|
Thymochares (groundhopper)
Thymochares ( Gr. ) was an Athenian general under the Four Hundred who may have come from the ''deme'' of Sphettos. In late 411 BC, commanding 36 triremes, he opposed the arrival of the Spartan commander Hegesandridas Hegesandridas or Agesandridas ( grc, Ἡγησανδρίδας or Ἀγησανδρίδας), son of a "Hegesander" or "Agesander", who could have been a member of the last Spartan embassy sent to Athens before the Peloponnesian War. Hegesandridas ... at Oropos, but was routed, losing 22 ships at the Battle of Eretria. Most of the rowers fled to Eretria where they were slaughtered. Thucydides does not say what happened to Thymochares after the defeat. He next appears in Xenophon at an unknown location (probably somewhere in Euboea), where he arrives with ‘a few ships’, but is again defeated by Hegesandridas.Xenophon, ''Hell''. i.1.1. References {{Reflist 5th-century BC Athenians Ancient Athenian generals Athenians of the Peloponnesian War 411 BC< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenian Coup Of 411 BC
The Athenian coup of 411 BC was the result of a revolution that took place during the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta. The coup overthrew the democratic government of ancient Athens and replaced it with a short-lived oligarchy known as the Four Hundred. In the wake of the financial crisis caused by the failed Sicilian Expedition of the Athenian military in 413 BC, some high-status Athenian men, who had disliked the broad-based democracy of the city-state for a long time, sought to establish an oligarchy of the elite. They believed that they could manage foreign, fiscal, and war policies better than the existing government. The movement toward oligarchy was led by a number of prominent and wealthy Athenians, who held positions of power in the Athenian army at Samos in coordination with Alcibiades. Background By the time of the Peloponnesian War, the democracy in Athens was approximately 100 years old. Most of the upper class accepted this form of government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphettos
Sphettus or Sphettos ( grc, Σφηττός) was one of the twelve cities of ancient Attica, and subsequently a deme. That it was situated either in the Mesogaea or the Paralia is certain from the legend, that Pallas, who had obtained these districts, marched upon Athens from Sphettus by the Sphettian Way. There are good reasons for believing that Pallas must have marched round the northern extremity of Hymettus; and consequently the Sphettian road must have taken that course. The site of Sphettus has been located northwest of Koropi below Christos chapel. People *Aeschines of Sphettus Aeschines of Sphettus ( grc, Αἰσχίνης Σφήττιος, c. 425 BC – c. 350 BC) or Aeschines Socraticus ( grc, Αἰσχίνης Σωκρατικός), son of Lysanias, of the deme Sphettus of Athens, was a philosopher who in his youth ... References Populated places in ancient Attica Former populated places in Greece Demoi {{AncientAttica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triremes
A trireme( ; derived from Latin: ''trirēmis'' "with three banks of oars"; cf. Greek ''triērēs'', literally "three-rower") was an ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greeks and Romans. The trireme derives its name from its three rows of oars, manned with one man per oar. The early trireme was a development of the penteconter, an ancient warship with a single row of 25 oars on each side (i.e., a single-banked boat), and of the bireme ( grc, διήρης, ''diērēs''), a warship with two banks of oars, of Phoenician origin. The word dieres does not appear until the Roman period. According to Morrison and Williams, "It must be assumed the term pentekontor covered the two-level type". As a ship, it was fast and agile and was the dominant warship in the Mediterranean from the 7th to the 4th centuries BC, when it was largely superseded by the larger quadriremes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegesandridas
Hegesandridas or Agesandridas ( grc, Ἡγησανδρίδας or Ἀγησανδρίδας), son of a "Hegesander" or "Agesander", who could have been a member of the last Spartan embassy sent to Athens before the Peloponnesian War. Hegesandridas was a Spartan general in the Peloponnesian War. In 411 BC he was placed in command of a fleet of 42 ships instructed to further a revolt in Euboea. News of their being seen off Las of Laconia arrived in Athens at the time when the Four Hundred were building their fort of Eëtioneia on a promontory commanding Piraeus, and the coincidence was used by Theramenes as evidence of their treasonable intentions. Further intelligence that the same fleet had sailed over from Megara to Salamis coincided again with the riot in Piraeus, and was held to be certain proof of Theramenes' allegations. Thucydides thought it possible that the movement was really made in concert with the Athenian oligarchs, but it is far more probable that Hegesandrida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oropos
Oropos ( el, Ωρωπός) is a small town and a municipality in East Attica, Greece. The village of Skala Oropou, within the bounds of the municipality, was the site an important ancient Greek city, Oropus, and the famous nearby sanctuary of Amphiaraos is stll visible today. Geography The municipality Oropos stretches between the Parnitha mountains and the South Euboean Gulf, opposite Eretria (on the island Euboea). The town Oropos, the seat of the municipality, is situated on the lower course of the river Asopos, 4 km south of the coast. It lies 4 km southwest of Nea Palatia and 55 km north of Athens city center. The community Oropos consists of the town Oropos and the nearby villages Kampos and Platania. The municipality has an area of 338.183 km2, the community 11.967 km2. Municipality The present municipality Oropos was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 9 former municipalities, that became municipal unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
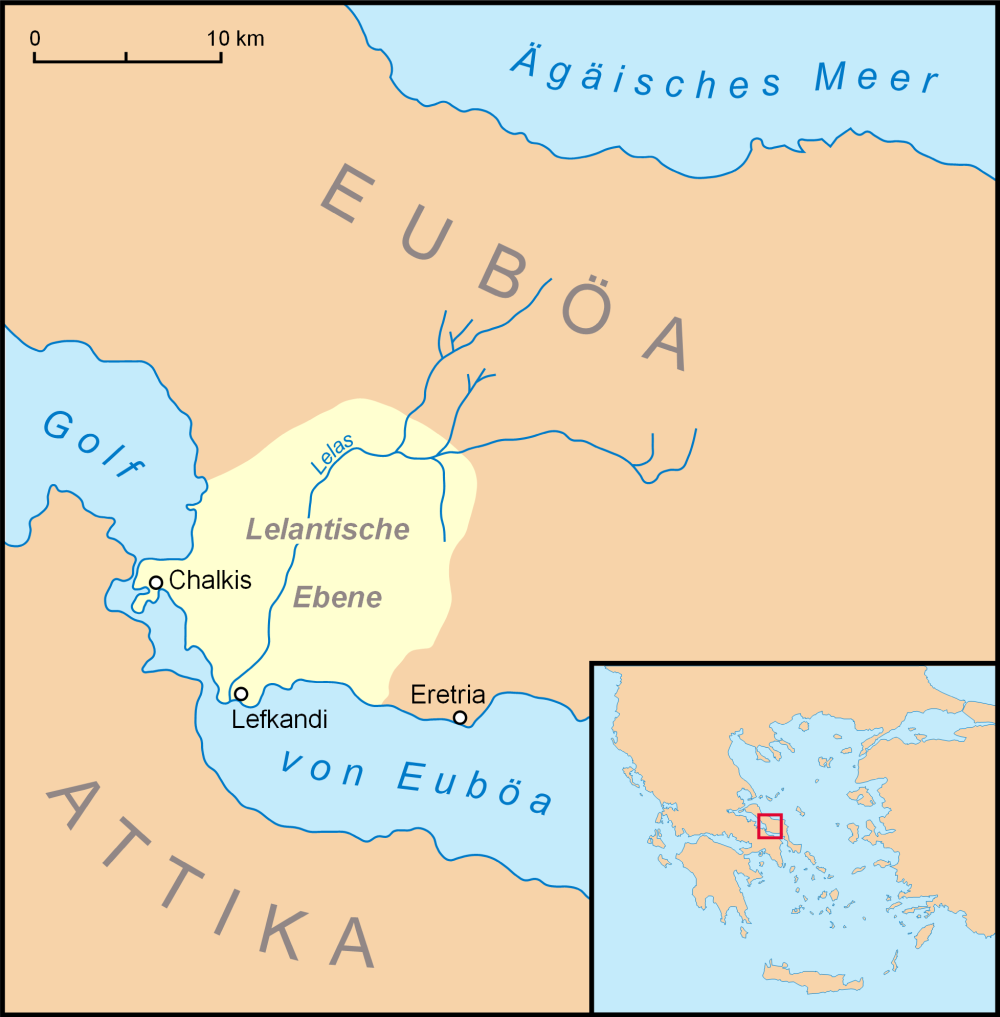
Battle Of Eretria
The naval Battle of Eretria, between Sparta and Athens, took place in September 411 BC, off the coast of Euboea. Background During the spring of 411 BC, the Eretrians drove the Athenians out of Oropos with the help of the Boeotians. This city was a strategic point for Athens because it allowed them to control all of Euboea. Moreover, all the commercial traffic was made through the city. The Eretrians would hope that Sparta would help them to end the Athenian rule on Euboea. Battle By the end of the summer 411 BC, a large Spartan fleet sailed towards Euboea. The Athenians tried to prevent the Euboeans from switching sides by sending a squadron to Eretria under Thymochares. However, the Eretrians supported the Spartans. While the Athenians were in the harbour of Eretria in order to supply themselves, the Eretrians informed the Spartan admiral Hegesandridas by a signal fire that it was an appropriate time to attack. The Athenians hurriedly embarked but were defeated during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scientific history" by those who accept his claims to have applied strict standards of impartiality and evidence-gathering and analysis of cause and effect, without reference to intervention by the gods, as outlined in his introduction to his work. He also has been called the father of the school of political realism, which views the political behavior of individuals and the subsequent outcomes of relations between states as ultimately mediated by, and constructed upon, fear and self-interest. His text is still studied at universities and military colleges worldwide. The Melian dialogue is regarded as a seminal work of international relations theory, while his version of Pericles' Funeral Oration is widely studied by political theorists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies of the Achaemenid Empire, the Ten Thousand, that marched on and came close to capturing Babylon in 401 BC. As the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge wrote, "the centuries since have devised nothing to surpass the genius of this warrior". Xenophon established precedents for many logistical operations, and was among the first to describe strategic flanking maneuvers and feints in combat. Xenophon's ''Anabasis'' recounts his adventures with the Ten Thousand while in the service of Cyrus the Younger, Cyrus's failed campaign to claim the Persian throne from Artaxerxes II of Persia, and the return of Greek mercenaries after Cyrus's death in the Battle of Cunaxa. ''Anabasis'' is a unique first-hand, humble, and self-reflective account of a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century BC Athenians
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |