|
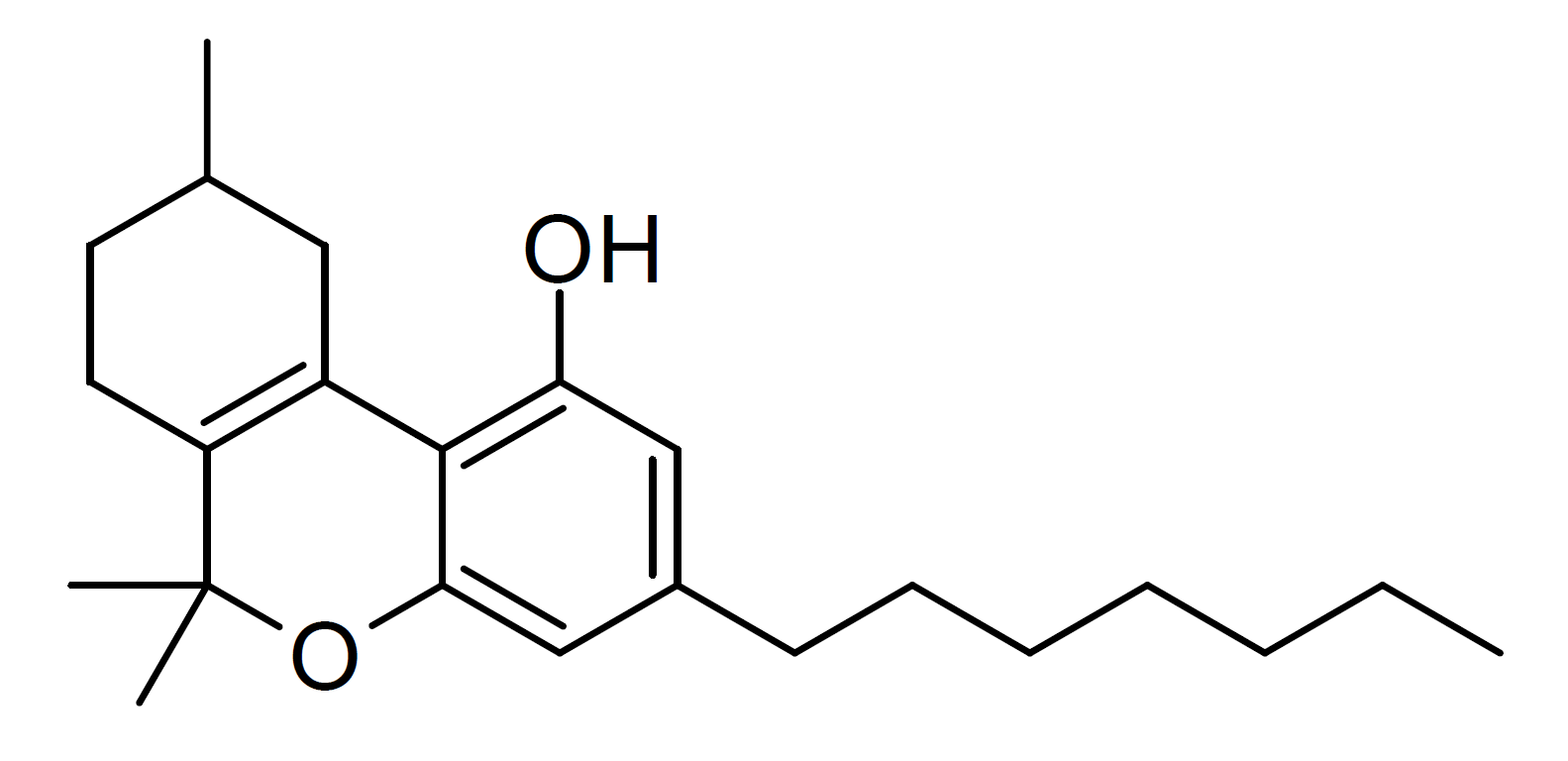
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a Cannabinoid receptor type 1, CB1 and Cannabinoid receptor type 2, CB2 agonist, receptor agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabis sativa''. THCP is structurally similar to Δ9-THC, the main active component of cannabis, but with the pentyl side chain extended to heptyl. Since it has a longer side chain, its cannabinoid effects are "far higher than Δ9-THC itself." Tetrahydrocannabiphorol has a reported binding affinity of 1.2 nM at CB1, approximately 33 times that of Δ9-THC (40 nM at CB1), however this does not mean it's 33x stronger per milligram. THCP was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942. Isomers Delta-3-THCP ] The Δ3/Δ6a(10a) isomer Δ3-THCP was synthesised in 1941, and was found to have around the same potency as Delta-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ3-THC, unl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidiphorol
Cannabidiphorol, the heptyl-homologue of cannabidiol was identified as a natural phytocannabinoid and named cannabidiphorol (CBDP) in 2019. It had previously been reported as a synthetic compound, but was not identified as a natural product prior to 2019. Recently, CBDP has been gained popularity due to it being synthesized and available on a commercial level. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics CBDP shows weak antagonism at both cannabinoid receptors ( CB1 and CB2), similar to cannabidiol (CBD). CBD, however, exhibits stronger antagonism at CB2, reaching a 33% maximum response of SR144528 versus CBDP's 23%. Both cannabinoids act as weak agonists at the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, contributing to potential anxiolytic effects. Unlike CBD, CBDP shows no sign of dopamine D2 receptor agonism. Unexpectedly, CBDP acts as a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) at the MOR, enhancing met-enkephalin signaling by 37%, potentially affecting pain perception. References See also * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV, O-4394, GWP42004) is a Homologous series, homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of pentyl (5-carbon), making it non-psychoactive in lower doses. It has been shown to exhibit neuroprotection, neuroprotective activity, appetite suppression, glycemic control and reduced side effects compared to THC, making it a potential treatment for management of obesity and diabetes. THCV was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942. Natural occurrence THCV is prevalent in certain central Asian and southern African strains of ''Cannabis''. Chemistry Similar to tetrahydrocannabinol, THC, THCV has 7 possible double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Tetrahydrocannabinol#Isomerism). The alternative isomer Δ8-THCV is known as a synthetic compound with a code number of O-4395, but it is not known to have been isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material. ] Description Plants with elevated levels of propyl cannab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexahydrocannabiphorol
Hexahydrocannabiphorol (HHCP, sometimes mistakenly referred to as ''hexahydroxycannabiphorol'') is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derivative which has been marketed since around 2021. It is believed to be made from the hydrogenation of tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP). THCP is only reported as a trace component of cannabis in 2019. HHCP was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942. Pharmacology HHC-P is a partial agonist of the CB1 receptors with an EC50 of 44.4nM for 9R-HHCP and 134nM for 9S-HHCP. Compared to Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) with an EC50 of 101nM for 9R-HHC and 1,190nM for 9S-HHC In 2021, HHC-P was positively identified in multiple gray market cannabis products in the United States. Legality The legal status of hexahydrocannabinol and derivatives varies between countries, leading to widespread sale in some parts of Europe and the US. In France, HHCP was banned in 2023. In Japan, Japanese Health Ministry announced that six synthetic cannabinoids with structures similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THCP-O-acetate
THCP-O-acetate (THCP-O) is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) derived by acetylation of the OH group. It has been found as a component of grey-market cannabis products such as e-cigarette liquids and edible gummy lollies, and is allegedly a potent and long-lasting psychoactive cannabinoid. Toxicity In 2022, researchers at Portland State University who screened for the presence of reacted ketene as N-benzylacetamide reported that Vitamin E acetate, CBD-acetate, CBN-acetate and THC-O-acetate may break down to release ketene gas when heated at . Legality Japan banned THCP-O-Acetate along with HHCP on December 26, 2023. See also * Tetrahydrocannabiphorol * Hexahydrocannabiphorol (HHCP) * HHCP-O-acetate * THC-O-acetate * Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP) * HU-210 * THC-O-phosphate * THC hemisuccinate * THC morpholinylbutyrate THC morpholinylbutyrate (SP-111, Δ9-THC-O- -(morpholin-4-yl)butyrate'') is a synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil. Medical uses THC, referred to as dronabinol in the pharmaceutical context, is approved in the United States as a capsule or solution to relieve chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia. THC is an active ingredient in nabiximols, a specific extract of ''Cannabis'' that was approved as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom in 2010 as a mouth spray for people with multiple sclerosis to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms. Nabiximols (as Sativex) is available as a prescription drug in Canada. In 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabihexol
Tetrahydrocannabihexol (Δ9-THCH, Δ9-Parahexyl, n-Hexyl-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid, the hexyl homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was first isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material in 2020 along with the corresponding hexyl homologue of cannabidiol, though it had been known for several decades prior to this as an isomer of the synthetic cannabinoid parahexyl. Another isomer Δ8-THCH is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code number JWH-124, though it is unclear whether this occurs naturally in ''Cannabis'', but likely is due to Δ8-THC itself being a degraded form of Δ9-THC. THC-Hexyl can be synthesized from 4-hexylresorcinol and was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942. ] ] See also * Cannabidiphorol * Hexahydrocannabihexol * Tetrahydrocannabiorcol * Tetrahydrocannabivarin * Tetrahydrocannabutol Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (Δ9-THCB, THC-B, tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, (C4)-Δ9-THC, or butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in canna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabutol
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (Δ9-THCB, THC-B, tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, (C4)-Δ9-THC, or butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main active component of Cannabis. Structurally, they are only different by the pentyl side chain being replaced by a butyl side chain. THCB was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942 Pharmacology Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (''K''i = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (''K''i = 51 nM) comparable to that of Δ9-THC. The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor. THCB has rarely been isolated from cannabis samples, but appears to be less commonly present than THC or THCV. It is metabolized in a similar manner to THC. In an analysis by the University of Rhode Island on phytocannabinoids it was found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of ''Cannabis'' and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil. Medical uses THC, referred to as dronabinol in the pharmaceutical context, is approved in the United States as a capsule or solution to relieve chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia. THC is an active ingredient in nabiximols, a specific extract of ''Cannabis'' that was approved as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom in 2010 as a mouth spray for people with multiple sclerosis to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms. Nabiximols (as Sativex) is available as a prescription drug in Canada. In 2021, nab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parahexyl
Parahexyl, also known as synhexyl, is a synthetic homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was invented in 1941 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of cannabis. Parahexyl is similar in both structure and activity to THC, differing only in the position of one double bond and the lengthening of the chain by one CH2 group to . Parahexyl produces effects typical of other cannabinoid receptor agonists in animals. It has a somewhat higher oral bioavailability than THC itself but is otherwise very similar. Presumably, it acts as a CB1 receptor agonist in the same way as THC, but as there has been no research published using parahexyl since the discovery of the CB1 receptor, this has not been definitively confirmed. Parahexyl was occasionally used as an anxiolytic in the mid-20th century, the dosage ranging from 5 mg to 90 mg. Parahexyl was made illegal under UN convention in 1971 on the basis of its structural similarit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in Cannabis (drug), cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |