|
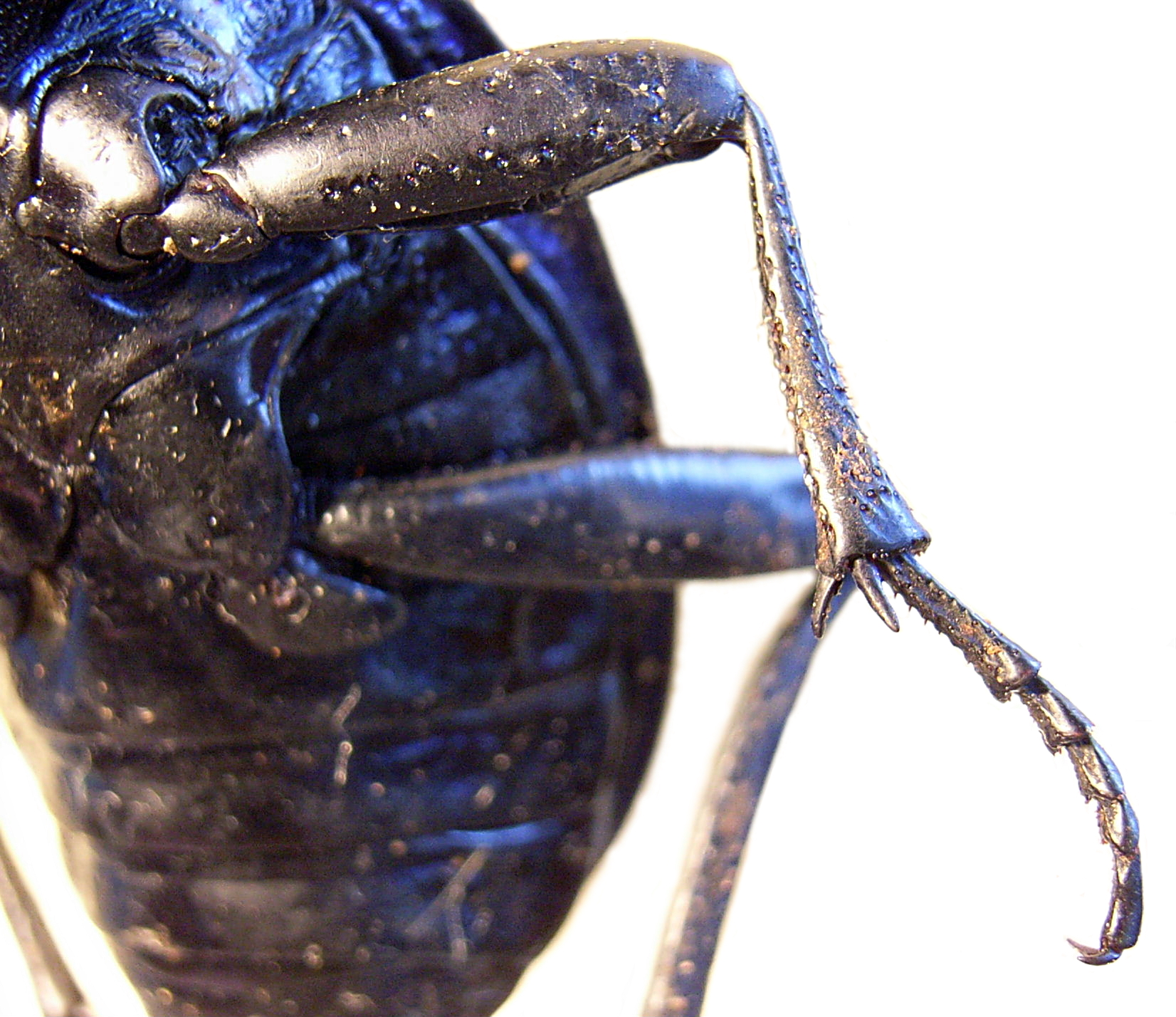
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip (anatomy), hip, : ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (: ''femora''), ''tibia'' (: ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (: ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (: ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (: ''patellae''). Homology (biology), Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of Neontology, extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a Homeobox, ''Hox''-gene, could result in Parallel evolution, parallel gains of leg segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward appendages among Chelicerata, chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the Arthropod leg#Trochanter, trochanter, the Arthropod leg#Femur, femur, the short Glossary_of_spider_terms#patella, patella, the Glossary_of_spider_terms#tibia, tibia, and the Arthropod_leg#Tarsus, tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called Glossary_of_spider_terms#maxilla , maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior arthropod leg, legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface appendages. In many kinds of eukaryotic cells, the protrusions are known as membrane protrusions or cell appendages (examples include microvilli and cilia). Types in animals In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs ( gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In annelids lateral protrusions from the body are called parapodia. In echinoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopod
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of Antenna (biology), antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the Thorax#In_arthropods, thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the Abdomen#In other animals, abdomen that are used in Respiration (physiology), respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax called the Brood pouch (Peracarida), marsupium. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are Grazing (behaviour), grazers or filter feeders, a few are Predation, predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or the bottom of freshwater body of water, bodies of water, but some Taxon, taxa can swim for short distance. Terre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chela (organ)
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer-shaped organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through Neo-Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. Uses Chelae have a wide variety of uses, but most commonly they are used for handling their prey and for defense. These uses are often reflected in the morphology of the chelae. For instance, some species, such as the members of the families Ocypodidae and Alpheidae show asymmetry between their paired claws. Possessing one enlarged chela used for defensive and courtship purposes and a smaller chela for shearing and feeding. For some species, this asym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
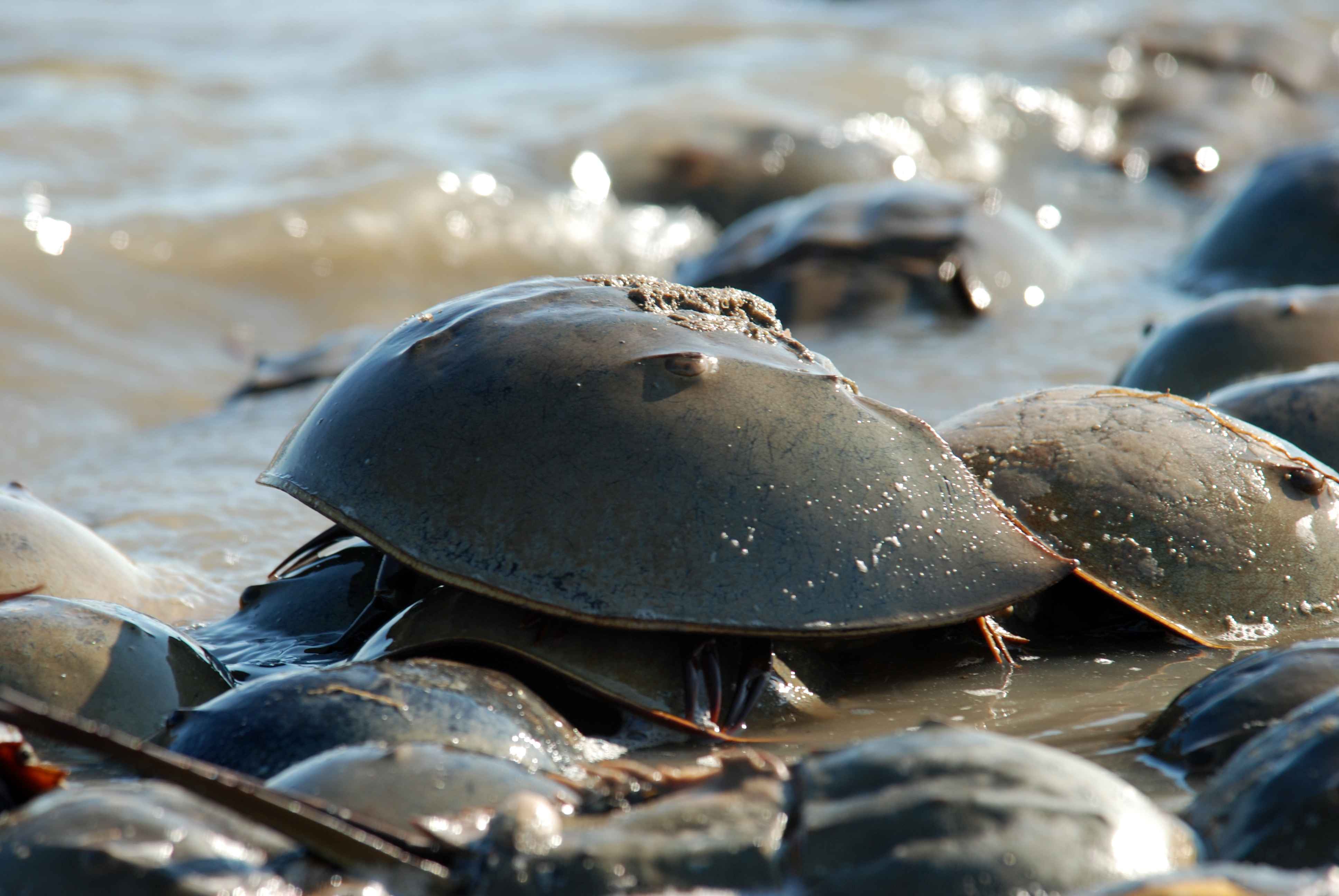
Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe crabs are arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only surviving xiphosurans. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or even crustaceans; they are chelicerates, more closely related to arachnids like spiders, ticks, and scorpions. The body of a horseshoe crab is divided into three main parts: the cephalothorax, abdomen, and telson. The largest of these, the cephalothorax, houses most of the animal's eyes, limbs, and internal organs. It is also where the animal gets its name, as its shape somewhat resembles that of a horseshoe. Horseshoe crabs have been described as "living fossils", having changed little since they first appeared in the Triassic. Only four species of horseshoe crab are extant today. Most are marine, though the mangrove horseshoe crab is often found in brackish water, and the Atlantic horseshoe crab is resident in brackish estuarine ecosystems such as the Delaware and Chesapeake bays. Additionally, certain extinct species transitioned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
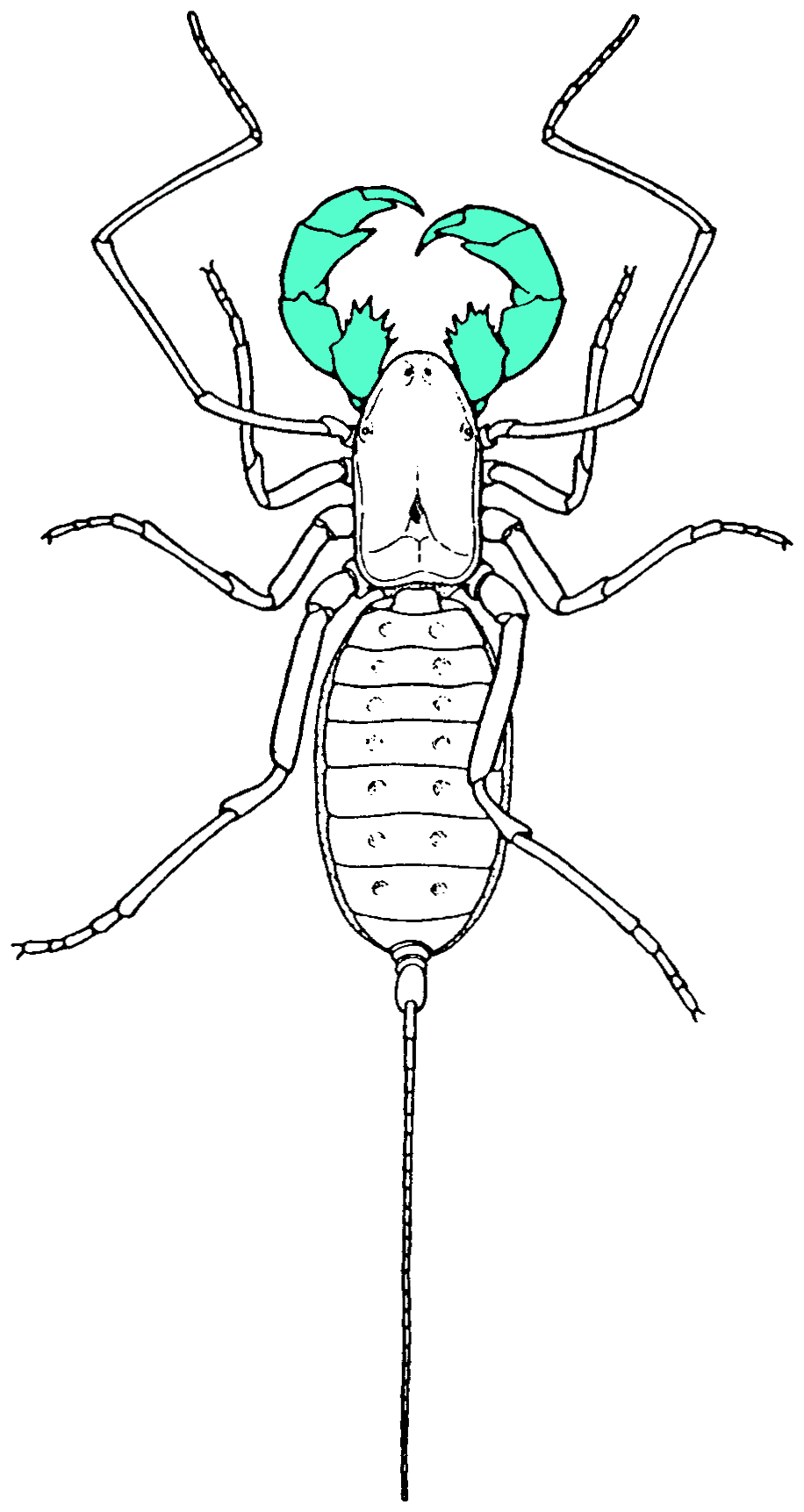
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back Silurian, 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The Scorpion sting, venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Spider Terms
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids. Links within the glossary are shown . Terms A * Abdomen or opisthosoma: One of the two main body parts (tagma (biology), tagmata), located towards the Posterior (anatomy), posterior end; see also Abdomen#Other animals, Abdomen § Other animals * Accessory claw: Modified at the tip of the in web-building spiders; used with to grip strands of the web * Anal tubercle: A small protuberance (tubercule) above the through which the anus opens * Apodeme: see * Apophysis (plural apophyses): An outgrowth or process changing the general shape of a body part, particularly the appendages; often used in describing the male : see * Atrium (plural atria): An internal chamber at the entrance to the in female Haplogynae, haplogyne spiders B * Bidentate: Having two * Book lungs: Respiratory organs on the ventral side (underside) of the , in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider External Anatomy Appendages En
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 53,034 spider species in 136 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel. However, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniramia
Uniramia (''uni'' – one, ''ramus'' – branch, i.e. single-branches) is a group within the arthropods. In the past this group included the Onychophora, which are now considered a separate category. The group is currently used in a narrower sense. Uniramia is one of three subphyla in the Arthropoda classification suggested by Sidnie Manton. This classification divided arthropods into a three-phyla polyphyletic group, with phylum Uniramia including the Hexapoda (insects), Myriapoda (centipedes and millipedes) and the Onychophora (velvetworms). The discovery of fossil lobopods, determined to be intermediate between onychophorans and arthropods led to the splintering of the Lobopoda and Onychophora into separate groups. This redefined the Uniramia as strictly "true" arthropods with exoskeletons and jointed appendages. Uniramians have strictly uniramous appendages. Systematics can result in rival taxonomies, and this seems to have happened to Uniramia. The name Uniramia was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |