|
Tillocheles
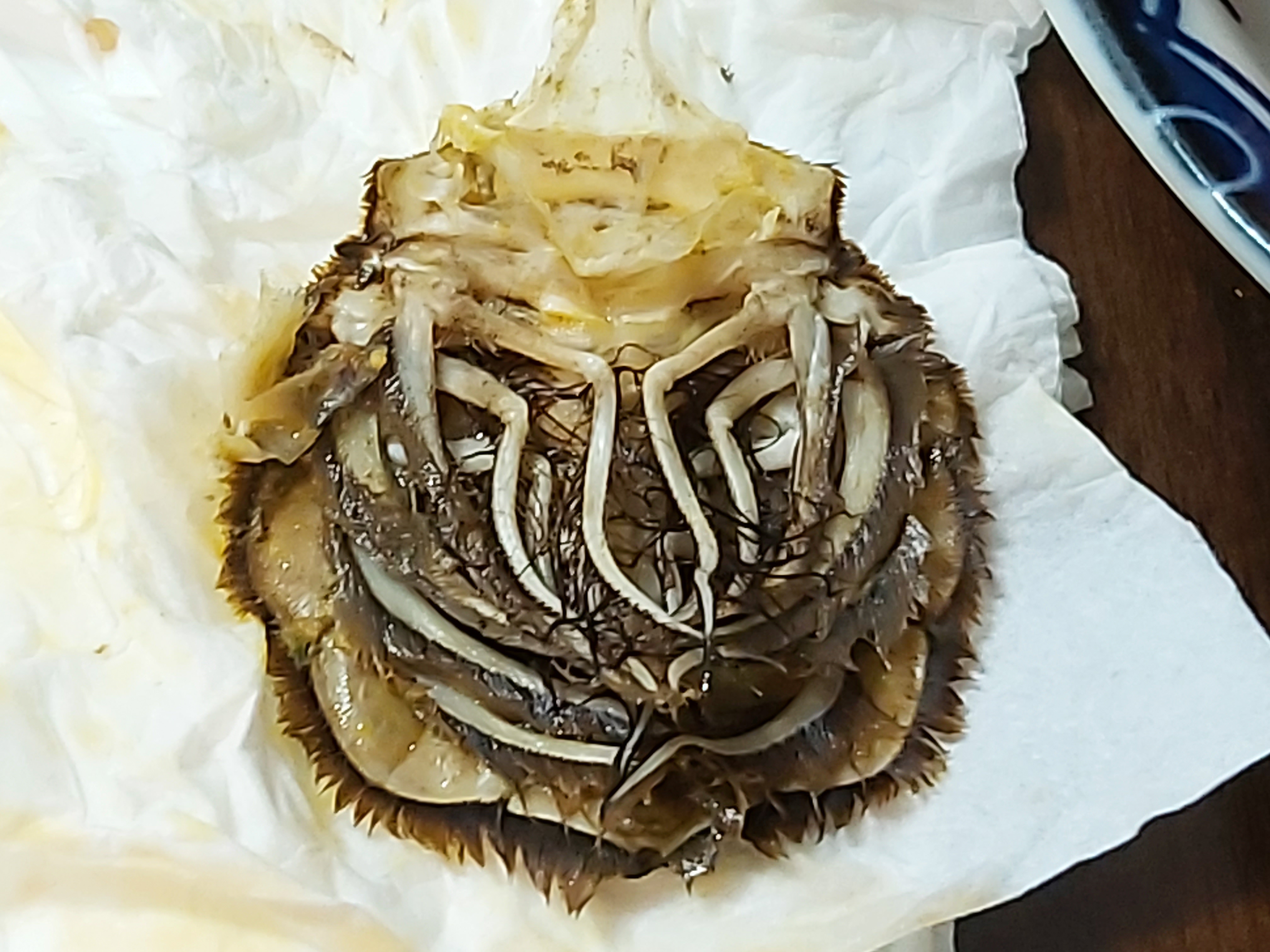
''Tillocheles'' is an extinct genus of decapod crustaceans that lived during the Cretaceous period. Two species are currently placed in the genus. Fossils of the earlier type species, ''T. shannonae'', have been found in Queensland, while remains of the later species, ''T. kaoriae'', are known from Hokkaido. Discovery and naming Fossils of ''Tillocheles'' were first described in 1957, when eight specimens were collected from the late Albian-aged Tambo Formation in Currane, central Queensland, Australia. Based on these specimens, Jack T. Woods erected the genus ''Tillocheles'', with ''T. shannonae'' as its type and only species. A specimen preserving part of the carapace, abdomen and appendages (F. 3252) was designated as the holotype of this species. The specific name honors Sanna Shannon, who discovered and collected fossils of decapod crustaceans at Currane. In addition to the type species, a second species was assigned to ''Tillocheles'' in 2000. Named ''T. kaoriae'' (after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/ Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0.9 Ma (million years ago). The Albian is preceded by the Aptian and followed by the Cenomanian. Stratigraphic definitions The Albian Stage was first proposed in 1842 by Alcide d'Orbigny. It was named after Alba, the Latin name for River Aube in France. A Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP), ratified by the IUGS in 2016, defines the base of the Albian as the first occurrence of the planktonic foraminiferan '' Microhedbergella renilaevis'' at the Col de Pré-Guittard section, Arnayon, Drôme, France. The top of the Albian Stage (the base of the Cenomanian Stage and Upper Cretaceous Series) is defined as the place where the foram species '' Rotalipora globotruncanoides'' first appears in the stratigraphic column. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactylus
The dactylus is the tip region of the tentacular club of cephalopods and of the leg of some crustaceans (see arthropod leg). In cephalopods, the dactylus is narrow and often characterized by the asymmetrical placement of suckers (i.e., the ventral expansion of the club) and the absence of a dorsal protective membrane. In crustaceans, the dactylus is the seventh and terminal segment of their thoracic appendages. In certain instances the dactylus, together with the propodus, form the claw. The term ''dactylus'' means "finger" in Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor .... References Cephalopod zootomy Crustacean anatomy {{Animal anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpus
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheliped
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer-like organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through New Latin New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy ... '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. See also * Pincer (biology) * Pincer (tool) References Arthropod anatomy {{Arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pincer (biology)
A pincer is the part of an arthropod that enables it to carry loads, to defend against other creatures, or to attack prey. In insects, the pincers are usually part of the creature's mandible, and often venom or acid can be injected through the pincer into an enemy during a pincer strike. Some arthropods such as crabs, lobsters, and scorpions possess pincers in the form of chelae A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer-like organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through New Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. ... at the ends of their front limbs ( pedipalps), to assist in feeding, defence or even courtship. See also * Chela (organ) * Krukenberg procedure * Pedipalp * Pincer (tool) References {{reflist Arthropod anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereiopod
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head #antennules # antennae # mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostrum (anatomy)
Rostrum (from Latin ', meaning ''beak'') is a term used in anatomy for a number of phylogenetically unrelated structures in different groups of animals. Invertebrates * In crustaceans, the rostrum is the forward extension of the carapace in front of the eyes. It is generally a rigid structure, but can be connected by a hinged joint, as seen in Leptostraca. * Among insects, the rostrum is the name for the piercing mouthparts of the order Hemiptera as well as those of the snow scorpionflies, among many others. The long snout of weevils is also called a rostrum. * Gastropod molluscs have a rostrum or proboscis. * Cephalopod molluscs have hard beak-like mouthparts referred to as the rostrum. File:Washington DC Zoo - Macrobrachium rosenbergii 6.jpg, Crustacean: the rostrum of the shrimp '' Macrobrachium rosenbergii'' is serrated along both edges. File:Gminatus australis with Beetle.jpg, Insect: assassin bug piercing its prey with its rostrum File:Architeuthis beak.jpg, Ceph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different ways: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikasa, Hokkaido
is a city located in Sorachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. As of September 2016, the city has an estimated population of 9,056, and the density of 30 persons per km2. Geography The total area is 302.64 km2. It is bordered on three sides by mountains, and on its east side is the man-made Lake Katsurazawa. History Mikasa is one of the birthplaces of the mining and railroad industries in Hokkaido, and the Hokkai Bon song was invented there. Though in the past it flourished due to its natural abundance of coal, the mines have largely closed down and this has caused the population of the city to fall rapidly. Quite a few fossil specimens have also been collected there, particularly ammonites and the prehistoric marine reptile '' Yezosaurus mikasaensis'', both of which can be viewed at the city's natural history museum. *1906 - Mikasayama village was founded. *1942 - Mikasayama village became Mikasa town. *1957 - Mikasa town became Mikasa city. Education High school * Hok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

