 at the 2021 census. ''plus'' Besides Milton Keynes, which is in the north-east, the largest settlements are in the southern half of the county and include Aylesbury, High Wycombe, and Chesham. For Local government in England, local government purposes Buckinghamshire comprises two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authorities, Buckinghamshire Council and Milton Keynes City Council. The Historic counties of England, historic county had slightly different borders, and included the towns of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from University of Cambridge, King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra (cryptography), Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |