|
Tombusvirus 5′ UTR
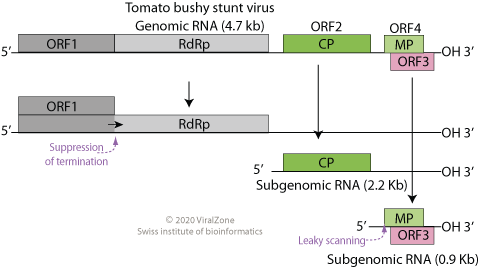
Tombusvirus 5′ UTR is an important cis-regulatory region of the Tombus virus genome. Tomato bushy stunt virus is the prototype member of the Tombusviridae family. The genome of this virus is positive sense single stranded RNA. Replication occurs via a negative strand RNA intermediate. In addition to viral proteins p33 and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase p92, and unknown host factors, conserved and structural regions within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) are important for regulating genome replication. 2 RNA domains in the 5′ UTR have been reported, a 5′ T-shaped domain (TSD) followed by a stem-loop (SL5) and a downstream domain (DSD). TSD-DSD interactions are proposed to be involved in the mediation of viral RNA replication. An interesting feature of Tombusvirus is its ability to support the replication of defective interfering (DI) RNAs. These sub-viral replicons are small, non-coding, deletion mutants of the viral genome that maintain cis-acting RNA elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 1949, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombusvirus
''Tombusvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Tombusviridae''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Symptoms associated with this genus include mosaic. The name of the genus comes from Tomato bushy stunt virus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by their common names: * ''Tombusvirus algeriaense'', Grapevine Algerian latent virus * ''Tombusvirus bulgariaense'', Cucumber Bulgarian latent virus * ''Tombusvirus cucumis'', Cucumber necrosis virus * ''Tombusvirus cymbidii'', Cymbidium ringspot virus * ''Tombusvirus cynarae'', Artichoke mottled crinkle virus * ''Tombusvirus dianthi'', Carnation Italian ringspot virus * ''Tombusvirus havelfluminis'', Havel River virus * ''Tombusvirus latofluminis'', Lato River virus * ''Tombusvirus limonii'', Limonium flower distortion virus * ''Tombusvirus lycopersici'', Tomato bushy stunt virus * ''Tombusvirus melongenae'', Eggplant mottled crinkl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombusviridae
''Tombusviridae'' is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. The family contains 18 genera in 3 subfamilies. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV). Genome All viruses in the family have a non-segmented (monopartite) linear genome, with the exception of Dianthoviruses, whose genome is bipartite. The genome is approximately 4.6–4.8kb in length, lacks a 5' cap and a poly(A) tail, and it encodes 4–6 ORFs. The polymerase encodes an amber stop codon which is the site of a readthrough event within ORF1, producing two products necessary for replication. There is no helicase encoded by the virus. ICTVFamily - Tombusviridae in: Virus Taxonomy. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses 2012, pp 1111-1138, 23 November 2011, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-384684-6.00096-3 Structure The RNA is encapsulated in an icosahedral (T=3) capsid, composed of 180 units of a single coat protein 27–42K in size; the virion meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-sense RNA
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, the negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply sense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Prime Untranslated Region
The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Despite its name, the 5′ UTR, or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product may involve in regulation of transcription, and translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA, such as the sex-lethal gene in '' Drosophila''. Regulatory elements within 5′ UTRs have also been linked to mRNA export. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming a complex secondary structure to regulate translation. General structure Length The 5′ UTR begins at the transcription start site and ends one nucleotide (nt) before the initiation sequence (usually AUG) of the coding region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not Translation (genetics), translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important list of RNAs, types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, Extracellular RNA, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long noncoding RNA, long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent Transcriptomics, transcriptomic and Bioinformatics, bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have unknown functions, if any. There is no consensus on how much of non-coding transcription is functional: some believe most ncRNAs to be non-functional "junk RNA", spurious transcriptions, while others expect that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombusvirus 3′ UTR Region IV
Tombusvirus 3′ UTR is an important cis-regulatory region of the Tombus virus genome. Tomato bushy stunt virus is the prototype member of the family Tombusviridae. The genome of this virus is positive sense single stranded RNA. Replication occurs via a negative strand RNA intermediate. In addition to viral proteins p33 and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase p92, and unknown host factors, conserved and structural regions within the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) are important for regulating genome replication. This 3′ structural element contains a pseudoknot. Other non-coding RNA structures in Tombusvirus include the 5′ UTR The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of t ... and an internal replication element. References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombusvirus Internal Replication Element (IRE)
In virology, the tombusvirus internal replication element (IRE) is a segment of RNA located within the region coding for p92 polymerase. This element is essential for viral replication; specifically, it is thought to be required at an early stage of replication, such as template recruitment and/or replicase complex assembly. Other non-coding RNA structures in Tombusvirus include the 3' UTR region IV and 5' UTR The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly Upstream and downstream (DNA), upstream from the initiation codon. This region is im .... References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory RNA Elements
''Cis-acting replication elements (cre)'' bring together the 5′ and 3′ ends during replication of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses (for example Picornavirus, Flavivirus, Coronavirus, Togaviruses, Hepatitis C virus) and double-stranded RNA viruses (for example rotavirus and reovirus). ''Cre'' are regions of the viral RNA that act as regulatory signals for essential steps in the virus life cycle. These regions typically fold into loop-like structures and are located in the protein-making part of the genome called the translated region or flanking these regions in parts of the genome called the untranslated region. These folded RNA structures interact with proteins from the virus or host to manage processes like making new viral proteins and replicating the virus’ genetic material. The exact shape and role of these structures vary between different types of viruses. Function of ''cres'' in Viral Replication Positive-Sense RNA Virus Replication The replication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |