|
Lucius Quinctius Flamininus
Lucius Quinctius Flamininus (died 170 BC) was a Roman politician and general who served as consul in 192 BC alongside Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus. He was eventually expelled from the Senate by Cato the Elder. Early career and the Second Macedonian War A member of the patrician gens Quinctia, Lucius Quinctius Flamininus was the brother of Titus Quinctius Flamininus. He was elected curule aedile in 201 BC, and in 199 BC, he served as praetor urbanus. In the following year (198 BC), his praetorial imperium was prorogued by the Senate, initially to take on the task of allocating land in Italy for veterans who had served in Hispania. However, his brother Titus ensured that he was given a propraetoral command in charge of a fleet around Greece, and made responsible for securing the Italian coastal regions during the Second Macedonian War. Flamininus initially sailed to Corcyra, and having the fleet handed over to him by his predecessor Lucius Apustius near the island of Zama, he tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; ; , Ancient: , Katharevousa: ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens city centre along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf in the Athens Riviera. The municipality of Piraeus and four other suburban municipalities form the regional unit of Piraeus, sometimes called the Greater Piraeus area, with a total population of 448,051. At the 2021 census, Piraeus had a population of 168,151 people, making it the fourth largest municipality in Greece and the second largest (after the municipality of Athens) within the Athens urban area. Piraeus has a long recorded history, dating back to ancient Greece. The city was founded in the early 5th century BC, when plans to make it the new port of Athens were implemented: A prototype harbour was constructed, which resulted in concentrating in one location all the import and transit trade of Athens, along with the navy's base. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατρίδα (patrida) or "native land" for its citizens. In ancient Greece, the polis was the native land; there was no other. It had a constitution and demanded the supreme loyalty of its citizens. χώρα was only the countryside, not a country. Ancient Greece was not a sovereign country, but was territory occupied by Hellenes, people who claimed as their native language some dialect of Ancient Greek. Poleis did not only exist within the area of the modern Republic of Greece. A collaborative study carried by the Copenhagen Polis Centre from 1993 to 2003 classified about 1,500 settlements of the Archaic and Classical ancient-Greek-speaking population as poleis. These ranged from the Caucasus to Southern Spain, and from Southern Russia to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaean League
The Achaean League () was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era confederation of polis, Greek city-states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea (ancient region), Achaea in the northwestern Peloponnese, which formed its original core. The first league was formed in the fifth century BC. Although the first Achaean League is much less well documented than its later revival, it maintained a recognizable federal structure through the early Hellenistic period, but later fell into a period of dormancy under growing Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian influence. The more famous second Achaean League was established in 280 BC. As a rival of Antigonid Macedon and an ally of the Roman Republic, the league played a major role in the Macedonian Wars, expansion of Rome into Greece. This process eventually led to the League's conquest and dissolution by the Romans in 146 BC. The League represents the most successful attempt by the Greek city- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a Roman consul, consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority. In the Roman Republic, military command, or ''imperium'', could be exercised constitutionally only by a consul. Only two consuls served at a time, each elected to a one-year term. They could not normally serve two terms in a row; if a military campaign was in progress at the end of a consul's term, the consul in command might have his command Prorogatio, prorogued, allowing him to continue in command. This custom allowed for continuity of command despite the high turnover of consuls. In the Roman Empire, proconsul was a title held by a civil governor and did not imply military command. In modern times, various officials with notable delegated authority have been referred to as proconsuls. Studies of leadership typically divide leaders into policymakers and subordinate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the Corinth (municipality), municipality of Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It is the capital of Corinthia. It was founded as Nea Korinthos (), or New Corinth, in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth, which had developed in and around the site of the ancient city. History Corinth derives its name from Ancient Corinth, a city-state of antiquity. The site was occupied from before 3000 BC. Ancient Greece Historical references begin with the early 8th century BC, when ancient Corinth began to develop as a commercial center. Between the 8th and 7th centuries, the Bacchiad family ruled Corinth. Cypselus overthrew the Bacchiad f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenchreae
Kechries (, rarely Κεχρεές) is a village in the municipality of Corinth in Corinthia in Greece, part of the community of Xylokeriza. Population 319 (2021). It takes its name from the ancient port town Kenchreai or Cenchreae (), which was situated at the same location. Geography Kechries is situated near a broad bay at the western end of the Saronic Gulf, called Kechries Bay. This coastline forms the easternmost point of the Corinth Fault. The area has frequently felt the impact of seismic activity, which has led to the moderate subsidence of the coastline since ancient times. Kechries is a small village with a school and a church. The number of permanent residents of Kechries is small, and many houses there are used seasonally by owners who reside elsewhere. The Oneia Mountains lie to the south, where a major stone quarry is located, and the village is surrounded by fertile land dedicated to the cultivation of olive, the vine, and fruit trees. Kechries is located about s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'' (after El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carystus
Carystus (; , near modern Karystos) was a polis (city-state) on ancient Euboea. It was situated on the south coast of the island, at the foot of Mount Oche. It is mentioned by Homer in the Catalogue of Ships in the ''Iliad'', as controlled by the Abantes. The name also appears in the Linear B tablets as ''"ka-ru-to"'' (identified as ''Carystus''). Thucydides writes that the town was founded by Dryopes. According to the legend, its name was derived from Carystus, the son of Cheiron. History Persian War In 490 BC during the Greco-Persian Wars a Persian Admiral named Datis laid siege to Carystus. Datis began the siege by destroying the crops around the city. His army of 80,000 soldiers with 200 triremes overwhelmed Carystus, causing it to surrender. Soon after the Battle of Salamis the Athenian fleet led by Themistocles extorted money from the city. Soon afterward Carystus refused to join the Delian League. The Athenians wanted Carystus to join the Delian Leagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (ancient Kingdom)
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The History of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid dynasty, Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasty, Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus (ancient state), Epirus to the southwest, Illyria to the northwest, Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Ancient Thessaly, Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Classical Athens, Athens, Sparta and Classical Thebes, Thebes, and Achaemenid Macedonia, briefly subordinate to Achaemeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
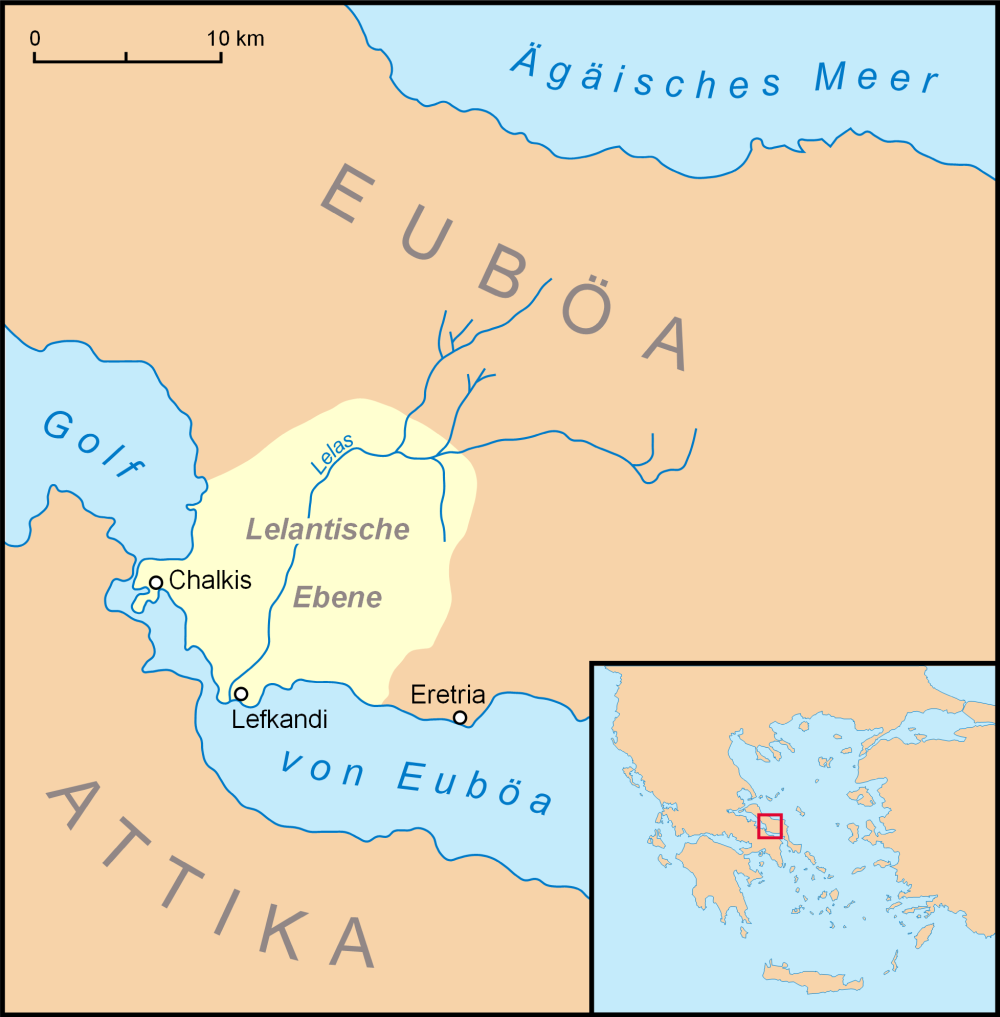
Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain. A granary and several other buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes (regional unit), Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean Administrative regions of Greece, administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is the Rhodes (city), city of Rhodes, which had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022, the island had a population of 125,113 people. It is located northeast of Crete and southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights Hospitaller, Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |