|
Toluca Otomi
Temoaya Otomi, also known as Toluca Otomi or Otomi of San Andrés Cuexcontitlan, is a variety of the Otomi language spoken in Mexico by ca. 37,000 people in and around the municipality of Temoaya, and in three communities within the municipality of Toluca: San Andrés Cuexcontitlán, San Pablo Autopan and San Cristobal Huichochitlan. The two varieties are quite different. The speakers themselves call the language . Lastra (2001) classifies it as a southwestern dialect along with the dialects of Mexico state. Lastra also notes that the endangered Otomí dialect of San Felipe in eastern Michoacán is most similar to the Otomí spoken in San Andrés Cuexcontitlan. Grammar Pronominal system The pronominal system of Toluca Otomi distinguish four persons: 1st inclusive and exclusive, second and third and three numbers singular, dual and plural. Nouns Otomi nouns are inflected for possession. The particular pattern of possessive inflection is widespread throughout the Mesoamerican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the List of countries by area, thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the List of countries by population, tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the Hispanophone#Countries, largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city, which ranks among the List of cities by population, most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subjunctive
The subjunctive (also known as the conjunctive in some languages) is a grammatical mood, a feature of an utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreality, such as wish, emotion, possibility, judgment, opinion, obligation, or action, that has not yet occurred. The precise situations in which they are used vary from language to language. The subjunctive is one of the irrealis moods, which refer to what is not necessarily real. It is often contrasted with the indicative, a realis mood which principally indicates that something is a statement of fact. Subjunctives occur most often, although not exclusively, in subordinate clauses, particularly ''that''-clauses. Examples of the subjunctive in English are found in the sentences "I suggest that you ''be'' careful" and "It is important that she ''stay'' by your side." Indo-European languages Proto-Indo-European The Proto-Indo-European lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allomorph
In linguistics, an allomorph is a variant phonetic form of a morpheme, or in other words, a unit of meaning that varies in sound and spelling without changing the meaning. The term ''allomorph'' describes the realization of phonological variations for a specific morpheme. The different allomorphs that a morpheme can become are governed by morphophonemic rules. These phonological rules determine what phonetic form, or specific pronunciation, a morpheme will take based on the phonological or morphological context in which it appears. Allomorphy in English involves the variation of morphemes in their phonetic form based on specific linguistic contexts, a phenomenon governed by morphophonemic rules. For instance, the past tense morpheme "-ed" can manifest in different forms—[-əd], [-t], or [-d]—depending on the final sound of the verb stem. This variability is not random but follows predictable patterns, such as the insertion of a schwa [ə] or assimilation to the voicing of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metathesis (linguistics)
Metathesis ( ; from Greek , from "to put in a different order"; Latin: ''transpositio'') is the transposition of sounds or syllables in a word or of words in a sentence. Most commonly, it refers to the interchange of two or more contiguous segments or syllables, known as adjacent metathesis or local metathesis: * ''anemone'' > ''**anenome'' (onset consonants of adjacent syllables) * ''cavalry'' > ''**calvary'' (codas of adjacent syllables) Metathesis may also involve interchanging non-contiguous sounds, known as nonadjacent metathesis, long-distance metathesis, or hyperthesis, as shown in these examples of metathesis sound change from Latin to Spanish: * Latin > Spanish "word" * Latin > Spanish "miracle" * Latin > Spanish "danger, peril" * Latin > Spanish "crocodile" Many languages have words that show this phenomenon, and some even use it as a regular part of their grammar, such as Hebrew and Fur. The process of metathesis has altered the shape of many familiar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibilant
Sibilants (from 'hissing') are fricative and affricate consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ''genre''. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to denote the sibilant sounds in these words are, respectively, . Sibilants have a characteristically intense sound, which accounts for their paralinguistic use in getting one's attention (e.g. calling someone using "psst!" or quieting someone using "shhhh!"). Overview In the hissing sibilants and , the back of the tongue forms a narrow channel (is '' grooved'') to focus the stream of air more intensely, resulting in a high pitch. With the hushing sibilants (occasionally termed ''shibilants''), such as English , , , and , the tongue is flatter, and the resulting pitch lower. A broader category is stridents, which include more fricati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is a phonological rule in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – must share certain distinctive features (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, meaning that the affected vowels do not need to be immediately adjacent, and there can be intervening segments between the affected vowels. Generally one vowel will trigger a shift in other vowels, either progressively or regressively, within the domain, such that the affected vowels match the relevant feature of the trigger vowel. Common phonological features that define the natural classes of vowels involved in vowel harmony include vowel backness, vowel height, nasalization, roundedness, and advanced and retracted tongue root. Vowel harmony is found in many agglutinative languages. The given domain of vowel harmony taking effect often spans across morpheme boundaries, and suffixes and prefixes will usually follow vowel harmony rules. Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusative
In grammar, the accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to receive the direct object of a transitive verb. In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: "me", "him", "her", "us", "whom", and "them". For example, the pronoun ''she'', as the subject of a clause, is in the nominative case ("She wrote a book"); but if the pronoun is instead the object of the verb, it is in the accusative case and ''she'' becomes ''her'' ("Fred greeted her"). For compound direct objects, it would be, e.g., "Fred invited her and me to the party". The accusative case is used in many languages for the objects of (some or all) prepositions. It is usually combined with the nominative case (for example in Latin). The English term, "accusative", derives from the Latin , which, in turn, is a translation of the Greek . The word can also mean "causative", and that might have derived from the Greeks, but the sense of the Roman translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphosyntactic Alignment
In linguistics, morphosyntactic alignment is the grammatical relationship between arguments—specifically, between the two arguments (in English, subject and object) of transitive verbs like ''the dog chased the cat'', and the single argument of intransitive verbs like ''the cat ran away''. English has a '' subject,'' which merges the more active argument of transitive verbs with the argument of intransitive verbs, leaving the '' object'' in transitive verbs distinct; other languages may have different strategies, or, rarely, make no distinction at all. Distinctions may be made morphologically (through case and agreement), syntactically (through word order), or both. Terminology Dixon (1994) The following notations will be used to discuss the various types of alignment: *S (from ''sole''), the subject of an intransitive verb; *A (from ''agent''), the subject of a transitive verb; *O (from ''object''), the object of a transitive verb. Some authors use the label P (from ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
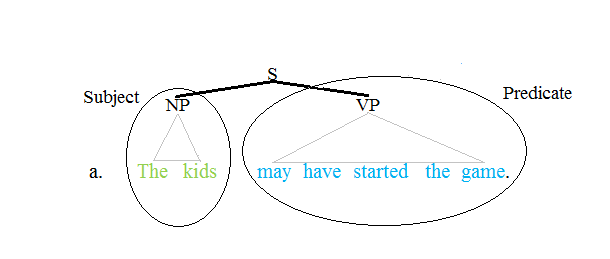
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Grammar
Spanish is a grammatically inflected language, which means that many words are modified ("marked") in small ways, usually at the end, according to their changing functions. Verbs are marked for tense, aspect, mood, person, and number (resulting in up to fifty conjugated forms per verb). Nouns follow a two-gender system and are marked for number. Personal pronouns are inflected for person, number, gender (including a residual neuter), and a very reduced case system; the Spanish pronominal system represents a simplification of the ancestral Latin system. Spanish was the first of the European vernaculars to have a grammar treatise, ', published in 1492 by the Andalusian philologist Antonio de Nebrija and presented to Queen Isabella of Castile at Salamanca. The (RAE, Royal Spanish Academy) traditionally dictates the normative rules of the Spanish language, as well as its orthography. Differences between formal varieties of Peninsular and American Spanish are remark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |