|
Termination Shock (novel)
''Termination Shock'' is a science fiction novel by American writer Neal Stephenson, published in 2021. The book is set in a near-future when climate change has significantly altered human society and follows the attempts of a solar geoengineering scheme. The novel focuses on the geopolitical and social consequences of the rogue fix for climate change, themes common in the growing climate fiction genre. Plot The book is about a solar geoengineering project conceived by a Texas oil-industry billionaire named T.R. Schmidt. Schmidt builds a launcher on the Texas-Mexico border to fire sulfur into the air, a form of stratospheric aerosol injection intended to cool the planet by reflecting sunlight into space. This technique replicates the effects of volcanic eruptions that inject sulfates into the atmosphere and produce global cooling, such as the 1991 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo, Mount Pinatubo eruption. Schmidt's plan has uneven effects, helping low-lying areas such as the Net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neal Stephenson
Neal Town Stephenson (born October 31, 1959) is an American writer known for his works of speculative fiction. His novels have been categorized as science fiction, historical fiction, cyberpunk, and baroque. Stephenson's work explores mathematics, cryptography, linguistics, philosophy, currency, and the history of science. He also writes nonfiction articles about technology in publications such as ''Wired (magazine), Wired''. He has written novels with his uncle, George Jewsbury ("J. Frederick George"), under the collective pseudonym Stephen Bury. Stephenson has worked part-time as an advisor for Blue Origin, a company (founded by Jeff Bezos) developing a spacecraft and a space launch system, and also co-founded the Subutai Corporation, whose first offering is the interactive fiction project ''The Mongoliad''. He was Magic Leap's Chief Futurist from 2014 to 2020. Early life Born on October 31, 1959, in Fort Meade, Maryland, Stephenson came from a family of engineers and scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the Sanskrit word ', meaning 'seeker', or . According to Article I of Chapter 1 of the Sikh ''Rehat Maryada'' (), the definition of Sikh is: Any human being who faithfully believes in One Immortal Being Ten Gurus, from Guru Nanak Sahib to Guru Gobind Singh Sahib The Guru Granth Sahib The utterances and teachings of the ten Gurus and The initiation, known as the Amrit Sanchar, bequeathed by the tenth Guru and who does not owe allegiance to any other religion, is a Sikh. Male Sikhs generally have '' Singh'' () as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have '' Kaur'' () as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Review Of Books
The ''Chicago Review of Books'' is an online literary publication of StoryStudio Chicago that reviews recent books covering diverse genres, presses, voices, and media. The magazine was started in 2016 by founding editor Adam Morgan. It is considered a sister publication of ''Arcturus'', which publishes original fiction, non-fiction, and poetry. The ''Chicago Review of Books'' is currently led by Editor-In-Chief Michael Welch. Content The ''Chicago Review of Books'' publishes regular reviews and interviews from authors publishing across independent and large publishers, as well as book lists, feature essays, and podcasts. With an international audience and editorial scope, the magazine is also dedicated to shining a light on Chicago's literary scene and serving as a forum for literature in the Midwest. The Chicago Review of Books Awards Since 2016, the Chicago Review of Books Awards have honored exemplary works of fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and essays & short stories publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reason (magazine)
''Reason'' is an American libertarian monthly magazine published by the Reason Foundation, with the tagline "Free Minds and Free Markets". The magazine aims to produce independent journalism that is "outside of the left/right echo chamber." As of 2016, the magazine had a circulation of around 50,000 and received about 2.5 million monthly unique website visitors. History ''Reason'' was founded in 1968 by Lanny Friedlander (1947–2011), a student at Boston University, as a more-or-less monthly mimeographed publication. In 1970, it was purchased by Robert W. Poole Jr., Manuel S. Klausner, and Tibor R. Machan, who set it on a more regular publishing schedule. During the 1970s and 1980s, the magazine's contributors included Milton Friedman, Murray Rothbard, Thomas Szasz, and Thomas Sowell. In 1978, Poole, Klausner, and Machan created the associated Reason Foundation, in order to expand the magazine's ideas into policy research. Marty Zupan joined ''Reason'' in 1975, and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omar El Akkad
Omar El Akkad (born 1982) is an Egyptian-Canadian novelist and journalist, whose novel '' What Strange Paradise'' was the winner of the 2021 Giller Prize. Early life and education Omar El Akkad was born in Cairo, Egypt, and grew up in Doha, Qatar. When he was 16 years old, he moved to Canada, completing high school in Montreal and university at Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario. He has a computer science degree. Career For ten years, he was a staff reporter for ''The Globe and Mail,'' where he covered the war in Afghanistan, military trials at Guantanamo Bay and the Arab Spring in Egypt. He was most recently a correspondent for the western United States, where he covered Black Lives Matter. His first novel, '' American War,'' was published in 2017. It received positive reviews from critics; ''The New York Times'' book critic Michiko Kakutani compared it favourably to Cormac McCarthy's '' The Road'' and Philip Roth's novel '' The Plot Against America''. She wrote th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
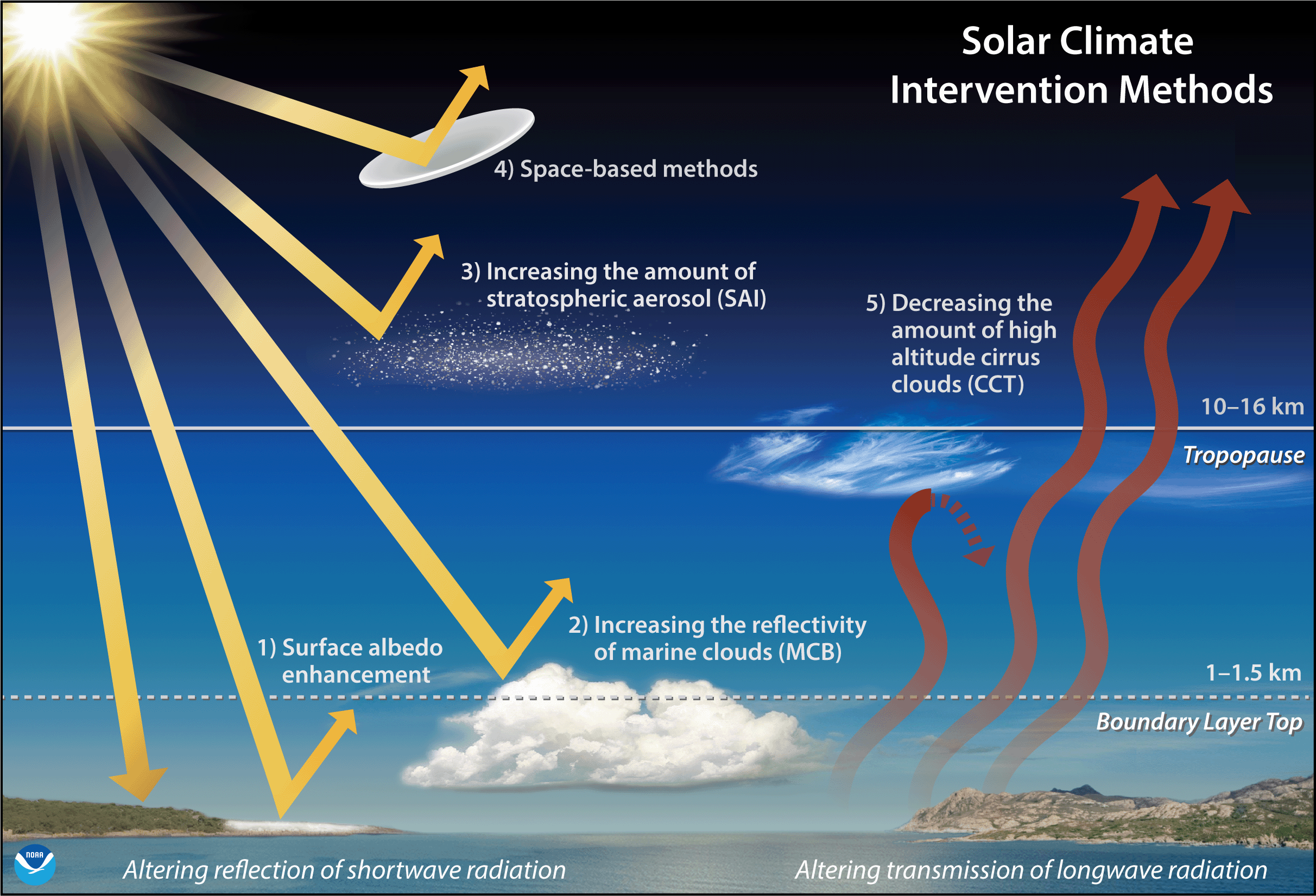
Solar Geoengineering
Solar radiation modification (SRM) (or solar geoengineering) is a group of large-scale approaches to reduce global warming by increasing the amount of sunlight that is reflected away from Earth and back to Outer space, space. It is not intended to replace Climate change mitigation, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but rather to complement them as a potential way to limit global warming. SRM is a form of geoengineering. The most-researched SRM method is stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI), in which small reflective particles would be introduced into the upper atmosphere to reflect sunlight. Other approaches include marine cloud brightening (MCB), which would increase the reflectivity of clouds over the oceans, or constructing a space sunshade or a space mirror, to reduce the amount of sunlight reaching earth. Climate models have consistently shown that SRM could reduce global warming and many effects of climate change, including some potential Tipping points in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Drone Warfare; 2024. e-ISBN (PDF) 978-3-11-074203-9.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage,F. Rekabi-Bana; Hu, J.; T. Krajník; Arvin, F.,Unified Robust Path Planning and Optimal Trajectory Generation for Efficient 3D Area Coverage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdication
Abdication is the act of formally relinquishing monarchical authority. Abdications have played various roles in the Order of succession, succession procedures of monarchies. While some cultures have viewed abdication as an extreme abandonment of duty, in other societies (such as pre-Meiji Restoration Japan), abdication was a regular event and helped maintain stability during political succession. Historically, abdications have occurred both by force (where the regnant was ''Dethronement, dethroned'', thus forced to abdicate on pain of death or other severe consequences) and voluntarily. Some rulers are deemed to have abdicated wiktionary:in absentia, ''in absentia'', vacating the physical throne and thus their position of power, although these judgements were generally pronounced by successors with vested interests in seeing the throne abdicated, and often without or despite the direct input of the abdicating monarch. Recently, due to the largely ceremonial nature of the regnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunami Bomb
The tsunami bomb was an attempt during World War II to develop a tectonic weapon that could create destructive tsunamis. The project commenced after United States Navy officer E.A. Gibson noticed small waves generated by explosions used to clear coral reefs. The idea was developed by the United States and New Zealand military in a program code named Project Seal. The weapons concept was deemed feasible, but the weapons themselves were never fully developed or used. A related concept, the bouncing bomb ''was'' developed and used in World War II, to be dropped into water as a means to destroy German dams and cause loss of industrial capacity and widespread flooding. Testing and development Tests were conducted by Professor Thomas Leech, of the University of Auckland, in Whangaparaoa off the coast of Auckland and off New Caledonia between 1944 and 1945. British and US defence chiefs were eager to see it developed, and it was considered potentially as important as the atomic bomb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyberattack, cyber attacks against an enemy State (polity), state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems. Some intended outcomes could be espionage, sabotage, propaganda, Internet manipulation, manipulation or economic warfare. There is significant debate among experts regarding the definition of cyberwarfare, and even if such a thing exists. One view is that the term is a misnomer since no cyber attacks to date could be described as a war. An alternative view is that it is a suitable label for cyber attacks which cause physical damage to people and objects in the real world. Many countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Russia, China, Israel, Iran, and North Korea, have active cyber capabilities for offensive and defensive operations. As states explore the use of cyber operations and combine capabilities, the likelihood of physical confrontation and violence playing out as a result of, or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Warfare
Psychological warfare (PSYWAR), or the basic aspects of modern psychological operations (PsyOp), has been known by many other names or terms, including Military Information Support Operations ( MISO), Psy Ops, political warfare, "Hearts and Minds", and propaganda. The term is used "to denote any action which is practiced mainly by psychological methods with the aim of evoking a planned psychological reaction in other people". Various techniques are used, and are aimed at influencing a target audience's value system, belief system, emotions, motives, reasoning, or behavior. It is used to induce confessions or reinforce attitudes and behaviors favorable to the originator's objectives, and are sometimes combined with black operations or false flag tactics. It is also used to destroy the morale of enemies through tactics that aim to depress troops' psychological states. Target audiences can be governments, organizations, groups, and individuals, and is not just limited to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |