|
Thermal Barrier Coating
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are advanced materials systems usually applied to metallic surfaces on parts operating at elevated temperatures, such as gas turbine combustors and turbines, and in automotive exhaust heat management. These 100 μm to 2 mm thick coatings of thermally insulating materials serve to insulate components from large and prolonged heat loads and can sustain an appreciable temperature difference between the load-bearing alloys and the coating surface. In doing so, these coatings can allow for higher operating temperatures while limiting the thermal exposure of structural components, extending part life by reducing oxidation and thermal fatigue. In conjunction with active film cooling, TBCs permit working fluid temperatures higher than the melting point of the metal airfoil in some turbine applications. Due to increasing demand for more efficient engines running at higher temperatures with better durability/lifetime and thinner coatings to reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repair Process For A V2500 High-pressure Turbine Guide Vane (8)
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installations. Terms such as "predictive" or "planned" maintenance describe various cost-effective practices aimed at keeping equipment operational; these activities occur either before or after a potential failure. Definitions Maintenance functions can be defined as maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO), and MRO is also used for maintenance, repair and operations. Over time, the terminology of maintenance and MRO has begun to become standardized. The United States Department of Defense uses the following definitions:Federal Standard 1037C and from MIL-STD-188 and from the Department of Defense Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms * Any activity—such as tests, measurements, replacements, adjustments, and repairs—intended to retain or r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphor Thermometry
Phosphor thermometry is an optical method for surface temperature measurement. The method exploits luminescence emitted by phosphor material. Phosphors are fine white or pastel-colored inorganic powders which may be stimulated by any of a variety of means to luminesce, i.e. emit light. Certain characteristics of the emitted light change with temperature, including brightness, color, and afterglow duration. The latter is most commonly used for temperature measurement. History The first mention of temperature measurement utilizing a phosphor is in two patents originally filed in 1932 by Paul Neubert. Time dependence of luminescence Typically a short duration ultraviolet lamp or laser source illuminates the phosphor coating which in turn luminesces visibly. When the illuminating source ceases, the luminescence will persist for a characteristic time, steadily decreasing. The time required for the brightness to decrease to 1/e of its original value is known as the decay time or lifeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and Copper(II) sulfate, copper. A typical example of an alloy is SAE 304 stainless steel, 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic phase (matter), phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystallinity, crystalline form of aluminium oxide. ruby, Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to undergo slow deformation while subject to persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increases as they near their melting point. The rate of deformation is a function of the material's properties, exposure time, exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Depending on the magnitude of the applied stress and its duration, the deformation may become so large that a component can no longer perform its function – for example creep of a turbine blade could cause the blade to contact the casing, resulting in the failure of the blade. Creep is usually of concern to engineers and metallurgists when evaluating components that operate under high stresses or high temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Deformation
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations ( rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Constant
A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. A simple cubic crystal has only one lattice constant, the distance between atoms, but, in general, lattices in three dimensions have six lattice constants: the lengths ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' of the three cell edges meeting at a vertex, and the angles ''α'', ''β'', and ''γ'' between those edges. The crystal lattice parameters ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' have the dimension of length. The three numbers represent the size of the unit cell, that is, the distance from a given atom to an identical atom in the same position and orientation in a neighboring cell (except for very simple crystal structures, this will not necessarily be distance to the nearest neighbor). Their SI unit is the meter, and they are traditionally specified in angstroms (Å); an angstrom being 0.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Lattice
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
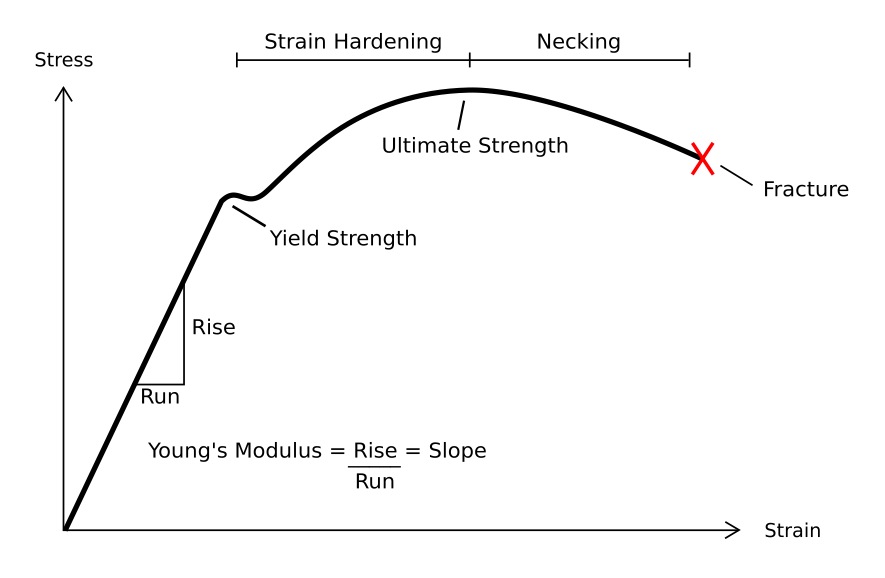
Strain (materials Science)
In mechanics, strain is defined as relative deformation, compared to a position configuration. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. Strain has dimension of a length ratio, with SI base units of meter per meter (m/m). Hence strains are dimensionless and are usually expressed as a decimal fraction or a percentage. Parts-per notation is also used, e.g., parts per million or parts per billion (sometimes called "microstrains" and "nanostrains", respectively), corresponding to μm/m and nm/m. Strain can be formulated as the spatial derivative of displacement: \boldsymbol \doteq \cfrac\left(\mathbf - \mathbf\right) = \boldsymbol'- \boldsymbol, where is the identity tensor. The displacement of a body may be expressed in the form , where is the reference position of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (mechanics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to ''tensile'' stress and may undergo elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has dimension of force per area, with SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spallation
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of metal oxidation, spallation refers to the breaking off of the oxide layer from a metal. For example, the flaking off of rust from iron. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metal in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen, hydrogen, or hydroxide. Rusting, the formation of red-orange iron oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of corrosion typically produces oxides or salts of the original metal and results in a distinctive coloration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including mechanical strength, appearance, and permeability to liquids and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |