|
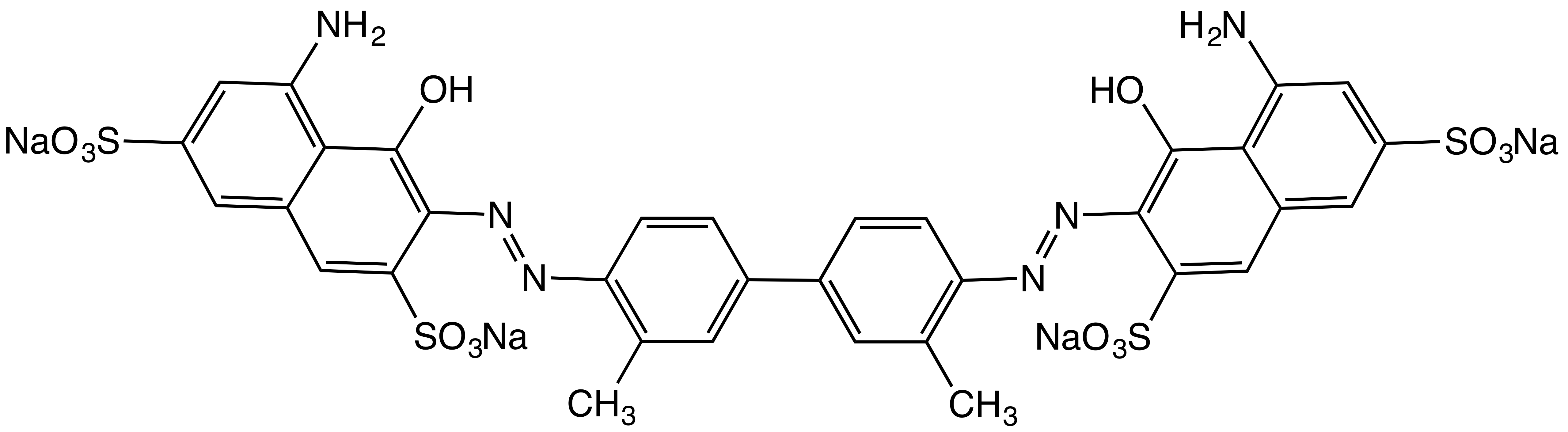
Tolidine
2-Tolidine (orthotolidine, o-tolidine; not to be confused with ''o''-toluidine) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Several isomers are known; the 3-tolidine derivative is also important commercially. It is a colorless compound although commercial samples are often colored. It is slightly soluble in water. It forms salts with acids, such as the hydrochloride, which is commercially available. 2-Tolidine can be produced by benzidine rearrangement from a hydrazone derivative of 2-nitrotoluene. : Uses 2-Tolidine is an aromatic amine used mainly for dye production.K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. 2-Tolidine is an intermediate for the production of soluble azo dyes and insoluble pigments used particularly in the textile, leather and paper industries. It is also used for the production of certain elastomers. left, 200px, Orthotolidine in chlorine test kit 2-Tolidine was widely u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IARC Group 2B Carcinogens
IARC group 2B substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances are those that have been classified as "possibly carcinogenic to humans" by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as This category is used when there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans and less than sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. It may also be used when there is insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but sufficient evidence in experimental animals. In some cases, an agent, mixture, or exposure circumstance with inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but limited evidence in experimental animals, combined with supporting evidence from other relevant data, may be included in this group. This list focuses on the hazard linked to the agents. This means that the carcinogenic agents are capable of causing cancer, but this does not take their risk into account, which is the probability of causing a cancer given the level of exposure to thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluidine
There are three isomers of toluidine, which are organic compounds discovered and named by James Sheridan Muspratt and August Wilhelm von Hofmann in 1845. These isomers are O-Toluidine, ''o''-toluidine, ''m''-toluidine, and ''p''-toluidine, with the prefixed letter abbreviating, respectively, arene substitution pattern#Ortho, meta, and para substitution, ''ortho''; ''meta''; and ''para''. All three are aryl amines whose chemical structures are similar to aniline except that a methyl group is substituted onto the benzene ring. The difference between these three isomers is the position where the methyl group (–CH3) is bonded to the ring relative to the amino functional group (–NH2); see illustration of the chemical structures below. The chemical properties of the toluidines are quite similar to those of aniline, and toluidines have properties in common with other aromatic amines. Due to the amino group bonded to the aromatic ring, the toluidines are weak base, weakly basic. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-Toluidine
''o''-Toluidine (''ortho''-toluidine) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3C6H4NH2. It is the most important of the three isomeric toluidines. It is a colorless liquid although commercial samples are often yellowish. It is a precursor to the herbicides metolachlor and acetochlor. Synthesis and reactions ''o''-Toluidine is produced industrially by nitration of toluene to give a mixture of nitrotoluenes, favoring the ortho isomer. This mixture is separated by distillation. 2-Nitrotoluene is hydrogenated to give o-toluidine. The conversion of ''o''-toluidine to the diazonium salt gives access to the 2-bromo, 2-cyano-, and 2-Chlorotoluene, 2-chlorotoluene derivatives. N-acetylation is also demonstrated. Safety The LD50 (oral, rats) is 670 mg/kg. Binding of hemoglobin ''o''-Nitrosotoluene, a metabolite of ''o''-toluidine, converts hemoglobin to methemoglobin, resulting in methemoglobinemia. ''o''-Nitrosotoluene is suspected of causing bladder cancer in rats. Nitro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions ( anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network. Salts usually form crystalline structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid. Uses Converting amines into their hydrochlorides is a common way to improve their water solubility, which can be desirable for substances used in medications. The European Pharmacopoeia lists more than 200 hydrochlorides as active ingredients in medications. These hydrochlorides, compared to free bases, may more readily dissolve in the gastrointestinal tract and be absorbed into the bloodstream more quickly. Additionally, many hydrochlorides of amines have a longer shelf-life than their respective free bases. Amine hydrochlorides represent latent forms of a more reactive free base. In this regard, formation of an amine hydrochloride confers protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzidine Rearrangement
Benzidine ( trivial name), also called 1,1'- biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer. Synthesis and properties Benzidine is prepared in a two step process from nitrobenzene. First, the nitrobenzene is converted to 1,2-diphenylhydrazine, usually using iron powder as the reducing agent. Treatment of this hydrazine with mineral acids induces a rearrangement reaction to 4,4'-benzidine. Smaller amounts of other isomers are also formed. The benzidine rearrangement, which proceeds intramolecularly, is a classic mechanistic puzzle in organic chemistry. : The conversion is described as a ,5 sigmatropic reaction. : In terms of its physical properties, 4,4'-benzidine is poorly soluble in cold water but can be recrystallized from hot water, where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazone
Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure . They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the = functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes. Synthesis Hydrazine, organohydrazines, and 1,1-diorganohydrazines react with aldehydes and ketones to give hydrazones. : Phenylhydrazine reacts with reducing sugars to form hydrazones known as osazones, which was developed by German chemist Emil Fischer as a test to differentiate monosaccharides. Uses image:Pigment Yellow 97.svg, left, Pigment Yellow 97, a popular yellow colorant, is a hydrazone., 160px Hydrazones are the basis for various analyses of ketones and aldehydes. For example, dinitrophenylhydrazine coated onto a silica sorbent is the basis of an adsorption cartridge. The hydrazones are then eluted and analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a ultraviolet, UV detector. The compound carbonyl cyanide-p-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Nitrotoluene
2-Nitrotoluene or ''ortho''-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is pale yellow liquid that crystallizes in two forms, called α (−9.27 °C) and β (−3.17 °C). It is mainly a precursor to o-toluidine, which is an intermediate in the production of various dyes. Synthesis and reactions It is made by nitrating toluene at above -10 °C. This reaction affords a 2:1 mixture of 2-nitro and 4-nitro isomers. Chlorination of 2-nitrotoluene gives two isomers of the chloronitrotoluenes. Similarly nitration gives two isomers of dinitrotoluene. 2-Nitrotoluene is mainly consumed in the production of o-toluidine ''o''-Toluidine (''ortho''-toluidine) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3C6H4NH2. It is the most important of the three isomeric toluidines. It is a colorless liquid although commercial samples are often yellowish. It is a precu ..., a precursor to dyes. References External linksCDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Amine
In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ... consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses anilines, but also many more complex aromatic rings and many amine substituents beyond . Such compounds occur widely. Aromatic amines are widely used as precursor to pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and dyes. Aromatic amines in textiles Since August 2012, the new standard EN 14362-1:2012 ''Textiles - Methods for determination of certain aromatic amines derived from azo colorants - Part 1: Detection of the use of certain azo colorants accessible with and without extracting the fibres'' is effective. It had been officially approved by the European Committee for Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for cellulose-based textil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |