|
Aluminium Oxide
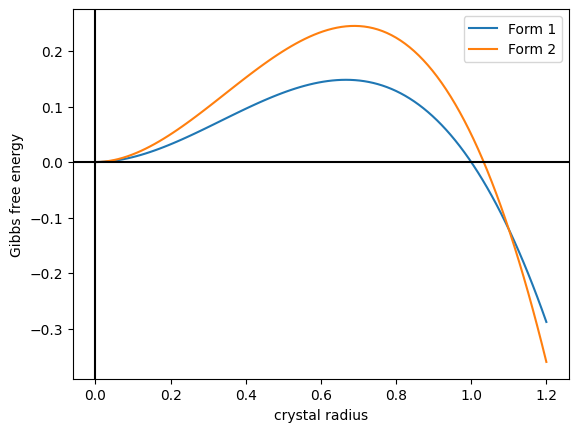
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic phase (matter), phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystallinity, crystalline form of aluminium oxide. ruby, Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polishing, polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared, infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a large influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In an ideal gas, the relative positions of the atoms or molecules are completely random. Amorphous materials, such as liquids and glasses, represent an intermediate case, having order over short distances (a few atomic or molecular spacings) but not over longer distances. Many materials, such as glass-ceramics and some polymers, can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions. In such cases, crystallinity is usually specified as a percentage of the volume of the material that is crystalline. Even within materials that are completely crystalline, however, the degree of structural perfection can vary. For instance, most metallic alloys are crystalline, but they usually comprise many independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium. It is a rock (geology), rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparency and translucency, transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gemstone, gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, Sapphire#Padparadscha, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil language, Tamil-Dravidian languages, Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. Emery (rock), Emery, a variety of corundum w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the '' refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion (mechanical), abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elasticity (physics), elastic stiffness, plasticity (physics), plasticity, deformation (mechanics), strain, strength of materials, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives. Abrasives are extremely commonplace and are used very extensively in a wide variety of industrial, domestic, and technological applications. This gives rise to a large variation in the physical and chemical composition of abrasives as well as the shape of the abrasive. Some common uses for abrasives include grinding, polishing, buffing, honing, cutting, drilling, sharpening, lapping, and sanding (see abrasive machining). (For simplicity, "mineral" in this article will be used loosely to refer to both minerals and mineral-like substances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire'' is derived from the Latin word ', itself from the Greek language, Greek word (), which referred to lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on the locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
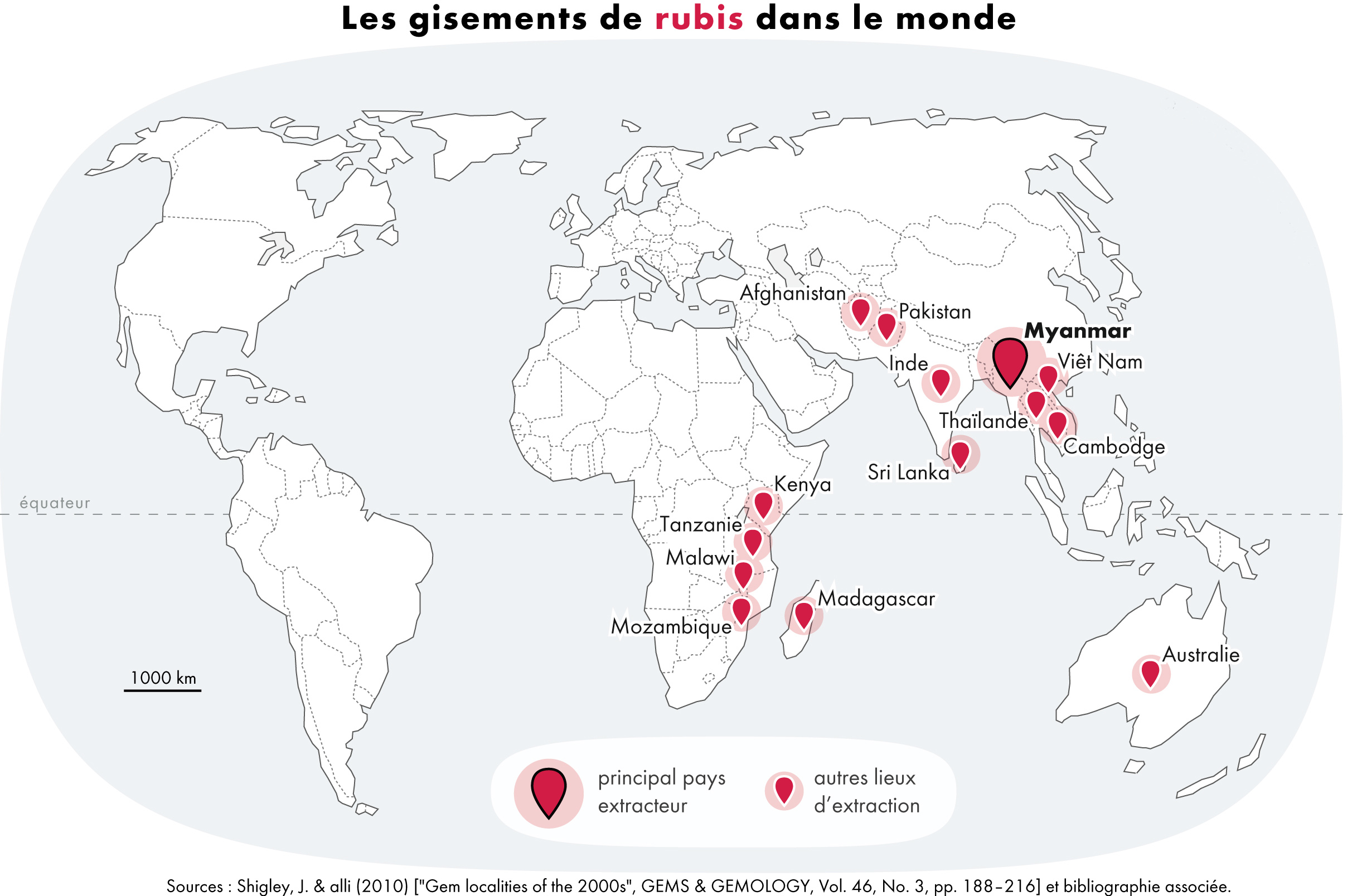
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |