Eretria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
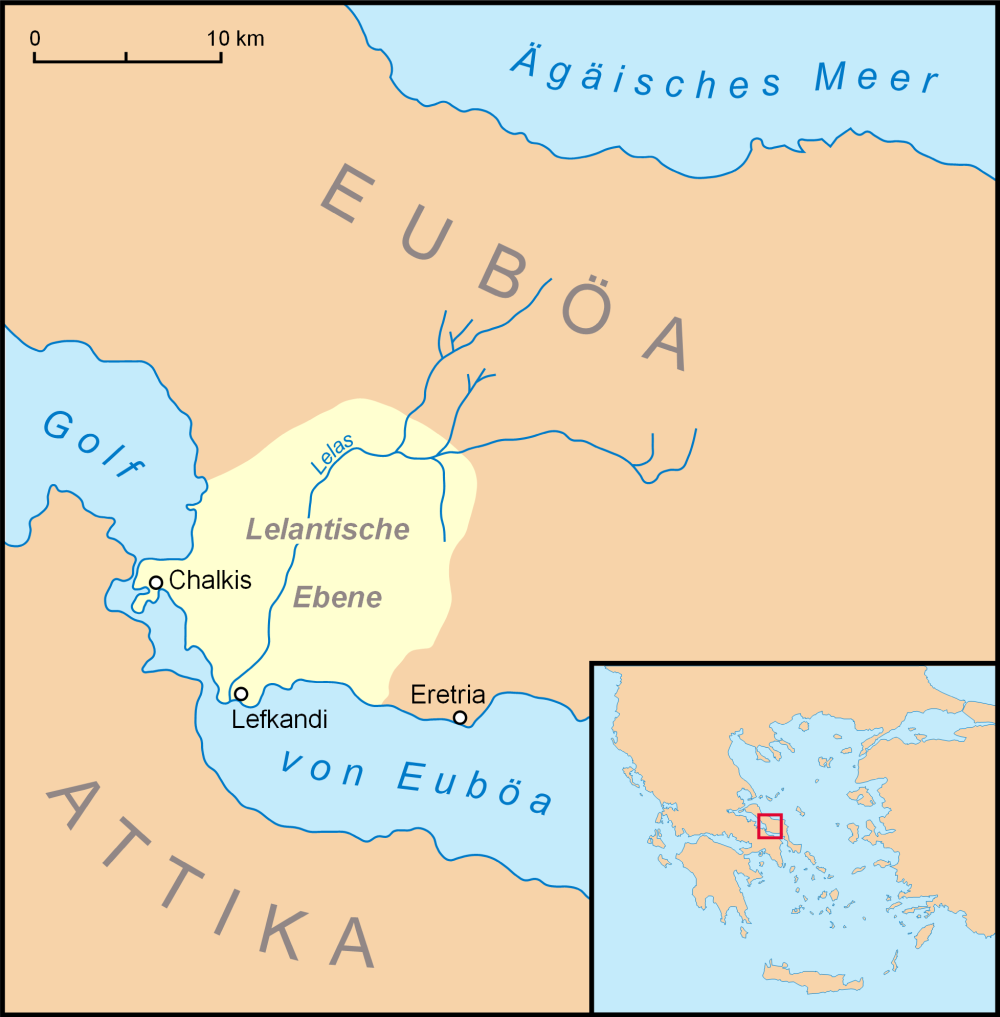 Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea,
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea,
 The earliest surviving mention of Eretria was by
The earliest surviving mention of Eretria was by  At the end of the 8th century BC, however, Eretria and Chalcis fought a prolonged war (known mainly from the account in
At the end of the 8th century BC, however, Eretria and Chalcis fought a prolonged war (known mainly from the account in

 The temple of
The temple of
 Among the most interesting monuments of ancient Eretria is the Iseion, a temple sacred to the goddess
Among the most interesting monuments of ancient Eretria is the Iseion, a temple sacred to the goddess
 This splendid house was built in ca. 370 B.C. and remained in use for about a century. It is distinguished by its floors, covered with elegant pebble mosaics representing mythological scenes: Nereids on the back of a seahorse, legendary battles between Arimaspians and
This splendid house was built in ca. 370 B.C. and remained in use for about a century. It is distinguished by its floors, covered with elegant pebble mosaics representing mythological scenes: Nereids on the back of a seahorse, legendary battles between Arimaspians and


Δήμος Ερέτρειας, Η ιστορία μας
, ανακτήθηκε 4 Δεκεμβρίου 2010 The modern town of Eretria is now a popular beachside resort. The historic and archaeological finds from Eretria and Lefkandi are displayed in th
Eretria Museum
established by the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. The town can be reached from Skala Oropou, Attica by ferry or via Halkida by road. It is an important station on the way to the south of the island. It has many taverns and a long beach promenade. The archaeological excavations are located on the northern edge of the modern town.
Eretria. A guide to the ancient city
Infolio éditions, Gollion, 2004. * ESAG
* Keith G. Walker, "Archaic Eretria. A Political and Social History from the Earliest Times to 490 BC", Routledge, London, 2004.
The Swiss School Website of the excavations at Eretria
Perseus – Eretria
Links to resources about ancient Eretria
Greek Ministry of CultureEretria Dream island beach photoEretria photo by nightMinistry of Culture and Sports
{{Authority control Populated places in Euboea Municipalities of Central Greece Cities in ancient Greece Populated places in ancient Euboea Populated places established in 1824 Former populated places in Greece Members of the Delian League Ancient Greek cities Greek city-states
 Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea,
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, facing the coast of Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core cit ...
across the narrow South Euboean Gulf
The South Euboean Gulf (, ''Notios Evvoïkos Kolpos'') is a gulf in Central Greece, between the island of Euboea and the Greek mainland (Boeotia and Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a h ...
. It was an important Greek polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events.
Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece.
History of Eretria
Prehistory
The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the lateNeolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time.
The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period
Helladic chronology is a relative dating system used in archaeology and art history. It complements the Minoan chronology scheme devised by Sir Arthur Evans for the categorisation of Bronze Age artefacts from the Minoan civilization within a his ...
(3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain. A granary and several other buildings, as well as a pottery kiln, have been found so far. This settlement was moved to the top of the Acropolis in the Middle Helladic period (2000–1600 BC) because the plain was flooded by the nearby lagoon. In the Late Helladic period (1600–1100 BC), the population dwindled and the remains found so far have been interpreted as an observation post. The site was abandoned during the Greek Dark Ages
The Greek Dark Ages ( 1180–800 BC) were earlier regarded as two continuous periods of Greek history: the Postpalatial Bronze Age (c. 1180–1050 BC) and the Prehistoric Iron Age or Early Iron Age (c. 1050–800 BC). The last included all the ...
.
Archaic to Roman period
The oldest archaeological finds date the foundation of the city to the Greek Dark Ages. The earliest surviving mention of Eretria was by
The earliest surviving mention of Eretria was by Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
(''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' 2.537), who listed Eretria as one of the Greek cities which sent ships to the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
. In the 8th century BC, Eretria and her near neighbour and rival, Chalcis
Chalcis (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: , ), also called Chalkida or Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief city of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from ...
, were both powerful and prosperous trading cities. Eretria controlled the Aegean islands of Andros
Andros (, ) is the northernmost island of the Greece, Greek Cyclades archipelago, about southeast of Euboea, and about north of Tinos. It is nearly long, and its greatest breadth is . It is for the most part mountainous, with many fruitful and ...
, Tenos and Ceos. They also held territory in Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (adm ...
on the Greek mainland. Eretria was also involved in the Greek colonisation and founded the colonies of Pithekoussai and Cumae
Cumae ( or or ; ) was the first ancient Greek colony of Magna Graecia on the mainland of Italy and was founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BCE. It became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of ...
in Italy together with Chalcis.
 At the end of the 8th century BC, however, Eretria and Chalcis fought a prolonged war (known mainly from the account in
At the end of the 8th century BC, however, Eretria and Chalcis fought a prolonged war (known mainly from the account in Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
as the Lelantine War) for control of the fertile Lelantine plain. Little is known of the details of this war, but it is clear that Eretria was defeated. The city was destroyed and Eretria lost her lands in Boeotia and her Aegean dependencies. Neither Eretria nor Chalcis ever again counted for much in Greek politics. As a result of this defeat, Eretria turned to colonisation. She planted colonies in the northern Aegean, on the coast of Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
, in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, and in Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
It became an important city in the 6th/5th century BC mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. The Eretrians were Ionians
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the ...
and were thus natural allies of Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
. When the Ionian Greeks in Asia Minor rebelled against Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
in 499 BC, Eretria joined Athens in sending aid to the rebels, because Miletus had supported Eretria in the Lelantine War. The rebels burned Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy) ...
, but were defeated and the Eretrian general Eualcides was killed. Darius made a point of punishing Eretria during his invasion of Greece. In 490 BC the city was sacked and burned by the Persians under the admiral Datis. In retribution for the stout resistance, the victors killed all the male citizens and deported women and children barefoot to Arderikka in Susiana, Persia, forcing them into slavery. The Persians also destroyed the great temple of Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
, built around 510 BC; parts of a pediment were found in 1900, including the torso of a statue of Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
.
Eretria was rebuilt shortly afterwards and took part with 600 hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldi ...
in the Battle of Plataea (479 BC). The ancient writer Plutarch mentions a woman of Eretria, "who was kept by Artabanus" at the Persian court of Artaxerxes, who facilitated the audience that Themistocles obtained with the Persian king.Plutarch's ''Lives'', Volume 1, The Dryden translation, , p. 165 During the fifth century BC the whole of Euboea became part of the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
, which later became the Athenian Empire
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
. Eretria and other cities of Euboea rebelled unsuccessfully against Athens in 446 BC. During the Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
Eretria was an Athenian ally against her Dorian rivals Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
and Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
. But soon the Eretrians, along with the rest of the Empire, found Athenian domination oppressive. When the Spartans defeated the Athenians at the Battle of Eretria in 411 BC, the Euboean cities all rebelled.
After her eventual defeat by Sparta in 404 BC, Athens soon recovered and re-established her hegemony over Euboea, which was an essential source of grain for the urban population. The Eretrians rebelled again in 349 BC and this time the Athenians could not recover control. In 343 BC supporters of Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon (; 382 BC – October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
gained control of the city, but the Athenians under Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; ; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prowess and provide insight into the politics and cu ...
recaptured it in 341 BC.
Macedonian period
The Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, in which Philip defeated the combined armies of the rest of the Greeks, marked the end of the Greek cities as independent states. However, under Macedonian rule Eretria experienced a new period of prosperity which lasted until the 3rd century as attested by many inscriptions, by extensions to the west and south sections of the walls and by many other private and public new buildings including the circus. From 318 to 312 BC King Cassander lived at Eretria and commissioned the painterPhiloxenus of Eretria
Philoxenus of Eretria () was a painter from Eretria. He was a disciple of Nicomachus of Thebes, whose speed in painting he imitated and even surpassed, having discovered new and rapid methods of coloring. According to Pliny the Elder, Pliny, a pic ...
to paint the battle of Issus
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on 5 November 333 BC between the League of Corinth, Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III of Persia, Darius III. It was the second g ...
, of which the famous Alexander Mosaic
The ''Alexander Mosaic,'' also known as the ''Battle of Issus Mosaic'', is a Roman mosaic, Roman floor mosaic originally from the House of the Faun in Pompeii, Italy.
It is typically dated between and Anno Domini, BC 100 and depicts a battle be ...
in the Naples museum is a copy and the wall paintings in Phillip's tomb at Vergina
Vergina (, ) is a small town in Northern Greece, part of the Veria municipality in Imathia, Central Macedonia. Vergina was established in 1922 in the aftermath of the Population exchange between Greece and Turkey, population exchanges after t ...
are connected.
From 304 BC Demetrius I granted the city partial autonomy. During this time the city was governed by Menedemos who founded the Eretrian school of philosophy. After the Chremonidean War
The Chremonidean War (267–261 BC) was fought by a coalition of Polis, Greek city-states and Ptolemaic Egypt against Antigonid Macedonia. It ended in a Macedonian victory that confirmed Antigonid dynasty, Antigonid control over Greece. The conf ...
(267–262 BC) a permanent Macedonian garrison was installed.
Roman period
In 198 BC in theSecond Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. ...
Eretria was plundered by the Romans. The admiral Lucius Quinctius Flamininus was joined by the allied fleets of Attalus I
Attalus I ( ), surnamed ''Soter'' (, ; 269–197 BC), was the ruler of the Greek polis of Pergamon (modern-day Bergama, Turkey) and the larger Pergamene Kingdom from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the adopted son of King Eumenes I ...
of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north s ...
and of Rhodes, and used them in besieging Eretria. He eventually took the town during a night-time assault during which the citizens surrendered. Flamininus came away with a large collection of art works as his share of the booty.
Eretria became an object of contention between the Romans and Macedonians, but was given partial independence and experienced a new period of prosperity. Under the Romans, athletic contests for children and youths called the Romaia were held.
In 87 BC it was finally destroyed in the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War /ˌmɪθrəˈdædɪk/ (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule ...
and gradually declined further.

Site monuments
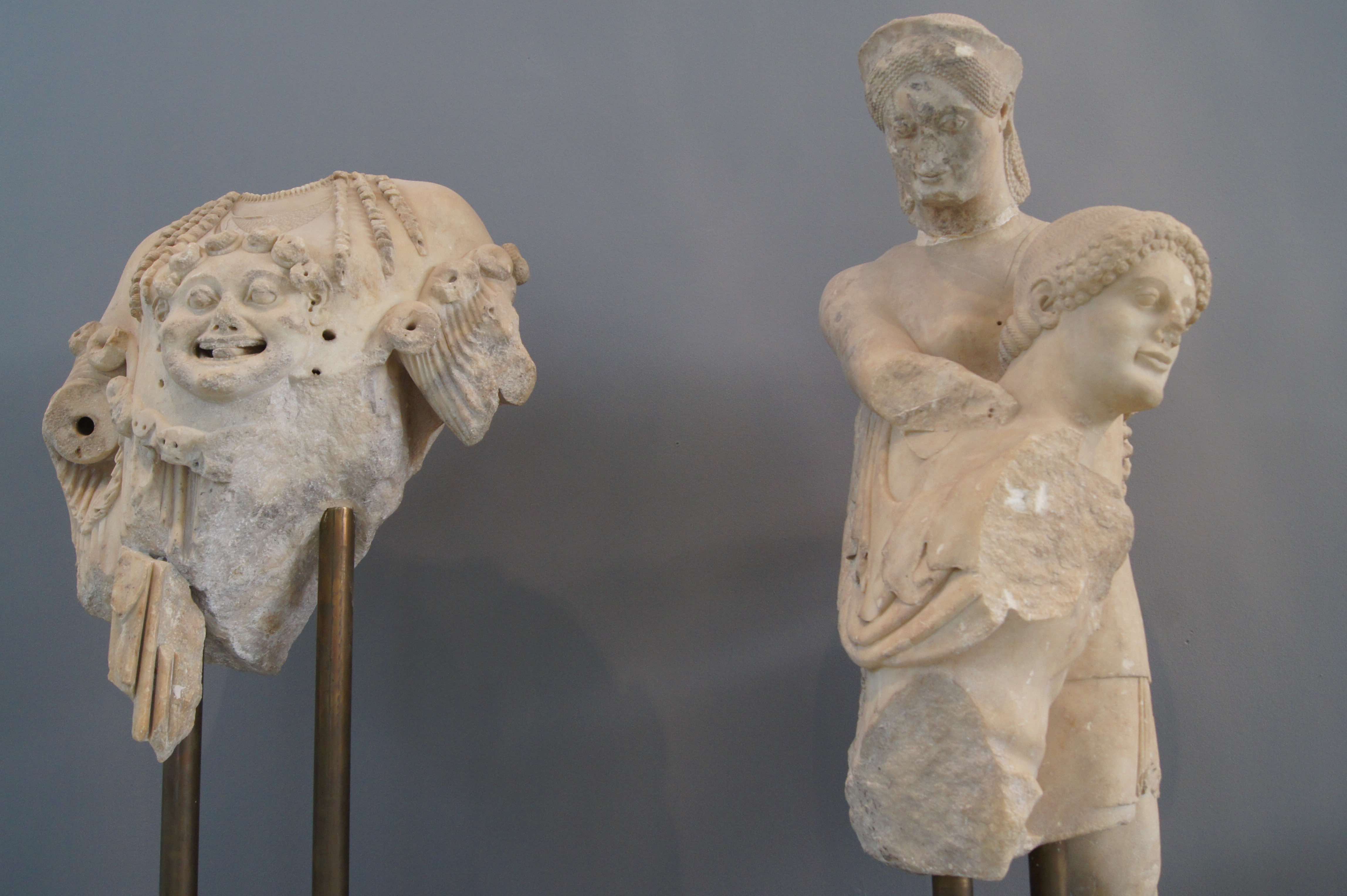
Many remains of the ancient city can be seen today including: *Parts of the city walls and gates (of 4 km length) *The Theatre *Palaces I and II *Upper and Lower Gymnasiums *House of the mosaics *The Baths *Temple of Apollo Daphnephoros *Temple of Artemis *Temple of Isis *Temple of Dionysos *The Acropolis *Macedonian tombTemple of Apollo Daphnephoros
 The temple of
The temple of Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
Daphnephoros is the most important and wider known monument of Eretria, featuring sparkling and sharp sculptures on the pediments, their postures well in advance of experiments in Athens of the time. Together with its enclosure it constituted the sacred temenos of Apollo, a religious centre and fundamental place of worship within the core of the ancient city, to the north of the Agora.
According to the Homeric
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is ...
hymn to Apollo, when the god was seeking for a location to found its oracle, he arrived to the Lelantine plain. The first temple is dated to the Geometric period and was situated probably near the harbour, as the sea then reached the area of the Agora. The ''hecatompedon'' (hundred-footer) apsidal edifice is the earliest in its type among those mentioned by Homer, and slightly after the hecatompedon temple of Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
on the island of Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
. It was flanked to the south by another apsidal building which also came to light: the so-called ''Daphniforio'' or "space with laurels" (7.5 x 11.5m) is the most ancient edifice in Eretria, related to the early cult of Apollo in Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
.
At the centre of this edifice were preserved the clay bases supporting the laurel trunks that propped up the roof. In the early sixteenth century a second hecatompedon temple was erected through earth fills upon its Geometric predecessor, on a solid artificial terrace. This temple had wooden columns (six at the narrow sides and nineteen at the longer sides), and was subsequently covered with earth in order to build the later and most renowned of all temples in the city.
Construction started at the late sixth century BC (520-490 BC) and the temple was perhaps still unfinished when the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
razed the city in 490 BC. Poros stone and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
were the materials used for this Doric peristyle (surrounded by colonnades) temple (6 x 14 columns). It had a ''prodomos'' (anteroom) and an ''opisthodomos ''(back section) arranged with two columns in antis; the cella (in Greek ''sekos'' was divided into three naves by two interior colonnades. After the destruction of the city by the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
, the temple was repaired and remained in use; yet in 198 BC it was destroyed again, this time by the Romans, a fact which initiated the gradual abandonment and dilapidation of the monument until the first century BC. Some important sculptures were found and are displayed in the Chalcis
Chalcis (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: , ), also called Chalkida or Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief city of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from ...
museum. One of the Amazons was salvaged in antiquity and carried off to Rome. Several Niobids perhaps from the pediment of the temple were probably taken to Rome by Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
including the dying Niobid and the running Niobid (now in the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek).
The majority of architectural parts from this temple and other sanctuaries of the city were re-used as construction material; only a few (column) drums together with fragmented capitals and triglyphs remain from the superstructure of the monument.
Of the sumptuous sculptural decoration survive only parts of the west pediment featuring in relief the fight of the Amazons
The Amazons (Ancient Greek: ', singular '; in Latin ', ') were a people in Greek mythology, portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, Labours of Heracles, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. ...
(or Amazonomachy, a usual motif for the iconography at the time). The centre was occupied by Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
and is partially preserved, depicting her trunk with the Gorgoneion on the thorax; a superb work of art is the complex of Theseus and Antiope marked by sensitivity and softness of the form, internal force and clarity, despite the ornamental tendency obvious in the coiffures and the folds of their clothes. These sculptures are impregnated by the rules of archaic plasticity; the analogies are rendered in an innovative manner, a precursor to the idealization and the force of the classical art. The entire composition supposedly featured chariots to Athena's right and left, one chariot presumably carrying Theseus
Theseus (, ; ) was a divine hero in Greek mythology, famous for slaying the Minotaur. The myths surrounding Theseus, his journeys, exploits, and friends, have provided material for storytelling throughout the ages.
Theseus is sometimes desc ...
and Antiope, while Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
might ride the other, and the picture could be complemented by fighting Amazons and a dead warrior. The east pediment possibly narrated the Gigantomachy (fight of the Giants). The details of the faces and the clothes were coloured, thus rendering the depiction more vivid. Fragmented sculptures that may be part of the temple after the destruction by the Persians (warrior, Amazon and Athena's trunk) have been located in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
. Today are visible only the foundations of the Post-Archaic temple, as well as remains of the Geometric temples uncovered in lower deposits.
The temples in the temenos of Apollo Daphniforos were excavated between 1899 and 1910 by Κ. Kourouniotis. Further investigations were conducted by Mrs. I. Konstantinou and by the Swiss Archaeological School.
The ancient theatre of Eretria
The most impressive monument of ancient Eretria, one of the oldest known theatres, lies in the western section of town, between the western gate, the stadium and the upper gymnasium; the temple of Dionysos was found at its south-west end. As indicated by the architectural remains of the scene, the initial construction phase followed the invasion by the Persians and the reconstruction of the city in the fifth century BC, whereas the fourth century BC marked the site's peak. A striking fact is the construction of the ''cavea'' (Gr. , auditorium) on an artificial hill surrounded by numerous retaining walls, instead of taking advantage of the citadel's slopes. During the first building phase, the scene looked like a palace, disposed of five adjacent rectangle rooms and found itself at the same level as the circular orchestra, leading to it via three entrances. At its peak (fourth century BC), the theatre suffered transformations and was shaped to a large extent in its present form. The cavea comprised eleven tiers divided by ten staircases. The circular orchestra was transferred for 8m to the north, and was lowered by 3m. The scene was amplified by two backstages connected through a portico with an Ionic façade, thus raising above the orchestra. This difference in heights was evened up by a vaulted underground gallery, leading through the scene to the centre of the orchestra; this was in all probability the "charonian stairway" (stairs ofHades
Hades (; , , later ), in the ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, is the god of the dead and the king of the Greek underworld, underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea ...
) allowing actors impersonating chthonic deities and the dead to appear and perform at the orchestra.
Local poros stone was used for the foundation and limestone for the parodoi (passageways), which sloped to the orchestra in order to diminish the difference in height with the cavea. The theatre seated 6,300 spectators and is reminiscent in form to the Theatre of Dionysos in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, after transformation of the latter in 330 BC. Following the destruction of Eretria by the Romans in 198 BC, it was rebuilt with lower quality materials and the rooms to the south of the ''parodos'' were then apparently decorated with colour mortars of the first Pompeian style.
Most benches have been looted. There are still the impressive remains of the scene, especially the vaulted underground passage leading to the orchestra centre. Excavation of the monument was undertaken by the American Archaeological School, while the local Ephorate of Antiquities strived greatly for its restoration.
Temple of Isis
Isis
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
and other Egyptian deities
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural for ...
. Situated to the south of the town, between the baths and the Lower Gymnasium or the palaistra (wrestling area), it extends behind the small harbour, a detail that correlates the temenos with merchants who had their interests in Eretria. According to excavation and inscription testimonies, the temple was probably built in the fourth century BC and was surrounded by other edifices and auxiliary spaces. The initiation to the cult of Isis and the Egyptian deities occurred during the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
by Greek merchants who came to Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
from Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
after the unification of the then known world by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. Their worship in Eretria has also been attested by inscriptions, of which the most important is set on a limestone block to the left of the prodomos (anteroom) before the cella.
The temple of Isis was initially simple and oriented to the east, with a prodomos that was distyle (two-columned) in antis. The ceremonial clay statue of the goddess stood on a base within the cella. In front of the temple was the altar and nearby a small drain tank. The temple was reconstructed after the destruction of the city by the Romans in 198 BC: it then acquired a larger external prodomos on ameliorated foundations and was surrounded by porticoes on three sides (north, south and west). Only the south-west end of the portico was covered by a roof. The columns were later replaced by a parapet. At the centre of the east forecourt was a portal facing the entrance of the sanctuary. Fifteen more edifices and auxiliary spaces lied to the north, considered by the excavators as places of purification. Among them was a courtyard and an ''andren'' (dining hall for male residents), while one room of the complex had a superb mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
floor featuring lozenges.
Excavations at the ''temenos'' sacred to Isis and other Egyptian deities were conducted in 1917 by the then Ephor of Antiquities for the island of Evia (Euboea), Ι. Papadakis. In recent years, the Archaeological Service of the Ministry of Culture undertook further excavations in the wider area of the temple, which brought to light an additional complex of courtyards and rooms directly related to the sanctuary.
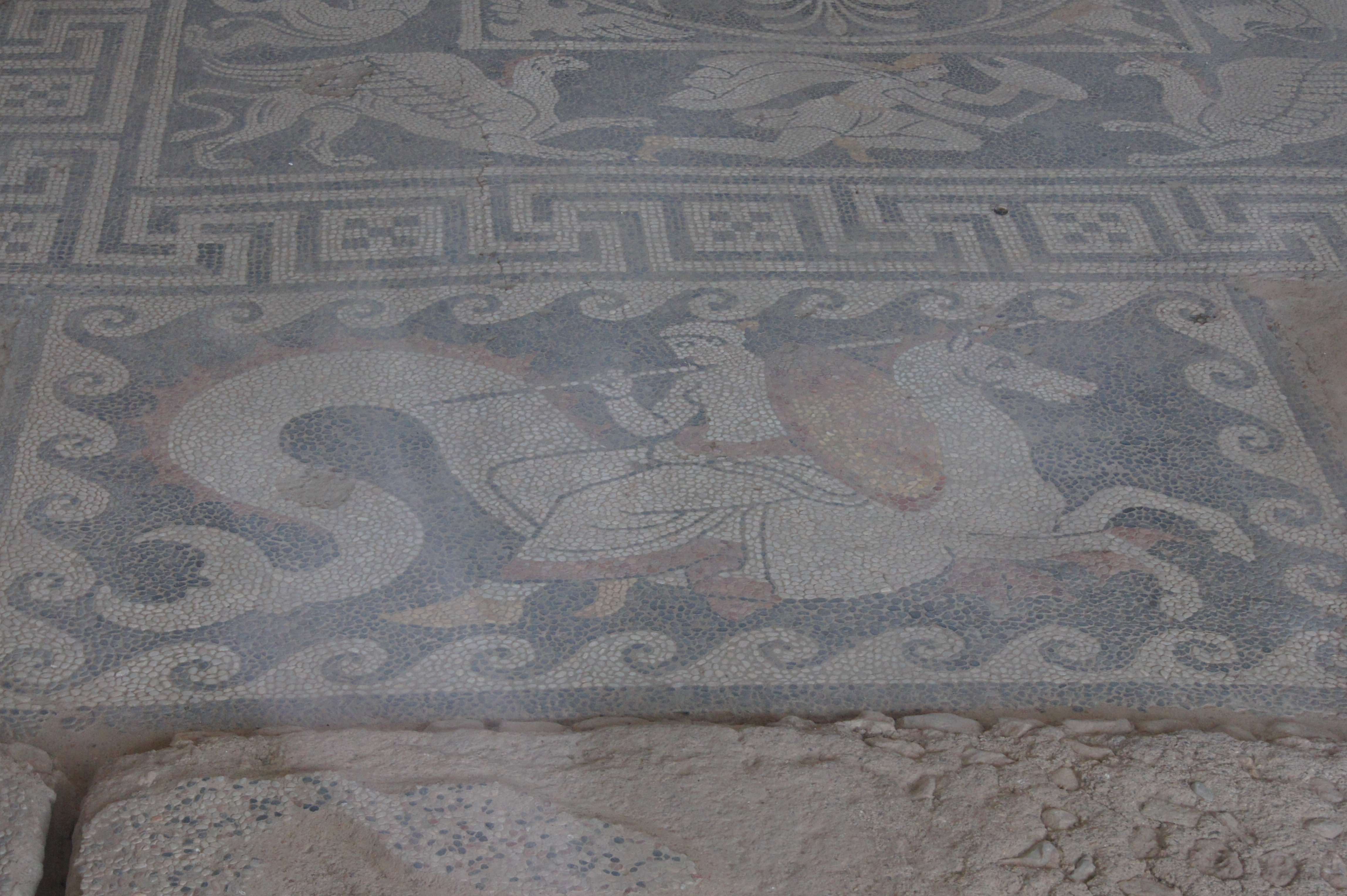
House with the mosaics
 This splendid house was built in ca. 370 B.C. and remained in use for about a century. It is distinguished by its floors, covered with elegant pebble mosaics representing mythological scenes: Nereids on the back of a seahorse, legendary battles between Arimaspians and
This splendid house was built in ca. 370 B.C. and remained in use for about a century. It is distinguished by its floors, covered with elegant pebble mosaics representing mythological scenes: Nereids on the back of a seahorse, legendary battles between Arimaspians and griffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (; Classical Latin: ''gryps'' or ''grypus''; Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk ...
s, sphinxes and panthers. The building is a representative specimen of the Classical and Hellenistic domestic architecture.
In the first century BC a funerary monument with a massive rectangular ''peribolos'' was erected over the ruins of the house.
The monument was excavated between 1975 and 1980.
Macedonian tomb of Erotes
The so-called "''tomb of Erotes''" lies on a hill to the northwest of Eretria city and counts among the most significant monuments of Evia island. Based on the findings, it is dated to the fourth century BC, the time when these characteristic burial monuments of the Macedonian type make their appearance in southern Greece after the descent of the Macedons. More Macedonian tombs were found in the wider area around Eretria, namely in the settlements of Kotroni and Amarynthos. The tomb of Erotes consists of a single vaulted chamber and a ''dromos'' (entrance passageway) of stone and bricks. The burial chamber is reminiscent of a residential room; it is built of poros stone plastered with white mortar. During the excavation were found two replicas of painted stone thrones bearing relief decoration. At the rear corners of the burial chamber were two marble bed-shapedsarcophagi
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φ� ...
. The tomb had been pillaged. Among the findings today exhibited in the New York Metropolitan Museum, are bronze vases and clay statuettes of Erotes (Amors), which inspired the tomb's conventional name. Above the tomb was uncovered a stone-built construction, probably the basis of a sepulchre.
The monument was excavated in 1897 and is well preserved to date.

Tholos
Excavations carried out by the Greek Archaeological Service have revealed the limestone foundations and crepis of a circular building. It was erected in the fifth century BC in theAgora
The agora (; , romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Ancient Greece, Greek polis, city-states. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center ...
of the city, and underwent several modifications in the fourth and the third centuries BC. A circular bothros has also survived at the centre of the monument.

Gymnasium and Eileithyia's sanctuary
In 1917, archaeologists uncovered traces of a gymnasium dating to the 4th century BC. A sanctuary dedicated to Eileithyia, had been placed in the northwestern section of the building. Also, excavations in the area of the sanctuary found a well containing some 100terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
cups dating to the 3rd century BC. In 2018, new excavations in the area revealed more buildings.
Modern Eretria
Modern Eretria was created in 1824 by refugees from Psara after the Destruction of Psara, who gave to their settlement the name "Nea Psara". The ancient name was revived during the first years of the independent Greek state. The new city plan was appointed by Stamatios Kleanthis and Eduard Schaubert., ανακτήθηκε 4 Δεκεμβρίου 2010 The modern town of Eretria is now a popular beachside resort. The historic and archaeological finds from Eretria and Lefkandi are displayed in th
Eretria Museum
established by the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. The town can be reached from Skala Oropou, Attica by ferry or via Halkida by road. It is an important station on the way to the south of the island. It has many taverns and a long beach promenade. The archaeological excavations are located on the northern edge of the modern town.
Municipality
The municipality Eretria was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following two former municipalities, that became municipal units: * Amarynthos *Eretria The municipality has an area of 168.557 km2, the municipal unit 58.648 km2.Historical population
Notable people
* Achaeus, tragic playwright * Menedemus (345/4-261/0 BC), Greek philosopher * Philoxenus (4th century BC), painterSee also
*List of traditional Greek place names
This is a list of Greek place names as they exist in the Greek language.
*Places involved in the history of Greek culture, including:
**Historic Greek regions, including:
***Ancient Greece, including colonies and contacted peoples
*** Hellenis ...
References
Further reading
* ESAGEretria. A guide to the ancient city
Infolio éditions, Gollion, 2004. * ESAG
* Keith G. Walker, "Archaic Eretria. A Political and Social History from the Earliest Times to 490 BC", Routledge, London, 2004.
External links
The Swiss School Website of the excavations at Eretria
Perseus – Eretria
Links to resources about ancient Eretria
Greek Ministry of Culture
{{Authority control Populated places in Euboea Municipalities of Central Greece Cities in ancient Greece Populated places in ancient Euboea Populated places established in 1824 Former populated places in Greece Members of the Delian League Ancient Greek cities Greek city-states