|
Tin-Lun Ho
Tin-Lun "Jason" Ho (born August 12, 1951) is a Chinese-American theoretical physicist, specializing in condensed matter theory, quantum gases, and Bose-Einstein condensates. He is known for the Mermin-Ho relation. Education and career Ho graduated in 1972 with a B.Sc. from Chung Chi College, Chinese University of Hong Kong. He was a graduate student for the academic year 1972–1973 at the University of Minnesota and in 1973 transferred to Cornell University. There he graduated in 1977 with a Ph.D. under the supervision of N. David Mermin. Ho was a postdoc from 1977 to 1980 under the supervision of Christopher J. Pethick at the University of Illinois, from 1978 to 1980 at NORDITA, and from 1980 to 1982 at the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics at the University of California, Santa Barbara. At Ohio State University (OSU), he was an assistant professor from 1983 to 1989 and an associate professor from 1989 to 1996, when he became a full professor. At OSU he is since 2002 a D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Theory
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases, that arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms and electrons. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic temperatures, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, the Bose–Einstein condensates found in ultracold atomic systems, and liquid crystals. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other physics theories to develop mathematical models and predict the properties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Association For The Advancement Of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is a United States–based international nonprofit with the stated mission of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsibility, and supporting science education, scientific education and science outreach for the betterment of all humanity. AAAS was the first permanent organization established to promote science and engineering nationally and to represent the interests of American researchers from across all scientific fields. It is the world's largest general scientific society, with over 120,000 members, and is the publisher of the well-known scientific journal ''Science (journal), Science''. History Creation The American Association for the Advancement of Science was created on September 20, 1848, at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was a reformation of the Association of American Geologists and Naturalists with the broaden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University Alumni
Cornell University is a private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson White in 1865. Since its founding, Cornell University has been a co-educational and nonsectarian institution. As of fall 2024, the student body included 16,128 undergraduate and 10,665 graduate students from all 50 U.S. states and 130 countries. The university is organized into eight undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions on its main Ithaca campus. Each college and academic division has near autonomy in defining its respective admission standards and academic curriculum. In addition to its primary campus in Ithaca, Cornell University administers three satellite campuses, including two in New York City, the medical school and Cornell Tech, and a branch of the medical school in Al Rayyan, Qatar's Education City. Cornell is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of The University Of Hong Kong
Alumni (: alumnus () or alumna ()) are former students or graduates of a school, college, or university. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women, and alums (: alum) or alumns (: alumn) as gender-neutral alternatives. The word comes from Latin, meaning nurslings, pupils or foster children, derived from "to nourish". The term is not synonymous with "graduates": people can be alumni without graduating, e.g. Burt Reynolds was an alumnus of Florida State University but did not graduate. The term is sometimes used to refer to former employees, former members of an organization, former contributors, or former inmates. Etymology The Latin noun means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from the Latin verb "to nourish". Separate, but from the same root, is the adjective "nourishing", found in the phrase '' alma mater'', a title for a person's home university. Usage in Roman law In Latin, is a legal term (Roman law) to describe a child placed in foste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physicists
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase. Condensation may also refer to: * DNA condensation, the process of compacting DNA molecules * Cloud condensation nuclei, airborne particles required for cloud formation * Condensation (aerosol dynamics), a phase transition from gas to liquid * Condensation cloud, observable at large explosions in humid air * Condensation reaction, in chemistry, a chemical reaction between two molecules or moieties * Condensation algorithm, in computer science, a computer vision algorithm * Condensation (graph theory), in mathematics, a directed acyclic graph formed by contracting the strongly connected components of another graph * Dodgson condensation, in mathematics, a method invented by Lewis Carroll for computing the determinants of square matrices * Bose–Einstein condensation, a state of matter of a dilute gas in which quantum effects become apparent on a macroscopic scale * Condensation (psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physicists
The following is a partial list of notable theoretical physicists. Arranged by century of birth, then century of death, then year of birth, then year of death, then alphabetically by surname. For explanation of symbols, see Notes at end of this article. Ancient times * Kaṇāda (6th century BCE or 2nd century BCE) * Thales (c. 624 – c. 546 BCE) * Pythagoras^* (c. 570 – c. 495 BCE) * Democritus° (c. 460 – c. 370 BCE) * Aristotle‡ (384–322 BCE) * Archimedesº* (c. 287 – c. 212 BCE) * Ptolemy (c. 100 – c. 170 AD) * Hypatia^ªº (c. 350–370; died 415 AD) Middle Ages * Al Farabi (c.872–c.950) * Ibn al-Haytham (c.965–c.1040) * Al Beruni (c.973–c.1048) * Omar Khayyám (c.1048–c.1131) * Bhaskara II (c.1114–c.1185) * Mu'ayyad al-Din al-Urdi (c.1200–c.1266) * Nasir al-Din Tusi (1201–1274) * Jean Buridan (1301–c.1359/62) * Nicole Oresme (c.1320/1325–1382) * Jamshid al-Kashi (1380–1429) * Sigismondo Polcastro (1384–1473) * Ulugh Beg (1394–1449) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century American Physicists
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Chinese Physicists
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
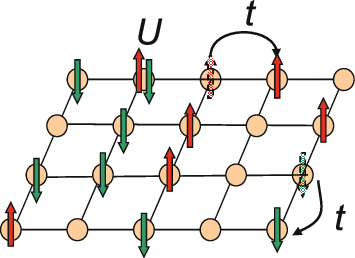
Hubbard Model
The Hubbard model is an Approximation, approximate model used to describe the transition between Conductor (material), conducting and Electrical insulation, insulating systems. It is particularly useful in solid-state physics. The model is named for John Hubbard (physicist), John Hubbard. The Hubbard model states that each electron experiences competing forces: one pushes it to tunnel to neighboring atoms, while the other pushes it away from its neighbors. Its Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics), Hamiltonian thus has two terms: a kinetic term allowing for Quantum tunneling, tunneling ("hopping") of particles between lattice sites and a potential term reflecting on-site interaction. The particles can either be fermions, as in Hubbard's original work, or bosons, in which case the model is referred to as the "Bose–Hubbard model". The Hubbard model is a useful approximation for particles in a periodic potential at sufficiently low temperatures, where all the particles may be assumed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Lattice
An optical lattice is formed by the Interference (wave propagation), interference of counter-propagating laser beams, creating a spatially periodic intensity pattern. The resulting periodic scalar potential, potential may trap neutral atoms via the Stark shift. Atoms are cooled and congregate at the potential extrema (at maxima for blue-detuned lattices, and minima for red-detuned lattices). The resulting arrangement of trapped atoms resembles a crystal lattice and can be used for Quantum simulator, quantum simulation. Atoms trapped in the optical lattice may move due to quantum tunneling, even if the potential well depth of the lattice points exceeds the kinetic energy of the atoms, which is similar to the electrons in a Electrical conductor, conductor. However, a superfluid–Mott insulator transition may occur, if the interaction energy between the atoms becomes larger than the hopping energy when the well depth is very large. In the Mott insulator phase, atoms will be trappe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |